The Kawasaki GPZ900R is a motorcycle that was manufactured by Kawasaki from 1984 to 2003. It is the earliest member of the Ninja family of sport bikes. The 1984 GPZ900R was a revolutionary design that became the immediate predecessor of the modern-day sport bike. Developed in secret over six years, it was Kawasaki's and the world's first 16-valve liquid-cooled inline four-cylinder motorcycle engine.

Waltham Manufacturing Company (WMC) was a manufacturer of bicycles, motorcycles, motorized tricycles and quadricycles, buckboards, and automobiles in Waltham, Massachusetts. It sold products under the brand names Orient, Waltham, and Waltham-Orient. The company was founded in 1893, moving to self-propelled vehicles after 1898.

A motorized bicycle is a bicycle with an attached motor or engine and transmission used either to power the vehicle unassisted, or to assist with pedalling. Since it sometimes retains both pedals and a discrete connected drive for rider-powered propulsion, the motorized bicycle is in technical terms a true bicycle, albeit a power-assisted one. Typically they are incapable of speeds above 52 km/h (32 mph).
This timeline of motorized bicycle history is a summary of the major events in the development and use of motorized bicycles and tricycles, which are defined as pedal cycles with motor assistance but which can be powered by pedals alone.

The Hildebrand & Wolfmüller was the world's first production motorcycle. Heinrich and Wilhelm Hildebrand were steam-engine engineers before they teamed up with Alois Wolfmüller to produce their internal combustion Motorrad in Munich in 1894.
The history of the motorcycle begins in the second half of the 19th century. Motorcycles are descended from the "safety bicycle," a bicycle with front and rear wheels of the same size and a pedal crank mechanism to drive the rear wheel. Despite some early landmarks in its development, the motorcycle lacks a rigid pedigree that can be traced back to a single idea or machine. Instead, the idea seems to have occurred to numerous engineers and inventors around Europe at around the same time.

The Art of the Motorcycle was an exhibition that presented 114 motorcycles chosen for their historic importance or design excellence in a display designed by Frank Gehry in the curved rotunda of the Frank Lloyd Wright-designed Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum in New York City, running for three months in late 1998. The exhibition attracted the largest crowds ever at that museum, and received mixed but positive reviews in the art world, with the exception of some art and social critics who rejected outright the existence of such a show at an institution like the Guggenheim, condemning it for excessive populism, and for being compromised by the financial influence of its sponsors.

Prinetti & Stucchi, later Stucchi & Co., was an Italian maker of sewing machines, bicycles and motorized vehicles, established in Milan in 1883. It was owned by engineers and politicians Augusto Stucchi and Giulio Prinetti (1851–1908).

The Harley-Davidson Model 7D of 1911 was the first successful v-twin from Harley-Davidson, inaugurating a motorcycle engine configuration that has continued unbroken from the Milwaukee motor company ever since.

Thomas Krens is the former director and Senior Advisor for International Affairs of the Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation in New York City. From the beginning of his work at the Guggenheim, Krens promised, and delivered, great change, and was frequently in the spotlight, often as a figure of controversy.

Motorized tricycles, or simply tricycles, is a type of motorized vehicle from the Philippines consisting of a motorcycle attached to a passenger cab. Along with the jeepney, it is one of the most common means of public or private transportation in the Philippines, especially in rural areas. These public utility vehicles either ply a set route or are for-hire, like taxis.

The Michaux-Perreaux steam velocipede was a steam powered velocipede made in France sometime from 1867 to 1871, when a small Louis-Guillaume Perreaux commercial steam engine was attached to a Pierre Michaux manufactured iron framed pedal bicycle. It is one of three motorcycles claimed to be the first motorcycle, along with the Roper steam velocipede of 1867 or 1868, and the internal combustion engine Daimler Reitwagen of 1885. Perreaux continued development of his steam cycle, and exhibited a tricycle version by 1884. The only Michaux-Perreaux steam velocipede made, on loan from the Musée de l'Île-de-France, Sceaux, was the first machine viewers saw upon entering the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum rotunda in The Art of the Motorcycle exhibition in New York in 1998.

The Roper steam velocipede was a steam-powered velocipede built by inventor Sylvester H. Roper of Roxbury, Boston, Massachusetts, United States sometime from 1867–1869. It is one of three machines which have been called the first motorcycle, along with the Michaux-Perreaux steam velocipede, also dated 1867–1869, and the 1885 Daimler Reitwagen. Historians disagree over whether the Roper or the Michaux-Perreaux came first. Though the Reitwagen came many years later than the two steam cycles, it is often labeled as the "first motorcycle" because there is doubt by some experts whether a steam cycle should meet the definition of a motorcycle.

The Daimler Reitwagen or Einspur was a motor vehicle made by Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach in 1885. It is widely recognized as the first motorcycle. Daimler is often called "the father of the motorcycle" for this invention. Even when the steam powered two-wheelers that preceded the Reitwagen, the Michaux-Perreaux and Roper of 1867–1869, and the 1884 Copeland, are considered motorcycles, it remains nonetheless the first gasoline internal combustion motorcycle, and the forerunner of all vehicles, land, sea and air, that use its overwhelmingly popular engine type.

The Curtiss V-8 motorcycle was a 269 cu in (4,410 cc) V8 engine-powered motorcycle designed and built by aviation and motorcycling pioneer Glenn Curtiss that set an unofficial land speed record of 136.36 miles per hour (219.45 km/h) on January 24, 1907. The air-cooled F-head engine was developed for use in dirigibles.

Alois Wolfmüller was a German engineer and inventor.
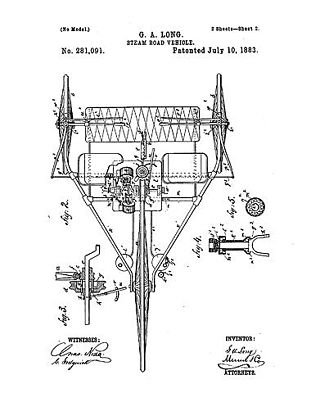
The Long steam tricycle appears to be one of the earliest preserved examples of a steam tricycle, built by George A. Long around 1880 and patented in 1883. One example was built, which after some years of use was dismantled and the parts dispersed. In 1946, one John H. Bateman, with assistance from the 96-year-old Long, reassembled the machine, which is now on display at the Smithsonian Institution. The example at the Smithsonian has been noted as the "oldest completely operable self-propelled road vehicle in the museum".