
Oro City is a ghost town in Lake County, Colorado, United States

Oro City is a ghost town in Lake County, Colorado, United States
The community was an early Colorado gold placer mining town located near Leadville in the California Gulch. Oro is the Spanish word for gold. Oro City was the site of one of the single richest placer gold strikes in Colorado, with estimated gold production of 120,000 to 150,000 troy ounces (4 to 5 metric tons), worth $2.5 to $3 million at the then-price of $20.67 per troy ounce (31.1 grams). [1]
The site of Oro City is at 39°14′05″N106°15′08″W / 39.23472°N 106.25222°W . It is in California Gulch, about a mile (1.6 km) northeast of Leadville in the Mosquito Range of Lake County, Colorado, United States.

Gold was discovered in the area in late 1859, during the Pike's Peak Gold Rush. However the initial discovery, where California Gulch empties into the Arkansas River, was not rich enough to cause excitement. On 26 April 1860, Abe Lee made a rich discovery of placer gold on California Gulch six miles (9.7 km) east of the Arkansas River, and Oro City was founded at the new diggings. [2] [3] By July 1860, the town and surrounding area had a population of 10,000. An estimated $2 million in gold was taken out the first summer from California Gulch and nearby Iowa Gulch, but within a few years the richest part of the placers had been exhausted, and the population of Oro City was several hundred. Many claims (each measuring 100 feet (30.5 meters) along the stream) were consolidated, and worked by ground sluicing. A ditch was dug in 1877 to provide water for hydraulic mining, but the hydraulic mining was reported to be unsuccessful. [4]
Placer mining had always been hampered by a heavy brown sand. As early as 1874, one of the miners determined that the brown sand was the lead mineral cerussite, and that the sand also carried high values of silver. Some veins of gold ore had already been found, but following the brown sand to its sources in the bedrock led to the discovery of large and rich silver deposits. The silver started a new and larger rush, and Oro City filled with silver prospectors, but most people went instead to the new city of Leadville nearby. [5] : 56 The 1890 census found the population of Oro to be 222.

Leadville is a statutory city that is the county seat, the most populous community, and the only incorporated municipality in Lake County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 2,633 at the 2020 census. It is situated at an elevation of 10,158 feet (3,096 m). Leadville is the highest incorporated city in the United States and is surrounded by two of the tallest peaks in the state.

The Pike's Peak gold rush was the boom in gold prospecting and mining in the Pike's Peak Country of western Kansas Territory and southwestern Nebraska Territory of the United States that began in July 1858 and lasted until roughly the creation of the Colorado Territory on February 28, 1861. An estimated 100,000 gold seekers took part in one of the greatest gold rushes in North American history.

Fairplay is a statutory town that is the county seat and the most populous municipality of Park County, Colorado, United States. The town population was 724 at the 2020 United States Census. Fairplay is located in South Park at an elevation of 9,953 feet (3,034 m). The town is the fifth-highest incorporated place in the State of Colorado. Fairplay is now a part of the Denver–Aurora–Lakewood, CO Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Front Range Urban Corridor.

A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, Greece, New Zealand, Brazil, Chile, South Africa, California, the United States, and Canada while smaller gold rushes took place elsewhere.

South Park is a grassland flat within the basin formed by the Rocky Mountains' Mosquito and Park Mountain Ranges within central Colorado. This high valley ranges in elevation from approximately 9,000 to 10,000 ft. It encompasses approximately 1,000 square miles around the headwaters of the South Platte River in Park County approximately 60 mi (100 km) southwest of Denver. It is the largest and southernmost of three similarly named high altitude basins in the Front Range of Colorado, the others being North Park and Middle Park. The largest town in the basin is Fairplay, with a population of 724.

The Colorado Silver Boom was a dramatic expansionist period of silver mining activity in the U.S. state of Colorado in the late 19th century. The boom started in 1879 with the discovery of silver at Leadville. Over 82 million dollars worth of silver was mined during the period, making it the second great mineral boom in the state, and coming 20 years after the earlier and shorter Colorado Gold Rush of 1859. The boom was largely the consequence of large-scale purchases of silver by the United States Government authorized by Congress in 1878. The boom endured throughout the 1880s, resulting in an intense increase in both the population and wealth of Colorado, especially in the mountains. It came to an end in 1893 in the wake of the collapse of silver prices caused by the repeal of Sherman Silver Purchase Act.

Horace Austin Warner "Haw" Tabor, also known as The Bonanza King of Leadville and The Silver King, was an American prospector, businessman, and Republican politician. His success in Leadville, Colorado's silver mines made him one of the wealthiest men in Colorado. He purchased more mining enterprises throughout Colorado and the Southwestern United States, and he was a philanthropist. After the collapse in the silver market during the Panic of 1893, Tabor was financially devastated. He lost most of his holdings, and he labored in the mines. In his last year, he was the postmaster of Denver.
Eben Smith was a successful mine owner, smelting company executive, railroad executive and bank owner in Colorado in the late 19th century and early 20th century.

Pack burro racing is a sport in Colorado, Arizona, California, and New Mexico that is rooted in the various western states' mining histories. In the early days of the mining industry in Colorado, miners would take donkeys through the mountains of Colorado while prospecting. Because the burros were carrying supplies, the miners could not ride the animals and so they would walk, leading the donkey. Burro races are held throughout small towns in Colorado, Arizona, California, and New Mexico to commemorate the miners and their burros. In 2012, pack burro racing was recognized as the official "summer heritage sport" in Colorado.

Ashcroft is an extinct mining town located in Pitkin County, Colorado, United States. The silver mining camp was founded as Castle Forks City in the spring of 1880. A post office named Ashcroft operated at the site from August 12, 1880, until August 5, 1881, when the name was changed to Chloride. The Chloride post office operated until January 3, 1882 when the name was changed back to Ashcroft. The renamed Ashcroft post office finally closed on November 30, 1912.

Granite is an unincorporated community with a U.S. Post Office in Chaffee County, Colorado, United States. The zip code of Granite is 81228. According to the 2010 census, the population is 116.
Arapahoe was one of the first settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Colorado. Nothing remains of the now deserted ghost town in Jefferson County, except a historical marker on the south side of 44th Avenue, between the towns of Golden and Wheat Ridge.

In the United States, gold mining has taken place continually since the discovery of gold at the Reed farm in North Carolina in 1799. The first documented occurrence of gold was in Virginia in 1782. Some minor gold production took place in North Carolina as early as 1793, but created no excitement. The discovery on the Reed farm in 1799 which was identified as gold in 1802 and subsequently mined marked the first commercial production.
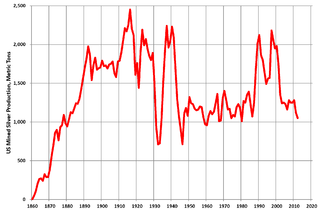
Silver mining in the United States began on a major scale with the discovery of the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1858. The industry suffered greatly from the demonetization of silver in 1873 by the Coinage Act of 1873, known pejoratively as the "Crime of 73", but silver mining continues today.
Gold mining in Colorado, a state of the United States, has been an industry since 1858. It also played a key role in the establishment of the state of Colorado.
Silver mining in Colorado has taken place since the 1860s. In the past, Colorado called itself the Silver State.

The Leadville mining district, located in the Colorado Mineral Belt, was the most productive silver-mining district in the state of Colorado and hosts one of the largest lead-zinc-silver deposits in the world. Oro City, an early Colorado gold placer mining town located about a mile east of Leadville in California Gulch, was the location to one of the richest placer gold strikes in Colorado, with estimated gold production of 120,000–150,000 ozt, worth $2.5 to $3 million at the then-price of $20.67 per troy ounce.

Buckskin Joe is an extinct gold mining town located in Park County, Colorado, United States. The town was founded in 1860 as Laurette in what was then the Kansas Territory. The Territory of Colorado was created on February 28, 1861, and the Laurette post office opened on November 14, 1861. Laurette was elected the Park County seat on January 7, 1862. The post office name was changed to Buckskin on December 21, 1865, although the town was popularly known as Buckskin Joe. The county seat was moved to Fair Play in 1867, and the Buckskin post office closed on January 24, 1873.

Confederate Gulch is a steeply incised gulch or valley on the west-facing slopes of the Big Belt Mountains in the U.S. state of Montana. Its small stream drains westward into Canyon Ferry Lake, on the upper Missouri River near present-day Townsend, Montana. In 1864, Confederate soldiers on parole during the American Civil War made a minor gold discovery in the gulch, but the discovery of the sensationally rich Montana Bar the following year—one of the richest placer strikes per acre ever made—led to other rich gold strikes up and down the gulch, and touched off a frantic boom period of placer gold mining in the area that extended through 1869. From 1866 to 1869, the gulch equaled or outstripped all other mining camps in the Montana Territory in gold production, producing an estimated $19–30 million worth of gold. For a time, Confederate Gulch was the largest community in Montana. In 1866, Montana had a total population of 28,000, and of these, about 10,000 (35%) were working in Confederate Gulch.

The California Gulch site consists of approximately 18 square miles in Lake County, Colorado. The area includes the city of Leadville, parts of the Leadville Historic Mining District and a section of the Arkansas River from the confluence of California Gulch downstream to the confluence of Two-Bit Gulch. The site was listed as a Superfund site in 1983.