
Algae are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as Chlorella, Prototheca and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to 50 metres (160 ft) in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds. In contrast, the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, Spirogyra and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton.

The Copeland Islands is a group of three islands in the north Irish Sea, north of Donaghadee, County Down, Northern Ireland, consisting of Lighthouse Island, Copeland Island and Mew Island. They lie within the civil parish of Bangor.

The Ulster Museum, located in the Botanic Gardens in Belfast, has around 8,000 square metres of public display space, featuring material from the collections of fine art and applied art, archaeology, ethnography, treasures from the Spanish Armada, local history, numismatics, industrial archaeology, botany, zoology and geology. It is the largest museum in Northern Ireland, and one of the components of National Museums Northern Ireland.

Coralline algae are red algae in the order Corallinales. They are characterized by a thallus that is hard because of calcareous deposits contained within the cell walls. The colors of these algae are most typically pink, or some other shade of red, but some species can be purple, yellow, blue, white, or gray-green. Coralline algae play an important role in the ecology of coral reefs. Sea urchins, parrot fish, and limpets and chitons feed on coralline algae. In the temperate Mediterranean Sea, coralline algae are the main builders of a typical algal reef, the Coralligène ("coralligenous"). Many are typically encrusting and rock-like, found in marine waters all over the world. Only one species lives in freshwater. Unattached specimens may form relatively smooth compact balls to warty or fruticose thalli.

William Thompson was an Irish naturalist celebrated for his founding studies of the natural history of Ireland, especially in ornithology and marine biology. Thompson published numerous notes on the distribution, breeding, eggs, habitat, song, plumage, behaviour, nesting and food of birds. These formed the basis of his four-volume The Natural History of Ireland, and were much used by contemporary and later authors such as Francis Orpen Morris.

John Templeton (1766–1825) was a pioneering Irish naturalist, sometimes referred to as the "Father of Irish Botany". He was a leading figure in Belfast's late eighteenth-century enlightenment, initially supported the United Irishmen, and figured prominently in the town's scientific and literary societies.

William Henry Harvey, FRS FLS was an Irish botanist and phycologist who specialised in algae.
William McCalla (1814–1849) was an Irish naturalist.

Mikael Heggelund Foslie was a Norwegian botanist and algaeologist. Foslie was curator of the Royal Norwegian Scientific Society Museum in Trondheim.

Lemanea is a genus of freshwater red algae, in the order Batrachospermales. Both species are considered to be widespread in the northern hemisphere. Although placed in the Rhodophyta it in fact is green in colour.
The history of phycology is the history of the scientific study of algae. Human interest in plants as food goes back into the origins of the species, and knowledge of algae can be traced back more than two thousand years. However, only in the last three hundred years has that knowledge evolved into a rapidly developing science.

Colpomenia peregrina, sometimes referred to by its vernacular names oyster thief and bladder weed, is a species of brown seaweed.

Gastroclonium reflexum is a small red alga (Rhodophyta) reported from Ireland and Britain.

Scutellastra cochlear is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Patellidae, one of the families of true limpets. It is commonly known as the snail patella, the pear limpet or the spoon limpet and is native to South Africa. It often grows in association with the crustose coralline alga Spongites yendoi and a filamentous red alga which it cultivates in a garden. It was first described by the malacologist Ignaz von Born in 1778 as Patella cochlear.

Porolithon is a genus of coralline red algae. although more species have been recently proposed. The Porolithon are the primary reef building algae. When coral reefs reach sea level, many corals break under the high energy impact of the waves, while coralline red algae, primarily Porolithon, continuing building and cementing the reef structure.

Spongites yendoi is a species of crustose red seaweed with a hard, calcareous skeleton in the family Corallinaceae. It is found on the lower shore as part of a diverse community in the southeastern Atlantic and the Indo-Pacific Oceans.

Bonnemaisonia hamifera is a species of red alga in the family Bonnemaisoniaceae. Originally from the Pacific Ocean, it has been introduced into the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, where it is considered invasive on European coasts. It exists in two phases which, at one time, were thought to be different species; a medium-sized feathery form attached to other seaweeds, and a small tufted form known as Trailliella.
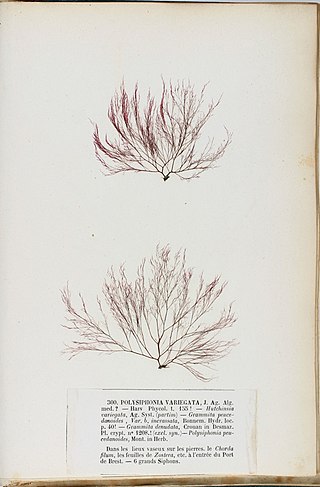
Polysiphonia denudata is a small red alga, Rhodophyta, growing as tufts up to 20 cm long without a main branch axis.
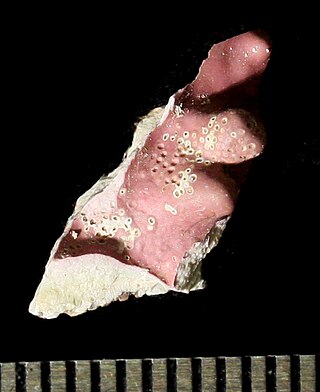
Lithothamnion glaciale is the botanical name for a species of multicellular red algae of the genus Lithothamnion, subfamily Melobesioideae.














