
The Watercress Line is the marketing name of the Mid-Hants Railway, a heritage railway in Hampshire, England, running 10 miles (16 km) from New Alresford to Alton where it connects to the National Rail network. The line gained its popular name in the days when it was used to transport locally grown watercress to markets in London. The railway currently operates regular scheduled services, along with dining trains, real ale trains and numerous special events throughout the year.

Slough railway station, in Slough, Berkshire, England, is on the Great Western Main Line, halfway between London Paddington and Reading. It is 18 miles 36 chains down the line from the zero point at Paddington and is situated between Langley to the east and Burnham to the west. The station is just to the north of the town centre, on the north side of the A4.

Exeter Central railway station is the most central of the stations in the city of Exeter, Devon, United Kingdom. It is 171 miles 30 chains (275.8 km) down the line from London Waterloo. The station is smaller than Exeter St Davids on the west side of the city. Great Western Railway manages the station and operates most services, as well as South Western Railway.

Newton Abbot railway station serves the town of Newton Abbot in Devon, England. It is 214 miles 5 chains from London, measured from the zero point at London Paddington to the junction for the branch to Paignton. The station today is managed by Great Western Railway, who provide train services along with CrossCountry.

Paignton railway station serves the town and seaside resort of Paignton in Devon, England. It is 222 miles 12 chains measured from London Paddington. The station is the current terminus of the Riviera Line from Exeter and is also an interchange station between National Rail services and the preserved Dartmouth Steam Railway.

Torquay railway station is on the Riviera Line and serves the seaside resort of Torquay, Devon, England. It is 219 miles 79 chains measured from London Paddington.

Newquay railway station serves the town and seaside resort of Newquay in Cornwall, England. It is the terminus of the Atlantic Coast Line from Par, 302 miles 49 chains measured from London Paddington. The station is situated in the heart of Newquay, close to the town centre itself and the beaches. The station is managed by Great Western Railway which operates local branch line services to and from Par. In the summer, there are also services to and from London.

Goodrington Sands railway station is on the Dartmouth Steam Railway, a heritage railway in Devon, England. It is close to Goodrington Sands beach and the Splashdown Quaywest water park in Paignton.

The Slough–Windsor & Eton line is a branch railway line 2 miles 63 chains (4.5 km) long, in Berkshire, England. Trains run between the line's only two stations, Slough and Windsor & Eton Central. At its northern end, the branch line joins the Great Western Main Line, but passenger trains from Windsor rarely use the connection, usually terminating at Slough.

The Ropes Creek Line is a closed railway line in the western suburbs of Sydney, Australia.

Harborne railway station was a railway station in Birmingham, England, built by the Harborne Railway and operated by the London and North Western Railway in 1874. In addition to the passenger facilities, there was a goods shed and sidings.
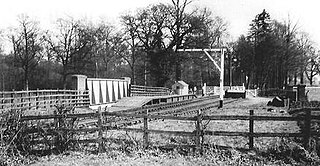
Wood Siding railway station was a halt in Bernwood Forest, Buckinghamshire, England. It opened in 1871 as a terminus of a short horse-drawn tramway built to assist the transport of goods from and around the Duke of Buckingham's extensive estates in Buckinghamshire, as well as connect the Duke's estates to the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway at Quainton Road.
Swithland Sidings is a set of railway sidings on the preserved Great Central Railway, situated just south of Swithland Reservoir and Swithland Viaduct which crosses it.

Kineton railway station was a railway station located to the west of Kineton, Warwickshire, England. It stood at the junction of Warwick Road (B4086) and Brookhampton Lane, on a site now occupied by the Plantagenet trading estate.

The Kurrajong railway line was a railway line in the distant rural western suburbs of Sydney, Australia. It was an extension of the branch off the Main Western line from Blacktown to Richmond and was operated by the New South Wales Government Railways.
The Brill Tramway, also known as the Quainton Tramway, Wotton Tramway, Oxford & Aylesbury Tramroad and Metropolitan Railway Brill Branch, was a six-mile (10 km) rail line in the Aylesbury Vale, Buckinghamshire, England. It was privately built in 1871 by the 3rd Duke of Buckingham as a horse tram line to transport goods between his lands around Wotton House and the national railway network. Lobbying from residents of the nearby town of Brill led to the line's extension to Brill and conversion to passenger use in early 1872. Two locomotives were bought for the line, but as it had been designed and built with horses in mind, services were very slow; trains travelled at an average speed of only 4 miles per hour (6.4 km/h).

The Hastings Miniature Railway is a 10+1⁄4 in gauge miniature railway located on the seafront at Hastings, a seaside resort, town, and ancient cinque port, in East Sussex, England. Opened in 1948, it remains a popular tourist attraction. The line was re-opened in the summer of 2011 after a period of reconstruction and restoration, which coincided with a forced closure of the eastern part of the line, to facilitate building work on a new art gallery adjacent to the railway.

The Carlingford railway line was a railway line in Sydney, Australia. It was opened from Clyde to Subiaco in January 1885, then by means of the construction of a bridge across the Parramatta River, to Carlingford in April 1896. It closed on 5 January 2020 with much of the line to be converted to light rail as part of the Parramatta Light Rail network, while a short section of the line was retained for use by Sydney Trains.

Preston Brook railway station was a station on the Grand Junction Railway serving the villages of Preston Brook and Preston on the Hill in what was then Cheshire, England. It opened on 4 July 1837 when the line opened.

Goodrington carriage holding sidings are located in Goodrington, Torbay, England, and served from Paignton railway station.





















