
Runaway Train is a 1985 American action thriller film directed by Andrei Konchalovsky and starring Jon Voight, Eric Roberts, Rebecca De Mornay and John P. Ryan. The screenplay by Djordje Milicevic, Paul Zindel and Edward Bunker was based on an original 1960s screenplay by Akira Kurosawa, with uncredited contributions by frequent Kurosawa collaborators Hideo Oguni and Ryūzō Kikushima. The film was also the feature debut of both Danny Trejo and Tommy "Tiny" Lister, who both proceeded to successful careers as "tough guy" character actors.

The Kansas City Southern Railway Company was an American Class I railroad. Founded in 1887, it operated in 10 Midwestern and Southeastern U.S. states: Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Tennessee, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana and Texas. KCS had the shortest north-south rail route between Kansas City, Missouri, and several key ports along the Gulf of Mexico.

The Southern Pacific was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the names Southern Pacific Railroad, Southern Pacific Company and Southern Pacific Transportation Company.
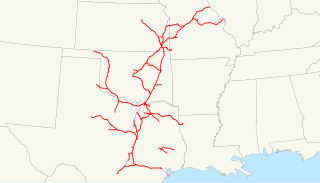
The Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad was a Class I railroad company in the United States, with its last headquarters in Dallas, Texas. Established in 1865 under the name Union Pacific Railroad (UP), Southern Branch, it came to serve an extensive rail network in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Missouri. In 1988, it merged with the Missouri Pacific Railroad; today, it is part of UP.

The Chicago and North Western was a Class I railroad in the Midwestern United States. It was also known as the "North Western". The railroad operated more than 5,000 miles (8,000 km) of track at the turn of the 20th century, and over 12,000 miles (19,000 km) of track in seven states before retrenchment in the late 1970s. Until 1972, when the employees purchased the company, it was named the Chicago and North Western Railway.

The Missouri Pacific Railroad, commonly abbreviated as MoPac, was one of the first railroads in the United States west of the Mississippi River. MoPac was a Class I railroad growing from dozens of predecessors and mergers. In 1967, the railroad operated 9,041 miles of road and 13,318 miles of track, not including DK&S, NO&LC, T&P, and its subsidiaries C&EI and Missouri-Illinois.

The EMD F7 is a model of 1,500-horsepower (1,100 kW) diesel-electric locomotive produced between February 1949 and December 1953 by the Electro-Motive Division of General Motors (EMD) and General Motors Diesel (GMD).

The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway, commonly known as the "Frisco", was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central United States from 1876 to April 17, 1980. At the end of 1970, it operated 4,547 miles (7,318 km) of road on 6,574 miles (10,580 km) of track, not including subsidiaries Quanah, Acme and Pacific Railway and the Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad; that year, it reported 12,795 million ton-miles of revenue freight and no passengers. It was purchased and absorbed into the Burlington Northern Railroad in 1980. Despite its name, it never came close to San Francisco.

The EMD GP7 is a four-axle (B-B) diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division and General Motors Diesel between October 1949 and May 1954.

The Chattooga and Chickamauga Railway is a short-line railroad which is headquartered in LaFayette, Georgia, USA. The railroad operated 22 miles (35 km) of the Tennessee, Alabama and Georgia Railway from Chattanooga, Tennessee to Kensington, Georgia, which reverted to the Norfolk Southern System and was partially removed after the Dow Reichhold Specialty Latex LLC plant in Kensington closed in August 2008. The "C&C" also operates 42 miles (68 km) of the former Central of Georgia Railway from Chattanooga to Lyerly, Georgia. That line is leased from the state of Georgia.

The Arizona Eastern Railway is a Class III railroad that operates 206 miles (332 km) of railroad between Clifton, Arizona, and Miami, Arizona, in the United States. This includes trackage rights over the Union Pacific Railroad between Lordsburg, New Mexico, and Bowie, Arizona. The railroad serves the copper mining region of southeastern Arizona, and the agricultural Gila River Valley. The railroad offers a transload location for lumber, building materials and other consumer commodities at Globe, Arizona. As of 2023, AZER has a maximum capacity of 286,000, and has one interchange: Union Pacific.

The EMD GP10 is a diesel-electric locomotive that is the result of rebuilding a GP7, GP9 or GP18.

The Branson Scenic Railway is a heritage railroad in Branson, Missouri. The Ozark Zephyr, Branson Scenic Railway's historic zephyr train, departs from an old depot in downtown Branson and operates in the scenic Ozark Mountains for an approximate 40-mile (64 km) round trip.

Lake State Railway is a railroad operating in the Saginaw Valley and northeastern quadrant of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. The railroad moves large quantities of aggregate and limestone, as well as coal, grain, and chemical products. Some of the company's largest customers include Dow Chemical Company, S. C. Johnson & Son, Lafarge, ConAgra Foods, Archer Daniels Midland, Conrad Yelvington Distributors, and Consumers Energy.

The Squaw Creek Southern Railroad is a Class III railroad subsidiary of Respondek Railroad operating in the southern portion of the State of Indiana. Originally, the Squaw Creek Southern started operating 21 miles of former Yankeetown Dock Corporation/Peabody Coal trackage owned by Norfolk Southern, but has since started servicing Foresight Energy's Sitran Coal Terminal near Evansville, Indiana and SABIC's Innovative Plastics plant in Mount Vernon, Indiana.
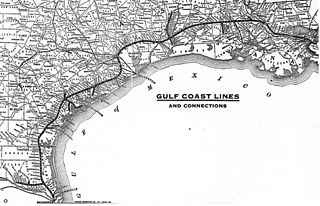
Chartered on June 6, 1903, the St. Louis, Brownsville & Mexico Railway was a 200-mile (321 km) U.S. railroad that operated from Brownsville, Texas, to Gulf Coast Junction in Houston, Texas. It served numerous towns and cities along its routes and operated a rail bridge between Brownsville and Matamoros, Tamaulipas, in junction with the Mexican government. The Brownie connected the citizens of Brownsville to nearby Corpus Christi for the first time on land rather than using water transportation.

The Stone Mountain Scenic Railroad (SMRR) is a standard gauge railroad that circles the perimeter of Stone Mountain Park in a loop, and provides views of the mountain en route.

The Wabash Railroad was a Class I railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. It served a large area, including track in the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, and Missouri and the province of Ontario. Its primary connections included Chicago, Illinois; Kansas City, Missouri; Detroit, Michigan; Buffalo, New York; St. Louis, Missouri; and Toledo, Ohio.
The Iowa and St. Louis Railway (I&SL) was a subsidiary United States railroad operating in south-east Iowa and north-east Missouri from 1902 to 1947. For most of its existence it was part of the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad (CBQ), familiarly known as the Burlington System.

















