Proliferation-associated protein 2G4 (PA2G4) also known as ErbB3-binding protein 1 (EBP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PA2G4 gene. [5]
Proliferation-associated protein 2G4 (PA2G4) also known as ErbB3-binding protein 1 (EBP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PA2G4 gene. [5]
This gene encodes an RNA-binding protein that is involved in growth regulation. This protein is present in pre-ribosomal ribonucleoprotein complexes and may be involved in ribosome assembly and the regulation of intermediate and late steps of rRNA processing. This protein can interact with the cytoplasmic domain of the ErbB3 receptor and may contribute to transducing growth regulatory signals. This protein is also a transcriptional corepressor of androgen receptor-regulated genes and other cell cycle regulatory genes through its interactions with histone deacetylases. This protein has been implicated in growth inhibition and the induction of differentiation of human cancer cells. Paradoxically, the expression of EBP1 is decreased in prostate cancer, [6] but increased in Acute Myelogneous Leukemia. [7] Six pseudogenes, located on chromosomes 3, 6, 9, 18, 20 and X, have been identified. [8]
PA2G4 has been shown to interact with ERBB3, [9] [10] retinoblastoma protein, [11] and androgen receptor. [12]

In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the right cell at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome.

The epidermal growth factor receptor is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family of extracellular protein ligands.
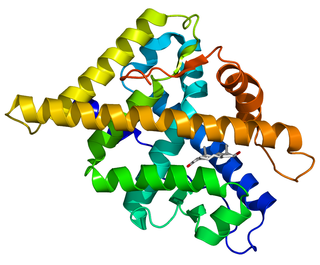
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.
Demethylases are enzymes that remove methyl (CH3-) groups from nucleic acids, proteins (in particular histones), and other molecules. Demethylase enzymes are important in epigenetic modification mechanisms. The demethylase proteins alter transcriptional regulation of the genome by controlling the methylation levels that occur on DNA and histones and, in turn, regulate the chromatin state at specific gene loci within organisms.
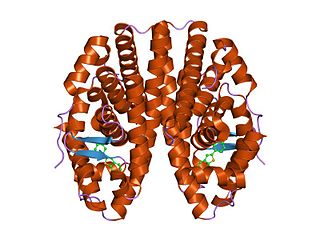
The nuclear receptor coactivator 2 also known as NCoA-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA2 gene. NCoA-2 is also frequently called glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 (GRIP1), steroid receptor coactivator-2 (SRC-2), or transcriptional mediators/intermediary factor 2 (TIF2).

RAR-related orphan receptor alpha (RORα), also known as NR1F1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RORA gene. RORα participates in the transcriptional regulation of some genes involved in circadian rhythm. In mice, RORα is essential for development of cerebellum through direct regulation of genes expressed in Purkinje cells. It also plays an essential role in the development of type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) and mutant animals are ILC2 deficient. In addition, although present in normal numbers, the ILC3 and Th17 cells from RORα deficient mice are defective for cytokine production.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAK1 gene.
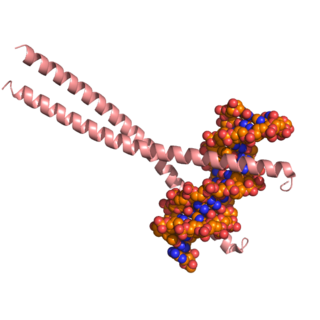
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPB gene.

Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3, also known as HER3, is a membrane bound protein that in humans is encoded by the ERBB3 gene.

Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ERBB4 gene. Alternatively spliced variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described; however, not all variants have been fully characterized.
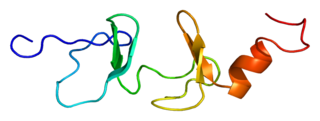
Four and a half LIM domains protein 2 also known as FHL-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FHL2 gene. LIM proteins contain a highly conserved double zinc finger motif called the LIM domain.

CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPD gene.

Thyroid hormone receptor alpha (TR-alpha) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group A, member 1 (NR1A1), is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the THRA gene.

DNA damage-inducible transcript 3, also known as C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), is a pro-apoptotic transcription factor that is encoded by the DDIT3 gene. It is a member of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) family of DNA-binding transcription factors. The protein functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor by forming heterodimers with other C/EBP members, preventing their DNA binding activity. The protein is implicated in adipogenesis and erythropoiesis, and has an important role in the cell's stress response.

ERG is an oncogene. ERG is a member of the ETS family of transcription factors. The ERG gene encodes for a protein, also called ERG, that functions as a transcriptional regulator. Genes in the ETS family regulate embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, inflammation, and apoptosis.

Metastasis-associated protein MTA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTA2 gene.

TATA element modulatory factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMF1 gene.

Forkhead box protein A1 (FOXA1), also known as hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-alpha (HNF-3A), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXA1 gene.

The retinoblastoma protein is a tumor suppressor protein that is dysfunctional in several major cancers. One function of Rb is to prevent excessive cell growth by inhibiting cell cycle progression until a cell is ready to divide. When the cell is ready to divide, Rb is phosphorylated to pRb, leading to the inactivation of Rb. This process allows cells to enter into the cell cycle state. It is also a recruiter of several chromatin remodeling enzymes such as methylases and acetylases.
EPI-001 is the first inhibitor of the androgen receptor amino-terminal domain. The single stereoisomer of EPI-001, EPI-002, is a first-in-class drug that the USAN council assigned a new stem class "-aniten" and the generic name "ralaniten". This distinguishes the anitens novel molecular mechanism from anti androgens that bind the C-terminus ligand-binding domain and have the stem class "lutamide". EPI-001 and its stereoisomers and analogues were discovered by Dr. Marianne Sadar and Dr. Raymond Andersen who co-founded the pharmaceutical company ESSA Pharma Inc for the clinical development of anitens for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
| This article on a gene on human chromosome 12 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |