Prickle planar cell polarity protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRICKLE1 gene. [5]
Prickle planar cell polarity protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRICKLE1 gene. [5]
This gene encodes a nuclear receptor that may be a negative regulator of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. The encoded protein localizes to the nuclear membrane and has been implicated in the nuclear trafficking of the transcription repressors REST/NRSF and REST4. Mutations in this gene have been linked to progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 3.
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans.
Prickle is also known as REST/NRSF-interacting LIM domain protein, which is a putative nuclear translocation receptor. Prickle is part of the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway that establishes planar cell polarity. A gain or loss of function of Prickle1 causes defects in the convergent extension movements of gastrulation. In epithelial cells, Prickle2 establishes and maintains cell apical/basal polarity. Prickle1 plays an important role in the development of the nervous system by regulating the movement of nerve cells.

Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LEF1 gene. It is a member of T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF) family.

Frizzled-2(Fz-2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD2 gene.

Frizzled-5(Fz-5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD5 gene.

Frizzled-3(Fz-3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD3 gene.

Frizzled-6(Fz-6) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD6 gene.

Transcriptional regulator Kaiso is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB33 gene. This gene encodes a transcriptional regulator with bimodal DNA-binding specificity, which binds to methylated CGCG and also to the non-methylated consensus KAISO-binding site TCCTGCNA. The protein contains an N-terminal POZ/BTB domain and 3 C-terminal zinc finger motifs. It recruits the N-CoR repressor complex to promote histone deacetylation and the formation of repressive chromatin structures in target gene promoters. It may contribute to the repression of target genes of the Wnt signaling pathway, and may also activate transcription of a subset of target genes by the recruitment of catenin delta-2 (CTNND2). Its interaction with catenin delta-1 (CTNND1) inhibits binding to both methylated and non-methylated DNA. It also interacts directly with the nuclear import receptor Importin-α2, which may mediate nuclear import of this protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified.

Transcription factor 7 is the gene that in humans encodes for the TCF1 protein.

ZIC3 is a member of the Zinc finger of the cerebellum (ZIC) protein family.

Segment polarity protein dishevelled homolog DVL-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DVL3 gene.

Protein chibby homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CBY1 gene.

Proto-oncogene protein Wnt-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT3 gene.

Protein Wnt-9a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT9A gene.

Tyrosine-protein kinase-like 7 also known as colon carcinoma kinase 4 (CCK4) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that in humans is encoded by the PTK7 gene.

Dishevelled (Dsh) is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors. It takes its name from its initial discovery in flies, where a mutation in the dishevelled gene was observed to cause improper orientation of body and wing hairs. There are vertebrate homologs in zebrafish, Xenopus (Xdsh), mice and humans. Dsh relays complex Wnt signals in tissues and cells, in normal and abnormal contexts. It is thought to interact with the SPATS1 protein when regulating the Wnt Signalling pathway.
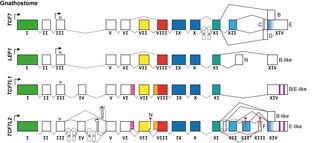
The TCF/LEF family is a group of genes that encode transcription factors which bind to DNA through a SOX-like high mobility group domain. They are involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, particularly during embryonic and stem-cell development, but also had been found to play a role in cancer and diabetes. TCF/LEF factors recruit the coactivator beta-catenin to enhancer elements of genes they target. They can also recruit members of the Groucho family of corepressors.

Transcription factor 7-like 1, also known as TCF7L1, is a human gene.

Protein Wnt-9b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT9B gene.

Prickle planar cell polarity protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRICKLE2 gene.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.