
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin-6 secretion by macrophages and T cells. Its physiological role is to bind to lysophosphatidylcholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells in order to activate the complement system via C1q.
Opsonins are extracellular proteins that, when bound to substances or cells, induce phagocytes to phagocytose the substances or cells with the opsonins bound. Thus, opsonins act as tags to label things in the body that should be phagocytosed by phagocytes. Different types of things ("targets") can be tagged by opsonins for phagocytosis, including: pathogens, cancer cells, aged cells, dead or dying cells, excess synapses, or protein aggregates. Opsonins help clear pathogens, as well as dead, dying and diseased cells.

Fas ligand is a type-II transmembrane protein expressed on various types of cells, including cytotoxic T lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, breast epithelial cells, vascular endothelial cells and natural killer (NK) cells. It binds with its receptor, called FAS receptor and plays a crucial role in the regulation of the immune system and in induction of apoptosis, a programmed cell death.

Pentraxins (PTX), also known as pentaxins, are an evolutionary conserved family of proteins characterised by containing a pentraxin protein domain. Proteins of the pentraxin family are involved in acute immunological responses. They are a class of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). They are a superfamily of multifunctional conserved proteins, some of which are components of the humoral arm of innate immunity and behave as functional ancestors of antibodies (Abs). They are known as classical acute phase proteins (APP), known for over a century.
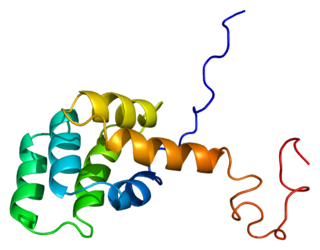
The Fas receptor, also known as Fas, FasR, apoptosis antigen 1, cluster of differentiation 95 (CD95) or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6 (TNFRSF6), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAS gene. Fas was first identified using a monoclonal antibody generated by immunizing mice with the FS-7 cell line. Thus, the name Fas is derived from FS-7-associated surface antigen.
Collectins (collagen-containing C-type lectins) are a part of the innate immune system. They form a family of collagenous Ca2+-dependent defense lectins, which are found in animals. Collectins are soluble pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Their function is to bind to oligosaccharide structure or lipids that are on the surface of microorganisms. Like other PRRs they bind pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) of oligosaccharide origin. Binding of collectins to microorganisms may trigger elimination of microorganisms by aggregation, complement activation, opsonization, activation of phagocytosis, or inhibition of microbial growth. Other functions of collectins are modulation of inflammatory, allergic responses, adaptive immune system and clearance of apoptotic cells.
Chemokine ligand 1 (CCL1) is also known as small inducible cytokine A1 and I-309 in humans. CCL1 is a small glycoprotein that belongs to the CC chemokine family.

Chemokine ligand 7 (CCL7) is a small cytokine that was previously called monocyte-chemotactic protein 3 (MCP3). CCL7 is a small protein that belongs to the CC chemokine family and is most closely related to CCL2.
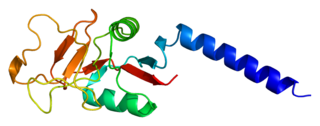
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), also called mannan-binding lectin or mannan-binding protein (MBP), is a lectin that is instrumental in innate immunity as an opsonin and via the lectin pathway.

C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2 or CD192 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR2 gene. CCR2 is a CC chemokine receptor.

Bcl-2-like protein 1 is a protein encoded in humans by the BCL2L1 gene. Through alternative splicing, the gene encodes both of the human proteins Bcl-xL and Bcl-xS.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAK2 gene.

C-C chemokine receptor type 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR7 gene. Two ligands have been identified for this receptor: the chemokines ligand 19 (CCL19/ELC) and ligand 21 (CCL21). The ligands have similar affinity for the receptor, though CCL19 has been shown to induce internalisation of CCR7 and desensitisation of the cell to CCL19/CCL21 signals. CCR7 is a transmembrane protein with 7 transmembrane domains, which is coupled with heterotrimeric G proteins, which transduce the signal downstream through various signalling cascades. The main function of the receptor is to guide immune cells to immune organs by detecting specific chemokines, which these tissues secrete.

Myb-related protein B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYBL2 gene.

Interleukin 1 receptor, type II (IL-1R2) also known as CD121b is an interleukin receptor. IL1R2 also denotes its human gene.

Serum amyloid A1 (SAA1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SAA1 gene. SAA1 is a major acute-phase protein mainly produced by hepatocytes in response to infection, tissue injury and malignancy. When released into blood circulation, SAA1 is present as an apolipoprotein associated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL). SAA1 is a major precursor of amyloid A (AA), the deposit of which leads to inflammatory amyloidosis.

DNA damage-inducible transcript 3, also known as C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), is a pro-apoptotic transcription factor that is encoded by the DDIT3 gene. It is a member of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) family of DNA-binding transcription factors. The protein functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor by forming heterodimers with other C/EBP members, preventing their DNA binding activity. The protein is implicated in adipogenesis and erythropoiesis and has an important role in the cell's stress response.

The TCIRG1 gene encodes for the V-type proton ATPase (V-ATPase) 116 kDa subunit a isoform 3 enzyme.

The Interleukin-1 family is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults.

Alberto Mantovani is an Italian physician and immunologist. He is Scientific Director of Istituto Clinico Humanitas, President and Founder of the Fondazione Humanitas per la Ricerca, and Professor of Pathology at the State University of Milan. He is known for his works in the roles of the immune system in the development of cancer. His research on tumor-associated macrophages established inflammation as one of the causes of cancer. He was the first to identify monocyte chemotactic protein - 1 / CCL2 in 1983, and PTX3 in 1997. His works revealed the existence of decoy receptors in cell-signalling. He has been the most cited scientist in Italy, and one of the ten most cited immunologists worldwide.




















