
The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named for Vitus Bering, a Danish navigator in Russian service, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean.

The underwater environment is the region below the surface of, and immersed in, liquid water in a natural or artificial feature, such as an ocean, sea, lake, pond, reservoir, river, canal, or aquifer. Some characteristics of the underwater environment are universal, but many depend on the local situation.
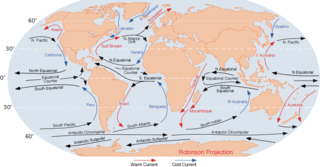
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements.

Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenic beauty, with snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.

The British Columbia Coast, popularly referred to as the BC Coast or simply the Coast, is a geographic region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. As the entire western continental coastline of Canada along the Pacific Ocean is in B.C., it is synonymous with being the West Coast of Canada.

The Arctic Cordillera is a terrestrial ecozone in northern Canada characterized by a vast, deeply dissected chain of mountain ranges extending along the northeastern flank of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago from Ellesmere Island to the northeasternmost part of the Labrador Peninsula in northern Labrador and northern Quebec, Canada. It spans most of the eastern coast of Nunavut with high glaciated peaks rising through ice fields and some of Canada's largest ice caps, including the Penny Ice Cap on Baffin Island. It is bounded to the east by Baffin Bay, Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea while its northern portion is bounded by the Arctic Ocean.
The effect of climate change on marine life and mammals is a growing concern. Many of the effects of global warming are currently unknown due to unpredictability, but many are becoming increasingly evident today. Some effects are very direct such as loss of habitat, temperature stress, and exposure to severe weather. Other effects are more indirect, such as changes in host pathogen associations, changes in body condition because of predator–prey interaction, changes in exposure to toxins and CO2 emissions, and increased human interactions. Despite the large potential impacts of ocean warming on marine mammals, the global vulnerability of marine mammals to global warming is still poorly understood.
The Chukchi Sea Shelf or Chukchi Shelf is the westernmost part of the continental shelf of the United States and the easternmost part of the continental shelf of Russia. Within this shelf, the 50-mile Chukchi Corridor acts as a passageway for one of the largest marine mammal migrations in the world.

The Arctic Archipelago Marine Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a marine ecozone in the Canadian Arctic, encompassing Hudson Bay, James Bay, the internal waters and some shores of the islands in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, and the shores of the territories, northern Ontario and western Quebec. Early exploration of these waters by Europeans were conducted to find a passage to the Orient, now referred to as the Northwest Passage.

The Hudson Plains Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a sparsely populated Canadian subarctic ecozone extending from the western coast of Quebec to the coast of Manitoba, encompassing all coastal areas of James Bay and those of southern Hudson Bay, stretching to about 50°N latitude. It includes the largest continuous wetland in the world. It covers nearly a quarter of Ontario's landmass, and 3.6% of Canada's total area, totalling approximately 369,000 square kilometres of land and 11,800 square kilometres of water. Its historical prominence is due to the harshness endured by pioneer explorers who established fortifications for Hudson's Bay Company, and as a result of regional wars between France and Britain. Today, it is primarily noted for the well-known Polar Bear Provincial Park, and to a lesser extent Wapusk National Park, as well as its vast wetlands which are used by migratory birds.

The Pacific Maritime Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian terrestrial ecozone, spanning a strip approximately 200 kilometres wide along the British Columbia Coast, then narrowing along the border with Alaska. It also includes all marine islands of British Columbia and a small portion of the southwestern corner of the Yukon. Fourteen ecoregions comprise the Ecozone, ranging from the Mount Logan Ecoregion in the north to the Cascade Ecoregion and Lower Mainland Ecoregion in the south.

The Taiga Plain Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian terrestrial ecozone that covers most of the western Northwest Territories, extending to northwest Alberta, northeast British Columbia and slightly overlapping northeastern Yukon.

The Boreal Cordillera Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian terrestrial ecozone occupying most of the northern third of British Columbia and southern half of Yukon. Within it is found Kluane National Park and Reserve, and a small portion of the southern range of Nahanni National Park Reserve. Most of the area's population is based in the city of Whitehorse, and it contains most of Yukon's population. The portion in British Columbia is barely populated.

The Northern Arctic Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian terrestrial ecozone which includes most of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the Boothia and Melville Peninsulas of Nunavut, and the northwestern tip of Quebec. Its marine borders are with the Arctic Archipelago Marine Ecozone, and it is adjacent to the mainland Southern Arctic Ecozone.

The Arctic Basin Marine Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian marine ecozone encompassing the northwestern areas of waters on the Arctic continental shelf. It is bitterly cold and permanently covered in ice. Polar nights and the midnight sun may last months in this region, which has come to characterize the stereotype of the north. Its only land contact is with the northern coast of Ellesmere Island. Because of this, there are no inhabitants in this zone. All human activity here involves scientific excursions, petroleum exploration, rare hunting groups and extreme adventurers.

The Northwest Atlantic Marine Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian marine ecozone forming a transitional region between the cold northern waters of the Arctic Ocean and the more temperate waters in its southern extent.

The Atlantic Marine Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian marine ecozone that stretches from the Davis Strait to encompass the Grand Banks, to the Avalon Peninsula on the shores of Newfoundland. It includes all of the southern coast of Newfoundland, all the eastern coast of Nova Scotia, and portions of the Bay of Fundy and the Gulf of Maine.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Oceanography.

Polar seas is a collective term for the Arctic Ocean and the southern part of the Southern Ocean. In the coldest years, sea ice can cover around 13 percent of the Earth's total surface at its maximum, but out of phase in the two hemispheres. The polar seas contain a huge biome with many organisms.

The Hudson Plains Ecoregion is a vast, flat, and waterlogged landscape. This ecoregion covers a 369,000 square kilometer area along the south shoreline of the Hudson Bay, which includes the Canadian provinces of Eastern Quebec, Northern Ontario and Western Manitoba. Because of the location of the ecoregion, winter prevails for many months of the year and rising temperatures, along with melting ice, makes fog common. The short summers provide a home for thousands of migrating birds. The region is used by humans for its mineral resources and hydroelectric power as a result of the abundance of water and emergent societal needs. Though relatively uninhabited and undisturbed, the natural resources of the Hudson Plains are still subject to anthropogenic activities. Its climatic, geographic, and evolutionary patterns categorize it as one of many ecoregions in North America.

















