

The Padaido Islands, also known as the Padaido Archipelago, is a group of Islands in Indonesia's Papua Province. They lie in Cenderawasih Bay, south and southeast of the island of Biak. The archipelago consists of many small islands and coral reefs.


The Padaido Islands, also known as the Padaido Archipelago, is a group of Islands in Indonesia's Papua Province. They lie in Cenderawasih Bay, south and southeast of the island of Biak. The archipelago consists of many small islands and coral reefs.
The Padaido Islands lie between 1°07’ and 1°22’ South Latitude, and 136°10’ and 136°46’ East Longitude. The archipelago consists of 29 islands. Owi lies furthest west. Auki, Pai, Mios Woendi, and Nusi islands are part of the extensive Woendi atoll, contained within a fringing coral reef, which comprise the Padaido District within the Regency. Pekreki Island lies west of the atoll. An eastern group of islands forming the Almando Padaido District includes Padaidori, Bromsi, Pasi, Manggwandi, Workbondi, Insamfursi, Samakur, Dauwi, Wamsor, Runi and other small islands and reefs. [1]
The islands are generally low, and composed of sand, limestone, or sandstone. [2]
Nine of the islands are inhabited. The residents mostly work as fishers, catching tuna and reef fish. Most fishers use traditional methods such as hook-and-line and nets. Some employ means like poisoning and dynamite fishing, which damage the coral reefs and plants and animals that live there. [1]
Politically the islands are part of Biak Numfor Regency.
The islands are in the Coral Triangle, which has the greatest diversity of coral reef species. Marine environments include extensive areas of coral reef and seagrass beds, and smaller areas of mangrove swamp, particularly on Padaidori. [1]
The islands have a wet tropical climate. Many of the islands are forested. Beach forests occur on most of the islands. Several islands have groves of coconut palms, and some of the larger islands have areas of lowland tropical forest growing on limestone substrates. Some beach forests are composed mostly of Casuarina , while others have a mix of species including the trees and shrubs Barringtonia asiatica, Pandanus tectorius, Hibiscus tiliaceus, Casuarina, Scaevola frutescens , and Terminalia catappa . Crinum asiaticum and the parasitic plant Cassytha filiformis are found the beach forest understory. [2]
Padaido Marine Recreation Park, established in 2009, encompasses the islands and the sea around them. [3]
The Republic of Palau consists of eight principal islands and more than 250 smaller ones lying roughly 500 miles southeast of the Philippines, in Oceania. The islands of Palau constitute the westernmost part of the Caroline Islands chain. The country includes the World War II battleground of Peleliu and world-famous rock islands. The total land area is 459 km2 (177 sq mi). It has the 42nd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 603,978 km2 (233,197 sq mi).

An atoll is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean.

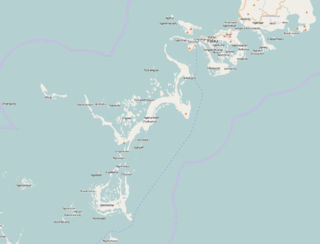
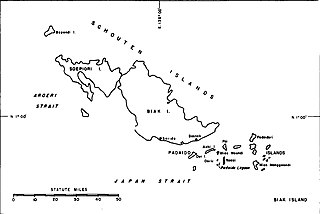
The Biak Islands are an island group of Papua province, eastern Indonesia in the Cenderawasih Bay 50 km off the north-western coast of the island of New Guinea. The group consists of the main islands of Biak, Supiori and Numfor, and numerous smaller islands, mostly covered in rain forest. The population of the archipelago is about 130,000.

Biak is the main island of Biak Archipelago located in Cenderawasih Bay near the northern coast of Papua, an Indonesian province, and is just northwest of New Guinea. Biak has many atolls, reefs, and corals.
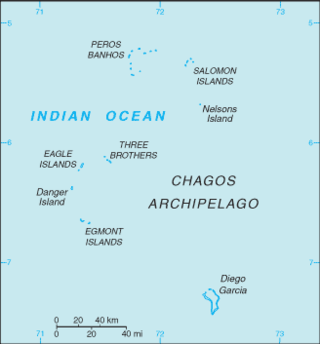
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an archipelago of 55 islands in the Indian Ocean, located south of India. It is situated approximately halfway between Africa and Indonesia. The islands form a semicircular group with an open sea towards the east. The largest, Diego Garcia, is located at the southern extreme end. It measures 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi) and accounts for almost three-quarters of the total land area of the territory. Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island and is home to the joint UK-US naval support facility. Other islands within the archipelago include Danger Island, Three Brothers Islands, Nelson Island, and Peros Banhos, as well as the island groups of the Egmont Islands, Eagle Islands, and the Salomon Islands.

Coral sand is a form of aragonite sand particles originating in tropical and sub-tropical marine environments primarily from bioerosion of limestone skeletal material of marine organisms. Often, this is due to corallivores, such as parrotfish, which excrete sand after digestion. However, the term "coral" in coral sand is used loosely in this sense to mean limestone of recent biological origin; corals are not the dominant contributors of sand particles to most such deposits. Rather, coral sand is a mix of coral and/or remnant skeletal fragments of foraminifera, calcareous algae, molluscs, and crustaceans. Because it is composed of limestone, coral sand is acid-soluble.
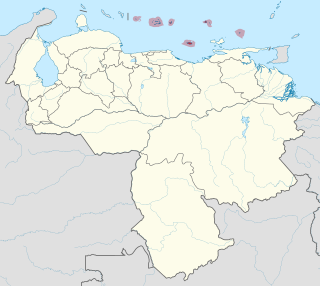
The Federal Dependencies of Venezuela encompass most of Venezuela's offshore islands in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Venezuela, excluding those islands that form the State of Nueva Esparta and some Caribbean coastal islands that are integrated with nearby states. These islands, with a total area of 342 square kilometres, are sparsely populated – according to the preliminary results of the 2011 Census only 2,155 people live there permanently, with another hundred from Margarita Island who live there seasonally to engage in fishing. Local government is officially under the authority of Central government in Caracas, although de facto power is often held by the heads of the sparse and somewhat isolated communities that decorate the territories.

Cenderawasih Bay, also known as Sarera Bay and formerly Geelvink Bay, is a large bay in northern Province of Papua, Central Papua and West Papua, New Guinea, Indonesia.

Raja Ampat, or the Four Kings, is an archipelago located off of the northwest tip of Bird's Head Peninsula, Southwest Papua province, Indonesia. It comprises over 1,500 small islands, cays, and shoals around the four main islands of Misool, Salawati, Batanta, and Waigeo, and the smaller island of Kofiau.
Ambai are the archipelago or the chain of islands off the southern coast of Yapen Island, in Cenderawasih Bay and Papua Province in Western New Guinea, northeastern Indonesia.
Mios Woendi island is an island in the Schouten Islands of Papua province, eastern Indonesia. It lies in Cenderawasih Bay 50 kilometres off the northwestern coast of the island nation of Papua New Guinea.

The Solomon Islands (archipelago) is an island group in the western South Pacific Ocean, north-east of Australia. The archipelago is in the Melanesian subregion and bioregion of Oceania and forms the eastern boundary of the Solomon Sea. The many islands of the archipelago are distributed across the sovereign states of Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands. The largest island in the archipelago is Bougainville Island, which is a part of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville along with Buka Island, the Nukumanu Islands, and a number of smaller nearby islands. Much of the remainder falls within the territory of Solomon Islands and include the atolls of Ontong Java, Sikaiana, the raised coral atolls of Bellona and Rennell, and the volcanic islands of Choiseul, Guadalcanal, Makira, Malaita, New Georgia, the Nggelas, Santa Isabel, and the Shortlands. The Santa Cruz Islands are not a part of the archipelago.

Biak Numfor Regency is one of the regencies (kabupaten) in Papua Province of Western New Guinea in northeastern Indonesia.

Supiori Regency is a regency in the Indonesian province of Papua. The Regency has an area of 634.24 km2 including the Aruri Islands group to the south, and had a population of 15,874 at the 2010 Census and 22,547 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 24,013 - comprising 12,434 males and 11,579 females. Until 8 January 2004, this area was part of the Biak Numfor Regency, from which it was split off in accordance with the Law dated 18 December 2003.

The Biak–Numfoor rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Indonesia. The ecoregion covers the islands of Biak, Supiori, Numfoor, and several smaller islands, which lie in Cenderawasih Bay north of Yapen and New Guinea.

Karimunjawa National Park, also Crimon Java National Park, is a national marine park designated in the Karimun Java archipelago, Jepara Regency, Central Java, Indonesia. It lies 80 km north west of Jepara, Central Java in the Java Sea. The national park was formally declared as Marine Protection Area in 2001. Based on popular local myth, this archipelago was discovered by Sunan Nyamplungan, the nephew of Sunan Kudus who is one of the Wali Sanga.

Teluk Cenderawasih National Park is the largest marine national park of Indonesia, located in Cenderawasih Bay, south-east of Bird's Head Peninsula. It includes the islands of Mioswaar, Nusrowi Island, Roon, Rumberpon, Anggrameos and Yoop. The park protects a rich marine ecosystem, with over 150 recorded coral species, for which it is considered a potential World Heritage Site.

The Maldives–Lakshadweep–Chagos Archipelago tropical moist forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in South Asia. It spans a chain of coralline islands in the Indian Ocean, including Lakshadweep, a union territory of India; the Maldives, an independent country; and the British Indian Ocean Territory, an overseas territory of the United Kingdom.

The Tongan tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion that includes the Tonga archipelago and Niue.

The Palau tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in Micronesia. It encompasses the nation of Palau.