Related Research Articles

The economy of Sudan is largely based on agriculture and oil exports, with additional revenue coming from mining and manufacturing. GDP growth registered more than 10% per year in 2006 and 2007. Sudan had $30.873 billion by gross domestic product as of 2019, and has been working with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to implement macroeconomic reforms, including a managed float of the exchange rate. Sudan began exporting crude oil in the last quarter of 1999.
Tengiz field is an oil field located in Zhylyoi District, Atyrau Region, northwestern Kazakhstan.

Petróleo Brasileiro S.A., better known by and trading as the portmanteau Petrobras, is a state-owned Brazilian multinational corporation in the petroleum industry headquartered in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The company's name translates to Brazilian Petroleum Corporation — Petrobras.

The Sullom Voe Terminal is an oil and gas terminal at Sullom Voe in the Shetland Islands of Scotland. It handles production from oilfields in the North Sea and East Shetland Basin and stores oil before it is transported by tanker.
B3 is a major oil and gas field in the Baltic Sea. The field is located 80 km north of the Polish coastal town Rozewie. The crude oil is also referred to as Rozewie crude. Processing, drilling and accommodation is based on the jack up rig Baltic Beta located in the field. Most of the oil is shipped by tanker to the Gdańsk refinery as a part of the refinery feedstock. The associated gas is transmitted by pipeline to the combined heat and power (CHP) plant in Wladyslawowo.

Ghana generates electric power from hydropower, fossil-fuel, and renewable energy sources such as wind and solar energy. Electricity generation is one of the key factors in order to achieve the development of the Ghanaian national economy, with aggressive and rapid industrialization; Ghana's national electric energy consumption was 265 kilowatt hours per each one in 2009.
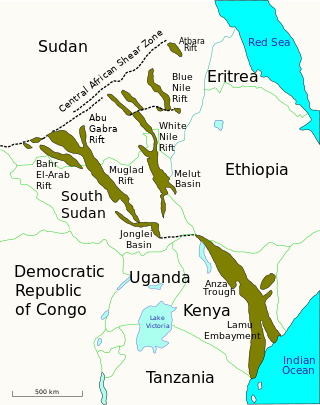
The Melut Basin is a rift basin in South Sudan, extending into Ethiopia, where it is called the Gambella basin. Melut is situated in the Upper Nile and Jonglei, south of the capital of Sudan, Khartoum and east of the river Nile. Some parts of the Melut contain several known hydrocarbon accumulations, although oil exploration, as elsewhere in Sudan and South Sudan, has been hindered by instability and conflict. The largest oil field in the Basin is the Great Palogue Field in South Sudan, with estimated reserves of 900 million barrels. The Melut oil export pipeline travels 1,380 km from Palogue to Port Sudan on the Red Sea, and has been on stream since June 2006.
The PetroDar Operating Company Ltd is a consortium of oil exploration and production companies operating in Sudan with its headquarters in Khartoum. The consortium was incorporated in the Virgin Islands on 31 October 2001. PetroDar is composed of the China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), Petronas of Malaysia (40%), Sudapet of Sudan (8%), SINOPEC of China (6%), and Egypt Kuwait Holding Company through its subsidiary Tri-Ocean Energy of Kuwait (5%).

The petroleum industry in Western Australia is the largest contributor to the country's petroleum exports. Western Australia's North West Shelf (NWS) is the primary location from which production originates. Oil exports are shipped from Port Hedland.
Energy in Ethiopia includes energy and electricity production, consumption, transport, exportation, and importation in the country of Ethiopia.
Perenco is an independent Anglo-French oil and gas company with a headquarters in London and Paris. It conducts exploration and production activities in 16 countries around the globe. Perenco is involved in operations both onshore and offshore with production equal to approximately 450,000-barrel (72,000 m3) of oil equivalent per day.

The oil and gas industry plays a central role in the economy of the United Kingdom. Oil and gas account for more than three-quarters of the UK's total primary energy needs. Oil provides 97 per cent of the fuel for transport, and gas is a key fuel for heating and electricity generation. Transport, heating and electricity each account for about one-third of the UK's primary energy needs. Oil and gas are also major feedstocks for the petrochemicals industries producing pharmaceuticals, plastics, cosmetics and domestic appliances.
The Hutton oil field, located on the UK continental shelf, was the location for the first ever production Tension Leg Platform (TLP).
Melut County is an administrative area of Upper Nile State in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan.

Cairn India was an Indian oil and gas exploration and production company, headquartered in Gurgaon, India. The company was merged with Vedanta Limited.
Energy in Serbia describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Serbia.
Paloich refers to an area in the Melut County of Upper Nile State in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan. It includes oil-related Paloich Airport and adjacent Palogue oil field.
The petroleum industry in Syria forms a major part of the economy of Syria. According to the International Monetary Fund, before the Syrian Civil War, oil sales for 2010 were projected to generate $3.2 billion for the Syrian government and accounted for 25.1% of the state's revenue.

The Pagak offensive was a major military operation by the South Sudanese government during the South Sudanese Civil War with the aim of capturing the strategic town of Pagak and the wider Maiwut County from Riek Machar's SPLM-IO rebels. Since the civil war's beginning, Pagak had served as headquarters and stronghold for the rebels, and its loss was believed to possibly greatly weaken the insurgency. A large part of the government forces that took part in the offensive are members of the SPLM-IO, a break-away group from Machar's movement that is loyal to First Vice President Taban Deng Gai. Though pro-government forces managed to capture Pagak on 6 August, their attempts to secure the surrounding areas proved unsuccessful. As result, the SPLA-held corridor between Mathiang and Pagak remained unsafe.
The petroleum industry in Sudan began in 1979, when the first commercial flow in the country occurred.
References
- ↑ "Great Palogue Field in Melut Basin, Sudan". search4oil.com. 2007. Retrieved 2013-05-27.
- ↑ "Palouge Power Plant DPOC · CFXG+R9G, Paloich, Южный Судан".
- ↑ "Government says oil installations secure after capture of Pagak". Radio Tamazuj. 31 August 2017. Retrieved 3 September 2017.
the oil was not discovery in 2003 but was in 1984 by Cheveron company and dug in 1996