
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Administratively, it forms the largest island in the East Nusa Tenggara Province. Including Komodo and Rinca islands off its west coast, the land area is 14,731.67 km2, and the population was 1,878,875 in the 2020 Census ; the official estimate as of mid-2023 was 1,962,405. The largest towns are Maumere and Ende. The name Flores is of Portuguese origin, meaning "Flowers".

Sumbawa is an Indonesian island, located in the middle of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain, with Lombok to the west, Flores to the east, and Sumba further to the southeast. Along with Lombok, it forms the province of West Nusa Tenggara, but there have been plans by the Indonesian government to split the island off into a separate province. Traditionally, the island is known as the source of sappanwood, as well as honey and sandalwood. Its savanna-like climate and vast grasslands are used to breed horses and cattle, as well as to hunt deer.

Mount Tambora, or Tomboro, is an active stratovolcano in West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Located on Sumbawa in the Lesser Sunda Islands, it was formed by the active subduction zones beneath it. Before 1815, its elevation reached more than 4,300 metres high, making it one of the tallest peaks in the Indonesian archipelago.

The Ring of Fire is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes.

Makian, known to local people as Mount Kie Besi, is a volcanic island, one of the Maluku Islands within the province of North Maluku in Indonesia. It lies near the southern end of a chain of volcanic islands off the western coast of the province's major island, Halmahera, and lies between the islands of Moti and Tidore to the north and Kayoa and the Bacan Group to the south. The island, which forms two districts within South Halmahera Regency of North Maluku Province, covers an area of 84.36 sq.km, and had a population of 12,394 at the 2010 Census, which rose to 14,000 at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2022 was 13,833.

Manam, known locally as Manam Motu, is an island located in the Bismarck Sea across the Stephan Strait from Yawar on the northeast coast of mainland Papua New Guinea's Bogia District. The island is 10 kilometers wide, and was created by the activity of the Manam Volcano, one of the country’s most active. It was evacuated in 2004 and its residents resettled elsewhere in Papua New Guinea, but many have begun to return despite concerns of future volcanic activity. Manam is still erupting as of January 2024.

Mount Merapi is an active stratovolcano located on the border between the province of Central Java and the Special Region of Yogyakarta, Indonesia. It is the most active volcano in Indonesia and has erupted regularly since 1548. It is located approximately 28 km (17 mi) north of Yogyakarta city which has a population of 2.4 million, and thousands of people live on the flanks of the volcano, with villages as high as 1,700 m (5,577 ft) above sea level.

Mount Rinjani is an active volcano in Indonesia on the island of Lombok. Administratively the mountain is in the Regency of North Lombok, West Nusa Tenggara. It rises to 3,726 metres (12,224 ft), making it the second highest volcano in Indonesia. It is also the highest point in the Indonesian province of West Nusa Tenggara.

Paluweh, also known as Rokatenda, is a stratovolcano that forms the small island of Palu'e, north of Flores Island in Sikka Regency in the province of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. While the volcano rises about 3,000 m (9,840 ft) above the sea floor, its cone rises just 875 metres (2,871 ft) above sea level and is the highest point on the island.

Sangeang Api is an active complex volcano on the island of Sangeang in Indonesia. It consists of two volcanic cones, 1,949 metres (6,394 ft) Doro Api and 1,795 m (5,889 ft) Doro Mantoi. Sangeang Api is one of the most active volcanoes in the Lesser Sunda Islands. It erupted in 1988 and the island's inhabitants were evacuated. Between its first recorded eruption in 1512 and 1989, it erupted 17 times. It erupted again during December 2012 and May 2014.

Karangetang is a volcano on the north side of Siau Island off the coast of Sulawesi, Indonesia. The island is inhabited by 22,000 people. It is one of the most active volcanoes in Indonesia having erupted 41 times since 1675. A pyroclastic flow in 1997 killed three people.

The Sikka people are an Indonesian ethnic group native to the region of east central Flores between the Bloh and Napung Rivers. In the city of Maumere, the center of the region, Sikka people occupy a separate block. The Sikka language, which is a member of the Timor-Ambon languages, is spoken by the Sikka people. The Sikka language has at least three recognized dialects, namely Sikka Natar dialect, Sara Krowe dialect and Ata Tana 'Ai or Sara Tana 'Ai dialect.
The Sikka language or Sikkanese, also known as Sika, is spoken by around 180,000 people of the Sika ethnic group on Flores island in East Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia. It is a member of the Central Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family.

Sikka is a regency within East Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia, on the island of Flores. It is bordered to the west by Ende Regency and to the east by East Flores Regency. It covers an area of 1,675.36 km2 and had a population of 300,301 at the 2010 census and 321,953 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 335,360 - comprising 163,060 males and 172,300 females). The capital is the town of Maumere, which comprises the districts of Alok Barat, Alok and Alok Timur.

Lewotobi is a twin volcano located in the southeastern part of the island of Flores, Indonesia. It is composed of the Lewotobi Lakilaki and Lewotobi Perempuan stratovolcanoes.

Mount Egon is a stratovolcano located in the southeastern part of the island of Flores, Indonesia in the area of Maumere bay. A landslide during the eruption on 29 January 2004 forced 6,000 people to evacuate the area. Activity of Gunung Egon on 15 April 2008 forced thousands of people to evacuate. Quakes and fumes from the volcano have been occurring since November 2010, designating Egon as one of 11 volcanoes in Indonesia on the highest level alert.

Mount Sinabung is a Pleistocene-to-Holocene stratovolcano of andesite and dacite in the Karo plateau of Karo Regency, North Sumatra, Indonesia, 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the Lake Toba supervolcano. Many old lava flows are on its flanks and the last known eruption, before recent times, occurred 1200 years before present, between 740 - 880 CE. Solfataric activities were last observed at the summit in 1912; recent documented events include an eruption in the early hours of 29 August 2010 and eruptions in September and November 2013, January, February and October 2014. The volcano has recently claimed the life of at least 23 people in a number of events since 2014. Between 2013 and 2014, the alert for a major event was increased with no significant activity. On 2 June 2015, the alert was again increased, and on 26 June 2015, at least 10,000 people were evacuated, fearing a major eruption. The long eruption of Mount Sinabung is similar to that of Mount Unzen in Japan, which erupted for five years after lying dormant for 400 years. A major eruption began on 10 August 2020.
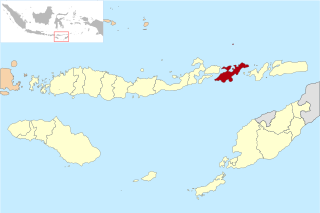
Lembata Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Established on 4 October 1999 from the most easterly part of East Flores Regency, the regency covers the island of Lembata, together with three small offshore islands together forming the eastern part of the Solor Archipelago, and has its administrative seat (capital) in Lewoleba. The population of the Regency was 117,829 at the 2010 decennial census and at the 2020 census was 135,930; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 141,391 - comprising 68,409 males and 72,982 females.

Indonesia is a volcanically active country, containing numerous major volcanoes. It has the most volcanoes of any country in the world, with 76 volcanoes that have erupted at least 1,171 times in total within historical times. The Smithsonian Institution has 141 Indonesian entries in its volcano database. Indonesia has around 130 active volcanoes that are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, and it has suffered the highest numbers of eruptions resulting in fatalities, damage to arable land, debris flows, tsunamis, lava domes, and pyroclastic flows. Indonesia's most active volcanoes are Kelut and Mount Merapi on the island of Java. The majority of Indonesia's volcano are located on a 3,000 km long chain called the Sunda Arc. Here, the subduction of the Indian Ocean crust underneath the Asian Plate produced most of these volcanoes.


















