Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,878 sq mi), bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. As of 2021, the country had an estimated population of 23,674,480. Previously called Republic of Upper Volta (1958–1984), it was renamed Burkina Faso by President Thomas Sankara. Its citizens are known as Burkinabè, and its capital and largest city is Ouagadougou.

Burkina Faso is a landlocked Sahel country that shares borders with six nations. It lies between the Sahara desert and the Gulf of Guinea, south of the loop of the Niger River, mostly between latitudes 9° and 15°N, and longitudes 6°W and 3°E. The land is green in the south, with forests and fruit trees, and semi-arid in the north. Most of central Burkina Faso lies on a savanna plateau, 198–305 metres (650–1,001 ft) above sea level, with fields, brush, and scattered trees. Burkina Faso's game preserves – the most important of which are Arly, Nazinga, and W National Park—contain lions, elephants, hippopotamus, monkeys, common warthogs, and antelopes. Previously the endangered painted hunting dog, Lycaon pictus occurred in Burkina Faso, but, although the last sightings were made in Arli National Park, the species is considered extirpated from Burkina Faso.

The Komoé River or Comoé River is a river in West Africa. The river originates on the Sikasso Plateau of Burkina Faso, flows through the Cascades de Karfiguéla, forms a short section of the border between Burkina Faso and Ivory Coast before entering Ivory Coast. It serves as the major drainage for the northeastern portion of that country before emptying into the Atlantic. The banks of the Komoé are shaded by riparian forests along most of its length, providing an important habitat for wildlife and a source of agricultural water. Where reliable floodplains form in Ivory Coast, rice may be grown. A portion of the river in northern Ivory Coast is the source of the vegetative richness that earned that area a UNESCO World Heritage Site designation, Comoé National Park.

The Red Volta or Nazinon is a waterway located in West Africa. It emerges near Ouagadougou in Burkina Faso and has a length of about 320 km which it joins the White Volta in Ghana.

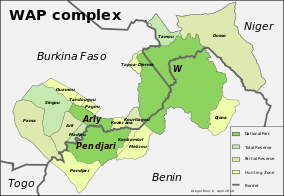
Arli National Park, often called Arly, is a national park located in Tapoa Province, southeastern Burkina Faso. It adjoins Benin's Pendjari National Park in the south and the Singou Reserve in the west.

Kompienga is one of the 45 provinces of Burkina Faso, located in its Est Region.

Cascades is one of Burkina Faso's 13 administrative regions. It was created on 2 July 2001. The population of Cascades was 812,062 in 2019. It is the second least populous region in Burkina Faso and contains 3.96% of all Burkinabé. The region's capital is Banfora. Two provinces, Comoé and Léraba, make up the region. The Cascades de Karfiguéla give the region its name.

Centre-Nord is one of thirteen administrative regions of Burkina Faso, a landlocked country in Africa. The population of Centre-Nord in 2019 was 1,872,126. The region's capital is Kaya. Three provinces—Bam, Namentenga, and Sanmatenga, make up the region.

Centre-Ouest is one of Burkina Faso's 13 administrative regions. The population of Centre-Ouest was 1,659,339 in 2019. The region's capital is Koudougou. Four provinces make up the region.

Est is one of Burkina Faso's 13 administrative regions. It was created on 2 July 2001. The region's capital is Fada N'gourma. Five provinces make up the region—Gnagna, Gourma, Komondjari, Kompienga, and Tapoa.

Plateau-Central is one of Burkina Faso's 13 administrative regions. It was created on 2 July 2001 and had a population of 977,510 in 2019. The region's capital is Ziniaré. Three provinces make up the region—Ganzourgou, Kourwéogo, and Oubritenga.
Articles related to Burkina Faso include:

Burkina Faso is largely wild bush country with a mixture of grass and small trees in varying proportions. The savanna region is mainly grassland in the rainy season and semi desert during the harmattan period. Fauna, one of the most diverse in West Africa, includes the elephant, hippopotamus, buffalo, monkey, lions, crocodile, giraffe, various types of antelope, and a vast variety of bird and insect life. The country has 147 mammal species, 330 aquatic species including 121 species of fish and 2067 different plant species. Of the plant species, the dominant endemic species are shea tree and the baobab, the former plant species has immense economic value to the country.

Arly-Singou is a 6,388 km2 (2,466 sq mi) large ecosystem in Burkina Faso. It encompasses the Arli National Park and the Singou Reserve. It is considered to comprise part of the most significant and important savanna woodland wildlife areas still existing in West Africa.
Singou Reserve is a complete reserve in Burkina Faso. Established in 1955, it is located in Gourma Province and covers an area of 1,926 km2 (744 sq mi).

Kourtiagou Reserve is a partial reserve in Burkina Faso. Established in 1957 it is located in Tapoa Province and covers an area of 510 km2. Its name stems from the river Kourtiagou which is the western border of the reserve. In the East it is divided from the W National Park by the road R7 from Tansarga to Banikoara. The southern border is the national border to Benin.
Pama Airport is a public use airport located near Pama, Kompienga Province, Burkina Faso.

W-Arly-Pendjari Complex, also known as the "WAP Complex", is a transboundary Natural UNESCO World Heritage Site in Benin, Burkina Faso and Niger covering:
Koalou or Kourou is a neutral zone between Benin and Burkina Faso containing the villages of Koalou, Niorgou I, and Niorgou II. The 68 km2 area of land is near the tripoint border with Togo and has been the subject of a dispute between the two countries for years. For Benin, the zone is part of the commune of Matéri in the department of Atakora; for Burkina Faso, the zone is part of the department of Pama in the province of Kompienga. The two countries chose to settle the issue peacefully in 2008 by removing all displayed symbols of sovereignty from both countries.