
Julia Aquilia Severa was the second and fourth wife of Roman emperor Elagabalus. She was the daughter of Quintus Aquilius. The praenomen of Julia was given to her after becoming an empress.

A Severa is a Portuguese 1931 film, directed by Leitão de Barros, famous for being the first Portuguese all-talking sound film, a biopic of the fado singer Maria Severa Onofriana, known as A Severa, based on the play by Júlio Dantas.

Maria Severa Onofriana, also known simply as A Severa, was a Portuguese fado singer and guitarist. She is regarded, in her short life, as the first fado singer to have risen to fame, attaining a near-mythical status after her death. Fado has been described as the Portuguese expression of "the blues," and fado roughly means 'fate.'
La Severa Matacera is a Colombian musical group, formed in Bogotá, at the end of 1995, with the idea of forming a band which could mix all the influences of its members.
Paracles is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was described by Francis Walker in 1855. The species range from Panama to Patagonia, with quite a few in the southern temperate region of South America.
Ronald "Ron" Duane Severa is an American water polo player who competed in the 1956 Summer Olympics and in the 1960 Summer Olympics.
Events in the year 1797 in Norway.
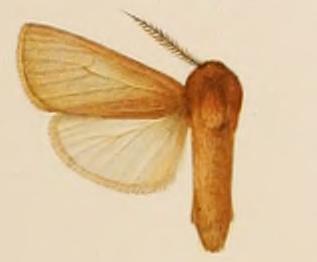
Paracles fosterana is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Watson and Goodger in 1986. It is found in Paraguay.

Thelcticopis severa is a species of huntsman spider found in China, Laos, Korea, and Japan. It is the type species for the genus Thelcticopis, and was first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1875.

Paracles azollae is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Berg in 1877. It is found in Argentina.

Paracles tenuis is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Carlos Berg in 1877. It is found in Argentina, Uruguay and Colombia.

Paracles deseticola is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Carlos Berg in 1875. It is found in Argentina and Patagonia.

Paracles burmeisteri is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Berg in 1877. It is found in Argentina.
Paracles palustris is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Peter Jörgensen in 1935. It is found in Paraguay.
Paracles sericea is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Schaus in 1896. It is found in Brazil.

Carlos Berg or Friedrich Wilhelm Karl Berg was an Argentinian naturalist and entomologist of Latvian and Baltic German origin.

Paracles argentina is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Carlos Berg in 1877. It is found in Corrientes Province, Argentina.

Paracles uruguayensis is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Carlos Berg in 1886. It is found in Uruguay.
Zarya severa is a red grape variety. It is a descendant of the Asiatic wild grape Vitis amurensis and the grape Malingre Précoce and is thus a hybrid vine. The crossing took place at the Potapenko Viticulture Research Institute in Rostov Oblast, Russia in 1936. Because of its high winter frost resistance as well as its resistance to downy mildew, this variety, often mentioned by breeders in Eastern Europe, became a major breeding stock in the search for new varieties.

The Chapeau à la Paméla, Pamela hat or Pamela bonnet described a type of straw hat or bonnet popular during the 1790s and into the first three quarters of the 19th century. It was named after the heroine of Samuel Richardson's 1741 novel Pamela; or, Virtue Rewarded. While Pamela hats and bonnets underwent a variety of changes in shape and form, they were always made from straw. The mid-19th-century version of the Pamela hat was a smaller version of an early 19th-century wide-brimmed style called the gipsy hat.












