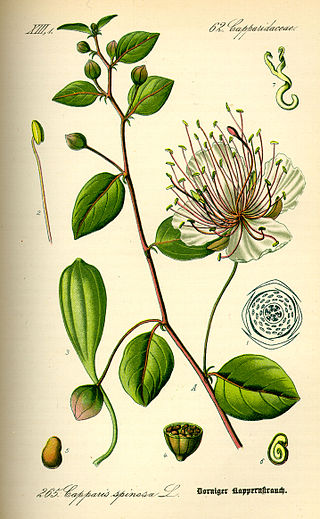
Capparis spinosa, the caper bush, also called Flinders rose, is a perennial plant that bears rounded, fleshy leaves and large white to pinkish-white flowers.

Prunus spinosa, called blackthorn or sloe, is a species of flowering plant in the rose family Rosaceae. The species is native to Europe, western Asia, and regionally in northwest Africa. It is locally naturalized in New Zealand, Tasmania, and the Pacific Northwest and New England regions of the United States.

Aralia spinosa, commonly known as devil's walking stick, is a woody species of plant in the genus Aralia, family Araliaceae, native to eastern North America. The various names refer to the viciously sharp, spiny stems, petioles, and even leaf midribs. It has also been known as Angelica-tree.

Jubilation is the tenth and final studio album by Canadian/American rock group the Band. Recorded in the spring of 1998 in Levon Helm's home studio in Woodstock, New York, it was released on September 15, 1998. For the first time since the group reformed without guitarist and songwriter Robbie Robertson, there were more originals than covers. Songs include "Last Train to Memphis", featuring guest guitarist Eric Clapton, Garth Hudson's solo instrumental closer "French Girls", Rick Danko's "High Cotton" and the ode to Ronnie Hawkins, "White Cadillac".

The spiny turtle is a South-East Asian turtle species. It inhabits lowland and hill rainforest, usually in the vicinity of small streams, mainly in hill areas up to 900 m above sea level.

Ononis spinosa is a plant belonging to the family Fabaceae, that is commonly known as spiny restharrow or just restharrow. It is found throughout much of Europe including Britain, but seldom as far north as Scotland.

Argania is a genus of flowering plants containing the sole species Argania spinosa, known as argan, a tree endemic to the calcareous semidesert Sous valley of southwestern Morocco and to the region of Tindouf in southwestern Algeria. Argan trees grow to 8–10 m (26–33 ft) high and live up to approximately 200 years. They are thorny, with gnarled trunks and wide spreading crown. The crown has a circumference of about 70 m (230 ft) and the branches lean towards the ground.

Tara spinosa, commonly known as tara (Quechua), also known as Peruvian carob or spiny holdback, is a small leguminous tree or thorny shrub native to Peru. T. spinosa is cultivated as a source of tannins based on a galloylated quinic acid structure. This chemical structure has been confirmed also by LC-MS. It is also grown as an ornamental plant because of its large colorful flowers and pods.

Strychnos spinosa, the Natal orange, is a tree indigenous to tropical and subtropical Africa. It produces sweet-sour, yellow fruits, containing numerous hard brown seeds. Greenish-white flowers grow in dense heads at the ends of branches. The fruits tend to appear only after good rains. It is related to the deadly Strychnos nux-vomica, which contains strychnine. The smooth, hard fruit are large and green, ripen to yellow colour. Inside the fruit are tightly packed seeds, which may be toxic, surrounded by a fleshy, brown, edible covering. Animals such as baboon, monkeys, bushpig, nyala and eland eat the fruit. The leaves are a popular food source for browsers such as duiker, kudu, impala, steenbok, nyala and elephant.

Quasipaa spinosa is a species of frog in the family Dicroglossidae. It is known under many common names, including Chinese spiny frog, giant spiny frog, Chinese edible frog, and spiny paa frog. Its names refer to the distinctive characteristics of the species, relatively large size and the spiny chest of male frogs. Giant in frog terms only, it can nevertheless grow to lengths above 10 cm (4 in); this makes it the largest frog in Hong Kong.

Bursaria spinosa is a small tree or shrub in the family Pittosporaceae. The species occurs mainly in the eastern and southern half of Australia and not in Western Australia and the Northern Territory. Reaching 10 m (35 ft) high, it bears fragrant white flowers at any time of year but particularly in summer. A common understorey shrub of eucalyptus woodland, it colonises disturbed areas and fallow farmland. It is an important food plant for several species of butterflies and moths, particularly those of the genus Paralucia, and native bees.

Grayia spinosa is a species of the genus Grayia in the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae, which is known by the common names hop sage and spiny hop sage. It is widely distributed across the Western United States, where it grows in a number of desert and mountain habitats.

Eupalitin is an O-methylated flavonol. It can be found in Ipomopsis aggregata.

Hydrolea is the only genus of the family Hydroleaceae of the order Solanales.

Pyrus spinosa, the almond-leaved pear, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rosaceae, native to the northern Mediterranean region. It grows to a height of 3–10 m (10–33 ft). It has white flowers which bloom in April–May. The fruits are bitter and astringent. It hybridizes easily with Pyrus communis and Pyrus pyraster.

Catunaregam spinosa, the mountain pomegranate, is a flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae, found in South Asia and other Asian countries. Almost all parts of the plant are used as a traditional medicine in Ayurveda and fruits have been reported to be used in medicine as well as in food. Various flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins, lignans, terpenoids, and volatile oils have been reported from this plant. Several studies have reported the modern pharmaceutical activities of C. spinosa such as piscicidal, molluscicidal, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, and antihyperlipidemic activities
Paradaxata is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Paradaxata alboplagiata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1938.
Paradaxata villosa is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1938. It is known from Australia.

Jacaratia spinosa is a species of tree, in the genus Jacaratia of the family Caricaceae. It is found in the tropical dry forests of central and southern Mexico, Nicaragua, and El Salvador. Its stem is used as a main ingredient in the manufacturing of candy. Its fruit is also appreciated by many animals including monkeys and birds.
















