
The Trans-Canada Highway is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast. The main route spans 7,476 km (4,645 mi) across the country, one of the longest routes of its type in the world. The highway system is recognizable by its distinctive white-on-green maple leaf route markers, although there are small variations in the markers in some provinces.

The Kettle Valley Railway was a subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) that operated across southern British Columbia, west of Midway running to Rock Creek, then north to Myra Canyon, down to Penticton over to Princeton, Coalmont, Brookmere, Coquihalla and finally Hope where it connected to the main CPR line.
Route 1 is a highway in the southern part of the Canadian province of New Brunswick. It begins west of the Canada–United States border at St. Stephen, and runs east for 239.11 kilometres (148.58 mi) to Route 2 at River Glade.
Highway 1 is a provincial highway in British Columbia, Canada, that carries the main route of the Trans-Canada Highway (TCH). The highway is 1,047 kilometres (651 mi) long and connects Vancouver Island, the Greater Vancouver region in the Lower Mainland, and the Interior. It is the westernmost portion of the main TCH to be numbered "Highway 1", which continues through Western Canada and extends to the Manitoba–Ontario boundary. The section of Highway 1 in the Lower Mainland is the second-busiest freeway in Canada, after Ontario Highway 401 in Toronto.
Highway 17 is a provincial highway in British Columbia, Canada. It comprises two separate sections connected by a ferry link. The Vancouver Island section is known as the Patricia Bay Highway and connects Victoria to the Swartz Bay ferry terminal in North Saanich. The Lower Mainland section is known as the South Fraser Perimeter Road and connects the Tsawwassen ferry terminal to Delta and Surrey, terminating at an interchange with Highway 1 in the Fraser Valley.
Highway 99 is a provincial highway in British Columbia that runs 377 kilometres (234 mi) from the U.S. border to near Cache Creek, serving Greater Vancouver and the Squamish–Lillooet corridor. It is a major north–south artery within Vancouver and connects the city to several suburbs as well as the U.S. border, where it continues south as Interstate 5. The central section of the route, also known as the Sea to Sky Highway, serves the communities of Squamish, Whistler, and Pemberton. Highway 99 continues through Lillooet and ends at a junction with Highway 97 near Cache Creek.
Highway 91 is an alternative freeway route to Highway 99 through Delta, New Westminster and Richmond, British Columbia. The highway was built in two sections, the first section from Delta to East Richmond in 1986, and the second section across Richmond in 1989.
There are many roads in the southwestern part of British Columbia and Vancouver Island that were designated as Highway 1A. These roads were sections of the original 1941 route of Highway 1 before its various re-alignments, and are used today as service routes and frontage roads. The "B.C. Highway 1A" designations were removed from these sections by the province between 2005 and 2010, although signage remains along some of the route and the designation on some maps.

Highway 7B, known as the Mary Hill Bypass, is a 7.27 km (4.52 mi) long riverside east-west link between the cities of Coquitlam to the west and Port Coquitlam to the east. The Mary Hill Bypass gained its numbered designation in 1996, when it was widened from two to four lanes north of Broadway. Highway 7B meets Highway 7 at both of its ends, and also links to Highway 1 within Coquitlam at the Cape Horn Interchange.
Highway 97 is a major highway in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is the longest continuously numbered route in the province, running 2,081 km (1,293 mi) and is the only route that runs the entire north–south length of British Columbia, connecting the Canada–United States border near Osoyoos in the south to the British Columbia–Yukon boundary in the north at Watson Lake, Yukon.
Route 2 is a major provincial highway in the Canadian province of New Brunswick, carrying the main route of the Trans-Canada Highway in the province. The highway connects with Autoroute 85 at the border with Quebec and Highway 104 at the border with Nova Scotia, as well as with traffic from Interstate 95 in the U.S. state of Maine via the short Route 95 connector. A core route in the National Highway System, Route 2 is a four-lane freeway in its entirety, and directly serves the cities of Edmundston, Fredericton, and Moncton.

The Kicking Horse River is in the Canadian Rockies of southeastern British Columbia, Canada. The river was named in 1858, when James Hector, a member of the Palliser Expedition, reported being kicked by his packhorse while exploring the river. Hector named the river and the associated pass as a result of the incident. The Kicking Horse Pass, which connects through the Rockies to the valley of the Bow River, was the route through the mountains subsequently taken by the Canadian Pacific Railway when it was constructed during the 1880s. The railway's Big Hill and associated Spiral Tunnels are in the Kicking Horse valley and were necessitated by the steep rate of descent of the river and its valley.

Kicking Horse Pass is a high mountain pass across the Continental Divide of the Americas of the Canadian Rockies on the Alberta–British Columbia border, and lying within Yoho and Banff national parks. Divide Creek forks onto both sides of the Continental Divide.
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 1, commonly referred to as Highway 1, is a major east–west highway in southern Alberta that forms the southern mainline of the Trans-Canada Highway. It runs from the British Columbia border near Lake Louise through Calgary to the Saskatchewan border east of Medicine Hat. It continues as Highway 1 into both provinces. It spans approximately 534 km (332 mi) from Alberta's border with British Columbia in the west to its border with Saskatchewan in the east. Highway 1 is designated as a core route in Canada's National Highway System and is a core part of the developing Alberta Freeway Network.
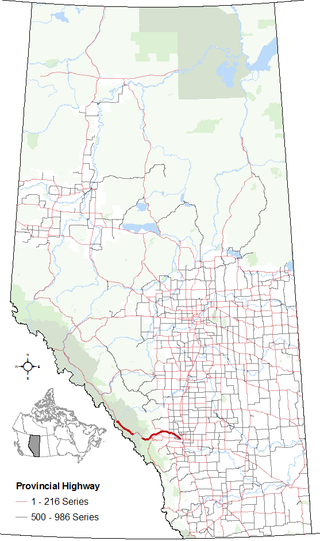
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 1A is the designation of two alternate routes off the Alberta portion of Trans-Canada Highway 1. However, it is not the only name used for spurs off Highway 1 - Highway 1X is another such designation. Despite these highways being suffixed routes of Highway 1, they are not part of the Trans-Canada Highway network, and are signed with Alberta's provincial primary highway shields instead of the Trans-Canada shields used for Highway 1.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 11, commonly referred to as Highway 11 and officially named the David Thompson Highway, is a provincial highway in central Alberta, Canada. It runs for 318 km (198 mi) from Highway 93 at Saskatchewan River Crossing near Mount Sarbach in Banff National Park east to Highway 12 near Nevis. It passes by Nordegg and through Rocky Mountain House, Sylvan Lake and Red Deer along its course. The highway is named after David Thompson, a British-Canadian fur trader, surveyor, and map-maker who explored the area between Rocky Mountain House and Kootenae House through Howse Pass.

The Cassiar Connector is a highway traffic tunnel on the Trans-Canada Highway. It is located in the north-east corner of Vancouver, British Columbia, near the Vancouver-Burnaby border. Travelling northward, the tunnel begins under Adanac Street and passes under the interchange between East Hastings Street and the Highway 1 offramps. It ends underneath Triumph Street, with the highway continuing north to the McGill Street interchange and the Ironworkers Memorial Second Narrows Crossing towards the District of North Vancouver. The tunnel is 730 metres (2,400 ft) long. Dangerous goods are not permitted to be transported through the tunnel.
British Columbia Highway 3, officially named the Crowsnest Highway, is an 841-kilometre (523 mi) highway that traverses southern British Columbia, Canada. It runs from the Trans-Canada Highway (Highway 1) at Hope to Crowsnest Pass at the Alberta border and forms the western portion of the interprovincial Crowsnest Highway that runs from Hope to Medicine Hat, Alberta. The highway is considered a Core Route of the National Highway System.

U.S. Route 395 (US 395) is a United States Numbered Highway that runs from California to the inland regions of Oregon and Washington. It travels north–south through Washington, including long concurrencies with Interstate 82 (I-82) and I-90, and connects the Tri-Cities region to Spokane and the Canadian border at Laurier.

In the U.S. state of Idaho, U.S. Route 95 (US-95) is a north–south highway near the western border of the state, stretching from Oregon to British Columbia for over 538 miles (866 km); it was earlier known in the state as the North and South Highway.










