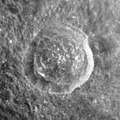
Anaxagoras is a young lunar impact crater that is located near the north pole of the Moon. It lies across the larger and more heavily worn crater Goldschmidt. To the south-southeast is Epigenes, and due south is the worn remains of Birmingham.
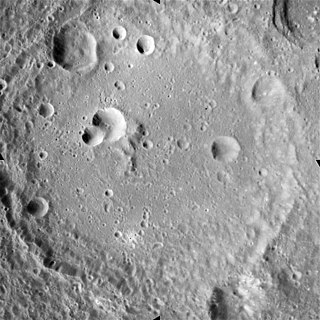
Hilbert is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, just past the southeast limb. It is named for German mathematician David Hilbert. It lies just beyond the region of the surface that is occasionally brought into view due to libration, and so this feature cannot be observed directly from the Earth.

Anders is a worn lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It lies just to the southeast of the outer rim of the huge walled basin named Apollo. To the south-southeast is the crater Leavitt.

Petavius is a large lunar impact crater located to the southeast of the Mare Fecunditatis, near the southeastern lunar limb. Attached to the northwest rim is the smaller crater Wrottesley. To the southeast are Palitzsch, Vallis Palitzsch, and Hase. Farther to the north is the large crater Vendelinus. Petavius appears oblong when viewed from the Earth due to foreshortening. Petavius is Imbrian in age.

Faraday is a lunar impact crater in the southern highlands of the Moon. It was named after British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday. It lies across the southeast rim of the larger crater Stöfler, and the northwest rim of Faraday forms a wide rampart across the otherwise flat floor of Stöfler. To the east of Faraday is Maurolycus.

Eudoxus is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies to the east of the northern tip of the Montes Caucasus range. It is named after the Greek astronomer Eudoxus of Cnidus. It is located to the south of the prominent crater Aristoteles in the northern regions of the visible Moon. To the south is the ruined formation of Alexander, and the small crater Lamèch lies to the southwest.

Kepler is a lunar impact crater that lies between the Oceanus Procellarum to the west and Mare Insularum in the east. To the southeast is the crater Encke. Kepler is named for the 17th century German astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler.

Bürg is a prominent lunar impact crater in the northeast part of the Moon. It lies within the lava-flooded, ruined crater formation designated Lacus Mortis. To the south and southeast is the crater pair Plana and Mason. To the west, beyond the rim of Lacus Mortis, is the prominent crater Eudoxus.

Backlund is a worn lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon, beyond the eastern limb, astride the southern rim of the walled plain Pasteur, to the west of the crater Hilbert. Further to the west-southwest is Sklodowska. Backlund's north and south ends are more worn and eroded than the intervening stretches. The interior floor is relatively flat, with the usual accompaniment of tiny impact craters marking the surface.

King is a prominent lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, and can not be viewed directly from Earth. The crater was named after Arthur Scott King and Edward Skinner King in 1970. Prior to that, this crater was known as Crater 211. It forms a pair with Ibn Firnas, which is only slightly larger and is attached to the northeast rim of King. To the northwest is the crater Lobachevskiy, and Guyot is located an equal distance to the north-northwest.

Banachiewicz is a largely degraded lunar impact crater that is located near the eastern limb of the Moon.

Carpenter is a lunar impact crater in the northern part of the Moon, relatively close to the limb. At this position the crater is foreshortened and appears oval in shape. It is, however, very nearly circular in outline. The outer rampart to the south is adjoined to the old crater Anaximander, and the satellite formation Anaximander B lies along the western rim. To the northeast is Anaximenes.

Crookes is a lunar impact crater that lies on the Moon's far side as seen from the Earth. It lies just to the southwest of the giant crater Korolev. To the southwest of Crookes is McKellar.

Hayn is a lunar impact crater that lies next to the northeast limb of the Moon. This location restricts the amount of detail that can be viewed from the Earth, as the western inner side is permanently hidden from sight. Observation of this crater can also be affected by libration, which can completely hide this crater from sight.

Gibbs is a lunar impact crater that lies near the eastern limb of the Moon. It is situated less than a crater diameter to the northeast of the larger crater Hecataeus. The crater chain Catena Humboldt passes to the south of Gibbs, following a line to the northeast. Due to its proximity to the limb, this crater appears foreshortened when viewed from the Earth, and visibility is subject to libration.

Das is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located to the north-west of the walled plain Chebyshev. To the south-west of Das is the irregular crater Mariotte, and Von der Pahlen lies to the east-northeast. The crater was named after Indian astronomer Anil Kumar Das.

Firsov is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located to due south of the crater Lobachevskiy, and to the northwest of Abul Wáfa. The circular rim of this crater has a small outward bulge along the southern edge, and smaller bulges along the western side. The inner walls have slumped to form talus piles along the base. The low-albedo interior floor is nearly level and featureless.

Sklodowska (Skłodowska) is a large lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies just past the southeastern limb, and can sometimes be viewed from Earth under favorable conditions of libration and illumination. The crater is located to the northeast of the older walled plain Curie, and to the southwest of Pasteur, another walled plain.

Necho is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon, and therefore cannot be seen directly from the Earth. It lies to the northeast of the larger crater Langemak, about a crater diameter to the south-southwest of Bečvář and further east is Love.

Lobachevskiy is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, beyond the eastern limb. It was named after Russian mathematician Nikolai Lobachevsky in 1961. This crater lies to the southeast of the larger crater Fleming. Less than a crater diameter to the east-northeast lies Guyot.