
The Kilsby Tunnel is a railway tunnel on the West Coast Main Line in England, near the village of Kilsby in Northamptonshire, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of Rugby. It is 2,423 yards (2,216 m) long.

Brighton railway station is the southern terminus of the Brighton Main Line, the western terminus of the East Coastway Line and the eastern terminus of the West Coastway Line in England, and the principal station serving the city of Brighton, East Sussex. It is 50 miles 49 chains from London Bridge via Redhill. The station has six bus stops which are served by Brighton & Hove bus routes 1, 1A, N1, 5B, 6, 7, N7, 12, 12A, 12X, 13X, 14, 14C, 18, 24, 26, 27, 27B, 27C, 46, 48, 49, 55, 59 and 79.

The Dearne and Dove Canal ran for almost ten miles through South Yorkshire, England from Swinton to Barnsley through nineteen locks, rising 127 feet (39 m). The canal also had two short branches, the Worsbrough branch and the Elsecar branch, both about two miles long with reservoirs at the head of each. The Elsecar branch also has another six locks. The only tunnel was bypassed by a cutting in 1840.
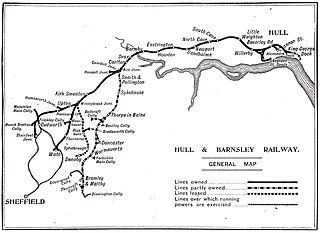
The Hull Barnsley & West Riding Junction Railway and Dock Company (HB&WRJR&DCo.) was opened on 20 July 1885. It had a total projected length of 66 miles but never reached Barnsley, stopping a few miles short at Stairfoot. The name was changed to The Hull and Barnsley Railway (H&BR) in 1905. Its Alexandra Dock in Hull opened 16 July 1885.
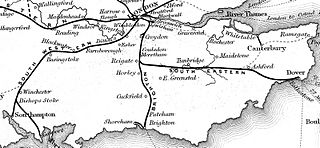
The London and Brighton Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in England which was incorporated in 1837 and survived until 1846. Its railway ran from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) at Norwood – which gives it access from London Bridge, just south of the River Thames in central London. It ran from Norwood to the South Coast at Brighton, together with a branch to Shoreham-by-Sea.

The Brighton Main Line is a railway line in southern England linking London to Brighton. It starts at two termini in the capital, London Victoria and London Bridge, and the branches from each meet at East Croydon, from where the route continues southwards via Gatwick Airport to the coast. The line serves the suburbs of South London, as well as the towns of Redhill, Horley, Crawley, Haywards Heath and Burgess Hill.

The Sutton and Mole Valley lines were constructed between 1847 and 1868 by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway, the London and South Western Railway and the LBSCR-sponsored Horsham, Dorking and Leatherhead Railway.

Hassocks railway station is on the Brighton Main Line in England, serving the village of Hassocks, West Sussex. It is 43 miles 42 chains (70.0 km) down the line from London Bridge via Redhill and is situated between Burgess Hill and Preston Park. It is managed by Southern.

The Eastleigh–Fareham line is the railway line from Eastleigh to Fareham in England. At Eastleigh, trains join the South West Main Line for onward travel to Basingstoke and London Waterloo. At Fareham trains join the West Coastway Line for onward travel to Portsmouth.
The Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway was an early British railway company which opened in stages between 1841 and 1845 between Sheffield and Manchester via Ashton-under-Lyne. The Peak District formed a formidable barrier, and the line's engineer constructed Woodhead Tunnel, over three miles (4.8 km) long. The company amalgamated with the Sheffield and Lincolnshire Junction Railway and Great Grimsby and Sheffield Junction Railway companies, together forming the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway in 1847.

Clayton Tunnel is a railway tunnel located near the villages of Clayton and Pyecombe in West Sussex, between Hassocks and Preston Park railway stations on the Brighton Main Line. This tunnel is notable for its turreted and castellated north portal with a single-storey cottage on the top, as well as for being the site of a serious accident in 1861 which was influential in the adoption of a robust signalling system in the UK and elsewhere.

The Scarborough & Whitby Railway was a railway line from Scarborough to Whitby in North Yorkshire, England. The line followed a difficult but scenic route along the North Yorkshire coast.
The Cheltenham and Great Western Union Railway was a railway company intended to link Cheltenham, Gloucester and Swindon, in England. It was authorised in 1836 but it found it very hard to raise money for the construction, and it opened only a part of its line, between Swindon and Cirencester, in 1841. It sold its business to the Great Western Railway, which quickly built the line through to Gloucester in 1845 and Cheltenham in 1847; part of that route was shared with other companies.

The Ouse Valley Railway was to have been part of the London, Brighton & South Coast Railway (LBSCR). It was authorised by an Act of Parliament in 1864 and construction of the 20 miles (32 km) long line was begun, but not completed. It never opened to traffic.
The Three Bridges–Tunbridge Wells line is a mostly disused railway line running from Three Bridges in West Sussex to Tunbridge Wells Central in Kent via East Grinstead in West Sussex, a distance of 20 miles 74 chains (33.7 km). Opened in 1855, the main section of the line was a casualty of the Beeching Axe – the last train ran on 1 January 1967. The remaining section to Tunbridge Wells closed on 6 July 1985, although the section between Groombridge and Tunbridge Wells West was reopened in 1997 under the auspices of the Spa Valley Railway.
The Cranleigh line was a railway line in England that connected Guildford in Surrey, with Horsham in West Sussex. Construction of the line was started by an independent company, the Horsham and Guildford Direct Railway, but management failures delayed construction, and the company was taken over by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR). The LBSCR completed the construction of the line and it was opened in 1865; it was nearly 16 miles in length.
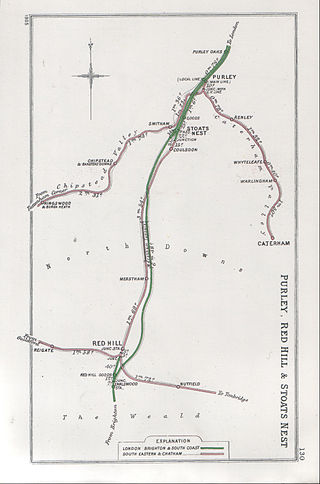
The Merstham and Quarry tunnels are two neighbouring railway tunnels on the Brighton Main Line between Merstham and Coulsdon in Surrey, Great Britain.
The Gosport and Cosham lines were a collection of railway lines in southern Hampshire. Most of the lines are now closed but some elements are still in use, forming part of the West Coastway line. The lines originally linked to the main London to Southampton line via the Eastleigh–Fareham line and subsequently with a line from Southampton via Bursledon, both of which are still in use.

Haywards Heath tunnel, is a railway tunnel on the Brighton Main Line between Haywards Heath and Wivelsfield. It is 264 yards long and is one of the shortest tunnels on the line.

The Portsmouth line is a secondary main line originally built by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway and the London and South Western Railway between 1847 and 1868. It leaves the South London Line at Peckham Rye, with connections to the Victoria branch of the Brighton Main Line at Streatham, and continues via Sutton, Epsom and Dorking to join the Mid-Sussex Line at Horsham.















