
Mount Erebus is the second-highest volcano in Antarctica, the highest active volcano in Antarctica, and the southernmost active volcano on Earth. It is the sixth-highest peak of an island and the second most prominent mountain in Antarctica after Mount Vinson. It has a summit elevation of 3,794 metres (12,448 ft). It is located in the Ross Dependency on Ross Island, which is also home to three inactive volcanoes: Mount Terror, Mount Bird, and Mount Terra Nova. The mountain was named by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841 for his ship, HMS Erebus.
Skelton Glacier is a large glacier flowing from the polar plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf at Skelton Inlet on the Hillary Coast, south of Victoria Land, Antarctica.
The Possession Islands are a group of small islands and rocks extending over an area of about 7 nautical miles, lying in the western part of the Ross Sea, lying 5 nautical miles south-east of Cape McCormick, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. The Possession Islands were named by Captain James Clark Ross, Royal Navy, in commemoration of the planting of the British flag here on January 12, 1841.

Franklin Island is an island 7 nautical miles long, lying in the Ross Sea about 80 nautical miles east of Cape Hickey, Victoria Land, Antarctica.

Black Island, is an island in the Ross Archipelago, 12 nautical miles long, projecting through the Ross Ice Shelf to a height of 1,040 metres (3,410 ft).meters. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition and named by them for its appearance. The island is largely ice free and principally composed of black volcanic rock. The island's northernmost point is named Cape Hodgson, commemorating Thomas Vere Hodgson, one of the oldest members of the Discovery Expedition.

Hut Point Peninsula is a long, narrow peninsula from 2 to 3 nautical miles wide and 15 nautical miles long, projecting south-west from the slopes of Mount Erebus on Ross Island, Antarctica. McMurdo Station (US) and Scott Base (NZ) are Antarctic research stations located on the Hut Point Peninsula.
Mount Bird is a 1,765 metres (5,791 ft) high shield volcano standing about 7 nautical miles south of Cape Bird, the northern extremity of Ross Island. It was mapped by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott, and apparently named by them after Cape Bird.

Cape Evans is a rocky cape on the west side of Ross Island, Antarctica, forming the north side of the entrance to Erebus Bay.

Convoy Range is a broad range in Antarctica. It is south of the Kirkwood Range and north of the Clare Range.
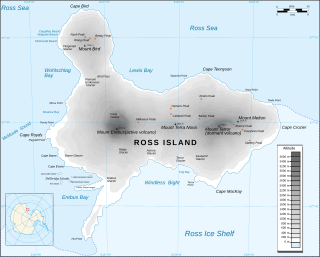
Cape Crozier is the most easterly point of Ross Island in Antarctica. It was discovered in 1841 during James Clark Ross's polar expedition of 1839 to 1843 with HMS Erebus and HMS Terror, and was named after Commander Francis Crozier, captain of HMS Terror, one of the two ships of Ross' expedition.
The Duroch Islands are a group of islands and rocks which extend over an area of about 3 nautical miles, centred about 1 nautical mile off Cape Legoupil on the north coast of Trinity Peninsula, Antarctica. The islands are close to Chile's Base General Bernardo O'Higgins Riquelme at Cape Legoupil.
Wohlschlag Bay is a large bay indenting the western side of Ross Island, Antarctica, and lying between Harrison Bluff and Cape Royds.
Evans Piedmont Glacier is a broad ice sheet occupying the low-lying coastal platform between Tripp Island and Cape Archer in Victoria Land, Antarctica.

Granite Harbour is a bay in the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica, about 14 nautical miles long, entered between Cape Archer and Cape Roberts. It was discovered and named by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) of 1901–04 in the Discovery in January 1902, while searching for safe winter quarters for the ship. The name derives from the great granite boulders found on its shores.
The Kirkwood Range is a massive coastal mountain range in Antarctica, extending north–south between Fry Glacier and Mawson Glacier. A broad low-level platform on the seaward side of the range is occupied by the Oates Piedmont Glacier. It is south of the Prince Albert Mountains and northeast of the Convoy Range.

Mackay Glacier is a large glacier in Victoria Land, descending eastward from the Antarctic Plateau, between the Convoy Range and Clare Range, into the southern part of Granite Harbour. It was discovered by the South magnetic pole party of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09, and named for Alistair Mackay, a member of the party. The glacier's tongue is called Mackay Glacier Tongue. First mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13 and named for Alistair F. Mackay, a member of the party. Its mouth is south of the Evans Piedmont Glacier and the Mawson Glacier. It is north of the Wilson Piedmont Glacier and the Ferrar Glacier.
Staten Island Heights is a predominantly flat, ice-covered upland between Greenville Valley and Alatna Valley in the Convoy Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica.
The Holland Range is a rugged coastal mountain range in the Ross Dependency, Antarctica, on the west coast of the Ross Ice Shelf. It is about 60 nautical miles (110 km) long.
Blue Glacier is a large glacier which flows into Bowers Piedmont Glacier about 10 nautical miles south of New Harbour, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) under Robert Falcon Scott, 1901–04, who gave it this name because of its clear blue ice at the time of discovery.

The Naze is a peninsula in north James Ross Island, marking the southeast entrance to Herbert Sound and extending about 5 nautical miles northeast from Terrapin Hill toward the south-central shore of Vega Island.

![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Paton Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Paton Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey. 








