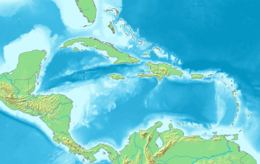
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It is 34 kilometres in length and up to 23 km (14 mi) in width, covering an area of 432 km2 (167 sq mi). It is in the western part of the North Atlantic, 100 km (62 mi) east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea. Barbados is east of the Windwards, part of the Lesser Antilles, at roughly 13°N of the equator. It is about 168 km (104 mi) east of both the countries of Saint Lucia and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and 180 km (110 mi) south-east of Martinique and 400 km (250 mi) north-east of Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados is outside the principal Atlantic hurricane belt. Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown.
Barbados, island country in the southeastern Caribbean Sea, situated about 100 miles east of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. Roughly triangular in shape, the island measures some 21 miles from northwest to southeast and about 14miles from east to west at its widest point. The capital and largest town is Bridgetown, which is also the main seaport.

Bridgetown is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Formerly The Town of Saint Michael, the Greater Bridgetown area is located within the parish of Saint Michael. Bridgetown is sometimes locally referred to as "The City", but the most common reference is simply "Town". As of 2014, its metropolitan population stands at roughly 110,000.

Barbados is an up-and-coming tourist country that provides reliable and safe transportation for natives and visitors alike. The country is very small with a length of 21 miles (34 km) and a width of 14 miles (23 km). Barbados has 1,600 kilometres (990 mi) of public paved roads, two active marine ports in, remnants of a railway system, and one airport; the Sir Grantley Adams International Airport, located in Christ Church.

The country of Barbados is divided into sub-regions known as parishes.

Bridgetown is a Canadian community located in north-central Annapolis County, Nova Scotia.

St. Ann's Garrison, or more commonly known as "The Garrison", is a small district located in the country of Barbados. This Garrison Historic Area is situated about 2 miles south of Heroes Square in the capital-city Bridgetown, and just west of the village of Hastings in the neighbouring parish of Christ Church. It is dominated by its historic horse race-track, located on the 30 acre parade ground called the Garrison Savannah. The Garrison area additionally contains many historic buildings including barracks for military personnel. The district is bisected by Highway 7, with Saint Ann's Fort, where the Barbados Defence Force (BDF) is based, lying to the west.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the nation of Barbados.

The Port of Bridgetown, is a seaport in Bridgetown on the southwest coast of Barbados. Situated at the North-Western end of Carlisle Bay, the harbour handles all of the country's international bulk ship-based trade and commerce. In addition to international-shipping the Deep Water Harbour is the port of entry for southern-Caribbean cruise ships. The port is one of three designated ports of entry in Barbados, along with the privately owned Port Saint Charles marina and the Sir Grantley Adams International Airport. The port's time zone is GMT −4, and it handles roughly 700,000 cruise passengers and 900,000 tonnes of containerised cargo per year.
This article describes the history of West Indies cricket from 1946 to 1970.
This article describes the history of West Indies cricket from 1991 to 2000.
A Jewish population has been in Barbados almost continually since 1654.
The United States and Barbados have had cordial bilateral relations since Barbados' independence in 1966. The United States has supported the government's efforts to expand the country's economic base and to provide a higher standard of living for its citizens. Barbados is a beneficiary of the U.S. Caribbean Basin Initiative. U.S. assistance is channeled primarily through multilateral agencies such as the Inter-American Development Bank and the World Bank, as well as the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) office in Bridgetown.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Barbados:

Barbados–Trinidad and Tobago relations describe relations between the governments of The Republic of Trinidad and Tobago and Barbados. Barbados maintains non-resident representation to Port of Spain, and the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago maintains non-resident representation to Bridgetown. Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago formally established diplomatic relations on Barbados' national date of independence 30 November 1966. Both countries are members of many shared organisations including: The Association of Caribbean States, the Commonwealth of Nations, CARICOM, CARIFORUM, and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States.
Foreign relations exist between Australia and Barbados. Neither country has a resident ambassador. The regional Australian High Commissioner to Barbados is accredited from Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados is represented in Australia through its High Commission in Ottawa, (Canada). Barbados maintains an honorary consul and a tourist office in Australia. Barbados and Australia established diplomatic relations on 7 January 1974. Both countries are members of the Commonwealth of Nations, and comprised as former parts of the British Empire.
National emblems of Barbados are the symbols that are used in Barbados to represent the independent nation. The emblems reflect different aspects of its cultural life and history.
The Lokono or Arawak are an Arawak people native to northern coastal areas of South America. Today, approximately 10,000 Lokono live primarily along the coasts and rivers of Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, Barbados and French Guiana. They speak the Arawak language, the eponymous language of the Arawakan language family, as well as various Creole languages, and English.
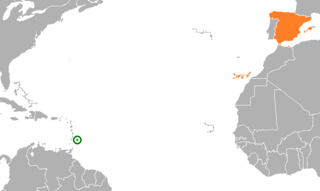
Barbados–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Barbados does not have embassy in Spain, but his embassy in Brussels is accredited to Spain. Spain does not have a resident embassy in Barbados, but the Spanish embassy in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago is accredited for this country, in addition Spain has an Consulate Honorary in Bridgetown.

Barbados–Turkey relations are foreign relations between Barbados and Turkey. Recognizing Barbados’s leading role in the Caribbean, Turkey has had friendly relations with Barbados since Barbados’ independence from the United Kingdom in 1966.