
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.

Aspergillus niger is a mold classified within the Nigri section of the Aspergillus genus. The Aspergillus genus consists of common molds found throughout the environment within soil and water, on vegetation, in fecal matter, on decomposing matter, and suspended in the air. Species within this genus often grow quickly and can sporulate within a few days of germination. A combination of characteristics unique to A. niger makes the microbe invaluable to the production of many acids, proteins and bioactive compounds. Characteristics including extensive metabolic diversity, high production yield, secretion capability, and the ability to conduct post-translational modifications are responsible for A. niger's robust production of secondary metabolites. A. niger's capability to withstand extremely acidic conditions makes it especially important to the industrial production of citric acid.

The glucose oxidase enzyme also known as notatin is an oxidoreductase that catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is produced by certain species of fungi and insects and displays antibacterial activity when oxygen and glucose are present.

Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mould species found in various climates worldwide.

A phytase is any type of phosphatase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phytic acid – an indigestible, organic form of phosphorus that is found in many plant tissues, especially in grains and oil seeds – and releases a usable form of inorganic phosphorus. While phytases have been found to occur in animals, plants, fungi and bacteria, phytases have been most commonly detected and characterized from fungi.
In enzymology, a 1,4-alpha-glucan 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction that transfers an alpha-D-glucosyl residue in a 1,4-alpha-D-glucan to the primary hydroxyl group of glucose or 1,4-alpha-D-glucan.
Mycotoxicology is the branch of mycology that focuses on analyzing and studying the toxins produced by fungi, known as mycotoxins. In the food industry it is important to adopt measures that keep mycotoxin levels as low as practicable, especially those that are heat-stable. These chemical compounds are the result of secondary metabolism initiated in response to specific developmental or environmental signals. This includes biological stress from the environment, such as lower nutrients or competition for those available. Under this secondary path the fungus produces a wide array of compounds in order to gain some level of advantage, such as incrementing the efficiency of metabolic processes to gain more energy from less food, or attacking other microorganisms and being able to use their remains as a food source.

Proline dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRODH gene.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.

Penicillium rubens is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium and was the first species known to produce the antibiotic penicillin. It was first described by Philibert Melchior Joseph Ehi Biourge in 1923. For the discovery of penicillin from this species Alexander Fleming shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945. The original penicillin-producing type has been variously identified as Penicillium rubrum, P. notatum, and P. chrysogenum among others, but genomic comparison and phylogenetic analysis in 2011 resolved that it is P. rubens. It is the best source of penicillins and produces benzylpenicillin (G), phenoxymethylpenicillin (V) and octanoylpenicillin (K). It also produces other important bioactive compounds such as andrastin, chrysogine, fungisporin, roquefortine, and sorbicillins.
Throughout human history, fungi have been utilized as a source of food and harnessed to ferment and preserve foods and beverages. In the 20th century, humans have learned to harness fungi to protect human health, while industry has utilized fungi for large scale production of enzymes, acids, and biosurfactants. With the advent of modern nanotechnology in the 1980s, fungi have remained important by providing a greener alternative to chemically synthesized nanoparticle.
Penicillium adametzii is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium.
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol and ergosterol synthesis inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, immunosuppressants and fungicides.
Penicillium chermesinum is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from soil from Nova Scotia in Canada.Penicillium chermesinum produces plastatin, luteosporin, xanthomegnin, azaphilones, p-terphenyls and costaclavine.
Penicillium corylophilum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which occurs in damp buildings in United States, Canada and western Europe but it can also be found in a variety of foods and mosquitoes. Penicillium corylophilum produces the alkaloid epoxyagroclavine and citrinin and is a pathogen to mosquitoes.
Penicillium pinophilum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from a radio set in Papua New Guinea. Penicillium pinophilum produces 3-O-methylfunicone and mycophenolic acid
Penicillium variabile is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which has been isolated from permafrost deposits. Penicillium variabile produces rugulovasine A and rugulovasine B This species occurs on wheat, flour, maize, rice, and barley, and it is also very common in indoor environments.
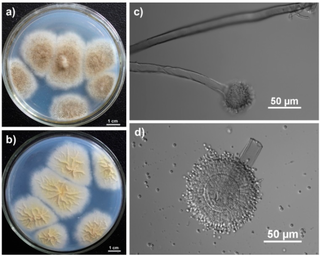
Aspergillus tubingensis is a darkly pigmented species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus section Nigri. It is often confused with Aspergillus niger due to their similar morphology and habitat. A. tubingensis is often involved in food spoilage of fruits and wheat, and industrial fermentation. This species is a rare agent of opportunistic infection.

Penicillium spinulosum is a non-branched, fast-growing fungus with a swelling at the terminal of the stipe (vesiculate) in the genus Penicillium. P. spinulosum is able to grow and reproduce in environment with low temperature and low water availability, and is known to be acidotolerant. P. spinulosum is ubiquitously distributed, and can often be isolated from soil. Each individual strain of P. spinulosum differs from others in their colony morphology, including colony texture, amount of sporulation and roughness of conidia and conidiophores.
Aspergillus wentii is an asexual, filamentous, endosymbiotic fungus belonging to the mold genus, Aspergillus. It is a common soil fungus with a cosmopolitan distribution, although it is primarily found in subtropical regions. Found on a variety of organic materials, A. wentii is known to colonize corn, cereals, moist grains, peanuts and other ground nut crops. It is also used in the manufacture of biodiesel from lipids and is known for its ability to produce enzymes used in the food industry.








