
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
Ehrlichiosis is a tick-borne disease of dogs usually caused by the rickettsial agent Ehrlichia canis. Ehrlichia canis is the pathogen of animals. Humans can become infected by E. canis and other species after tick exposure. German Shepherd Dogs are thought to be susceptible to a particularly severe form of the disease; other breeds generally have milder clinical signs. Cats can also be infected.

Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults.

Mange is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites. Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infection, is sometimes reserved for pathological mite-infestation of nonhuman mammals. Thus, mange includes mite-associated skin disease in domestic mammals, in livestock, and in wild mammals (for example, foxes, coyotes, cougars and wombats. Severe mange caused by mites has been observed in wild bears. Since mites belong to the arachnid subclass Acari, another term for mite infestation is acariasis.
Toxocariasis is an illness of humans caused by the dog roundworm and, less frequently, the cat roundworm. These are the most common intestinal roundworms of dogs, coyotes, wolves and foxes and domestic cats, respectively. Humans are among the many "accidental" or paratenic hosts of these roundworms.

Brucella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, named after David Bruce (1855–1931). They are small, nonencapsulated, nonmotile, facultatively intracellular coccobacilli.

The dog is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from extinct gray wolves, and the gray wolf is the dog's closest living relative. The dog was the first species to be domesticated by humans. Hunter-gatherers did this over 15,000 years ago in Oberkassel, Bonn, which was before the development of agriculture. Due to their long association with humans, dogs have expanded to a large number of domestic individuals and gained the ability to thrive on a starch-rich diet that would be inadequate for other canids.

Mycobacterium fortuitum is a nontuberculous species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Brucella canis is a Gram-negative bacterium in the family Brucellaceae that causes brucellosis in dogs and other canids. It is a non-motile short-rod or coccus-shaped organism, and is oxidase, catalase, and urease positive. B. canis causes infertility in both male and female dogs. It can also cause inflammation in the eyes. The hosts of B. canis ranges from domestic animals to foxes and coyotes. It is passed from species to species via genital fluids. Treatments such as spaying, neutering, and long-term antibiotics have been used to combat B. canis. The species was first described in the United States in 1966 where mass abortions of beagles were documented. Brucella canis can be found in both pets and wild animals and lasts the lifespan of the animal it has affected. B. canis has two distinct circular chromosomes that can attribute to horizontal gene transfer.

Streptococcus canis is a group G beta-hemolytic species of Streptococcus. It was first isolated in dogs, giving the bacterium its name. These bacteria are characteristically different from Streptococcus dysgalactiae, which is a human-specific group G species that has a different phenotypic chemical composition. S. canis is important to the skin and mucosal health of cats and dogs, but under certain circumstances, these bacteria can cause opportunistic infections. These infections were known to afflict dogs and cats prior to the formal description of the species in Devriese et al., 1986. However, additional studies revealed cases of infection in other mammal species, including cattle and even humans. Instances of mortality from S. canis in humans are very low with only a few reported cases, while actual instances of infection may be underreported due to mischaracterizations of the bacteria as S. dysgalactiae. This species, in general, is highly susceptible to antibiotics, and plans to develop a vaccine to prevent human infections are currently being considered.
Ehrlichia canis is an obligate intracellular bacterium that acts as the causative agent of ehrlichiosis, a disease most commonly affecting canine species. This pathogen is present throughout the United States, South America, Asia, Africa and recently in the Kimberley region of Australia. First defined in 1935, E. canis emerged in the United States in 1963 and its presence has since been found in all 48 contiguous United States. Reported primarily in dogs, E. canis has also been documented in felines and humans, where it is transferred most commonly via Rhipicephalus sanguineus, the brown dog tick.
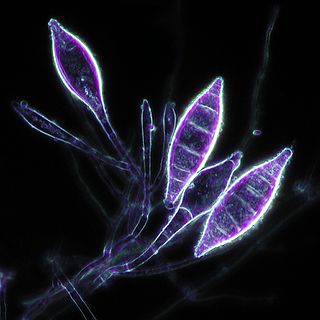
Microsporum canis is a pathogenic, asexual fungus in the phylum Ascomycota that infects the upper, dead layers of skin on domesticated cats, and occasionally dogs and humans. The species has a worldwide distribution.
Mycobacterium arosiense is a newly described species of Mycobacterium. It is a scotochromogen that derives its name from Arosia, the Latin name for the city of Aarhus (Denmark), where the strain was first isolated.

In the taxonomic treatment presented in the third (2005) edition of Mammal Species of the World, Canis lupus dingo is a taxonomic rank that includes both the dingo that is native to Australia and the New Guinea singing dog that is native to the New Guinea Highlands. It also includes some extinct dogs that were once found in coastal Papua New Guinea and the island of Java in the Indonesian Archipelago. In this treatment it is a subspecies of Canis lupus, the wolf, although other treatments consider the dog as a full species, with the dingo and its relatives either as a subspecies of the dog, a species in its own right, or simply as an unnamed variant or genetic clade within the larger population of dogs. The genetic evidence indicates that the dingo clade originated from East Asian domestic dogs and was introduced through the Malay Archipelago into Australia, with a common ancestry between the Australian dingo and the New Guinea singing dog. The New Guinea singing dog is genetically closer to those dingoes that live in southeastern Australia than to those that live in the northwest.
Pasteurella canis is a Gram-negative, nonmotile, penicillin-sensitive coccobacillus of the family Pasteurellaceae. Bacteria from this family cause zoonotic infections in humans, which manifest themselves as skin or soft-tissue infections after an animal bite. It has been known to cause serious disease in immunocompromised patients.
Helicobacter canis is a bacterium in the Helicobacteraceae family, Campylobacterales order. Its type strain is NCTC 12739T. It colonises the lower bowel, but is also present in cases of hepatitis. Besides infecting dogs, this bacterium is known to cause infections in immunocompromised humans.
Penicillium citrinum is an anamorph, mesophilic fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces tanzawaic acid A-D, ACC, Mevastatin, Quinocitrinine A, Quinocitrinine B, and nephrotoxic citrinin. Penicillium citrinum is often found on moldy citrus fruits and occasionally it occurs in tropical spices and cereals. This Penicillium species also causes mortality for the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. Because of its mesophilic character, Penicillium citrinum occurs worldwide. The first statin (Mevastatin) was 1970 isolated from this species.
Penicillium velutinum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from soil in the United States. It produces verruculogen, verrucosidin, verruculotoxin, decalpenic acid, dehydroaltenusin, cyciooctasulfur, atrovenetinone, altenusin and penitrem A

Penicillium spinulosum is a non-branched, fast-growing fungus with a swelling at the terminal of the stipe (vesiculate) in the genus Penicillium. P. spinulosum is able to grow and reproduce in environment with low temperature and low water availability, and is known to be acidotolerant. P. spinulosum is ubiquitously distributed, and can often be isolated from soil. Each individual strain of P. spinulosum differs from others in their colony morphology, including colony texture, amount of sporulation and roughness of conidia and conidiophores.










