
Aureobasidium pullulans is a ubiquitous and generalistic black, yeast-like fungus that can be found in different environments. It is well known as a naturally occurring epiphyte or endophyte of a wide range of plant species without causing any symptoms of disease. A. pullulans has a high importance in biotechnology for the production of different enzymes, siderophores and pullulan. Furthermore, A. pullulans is used in biological control of plant diseases, especially storage diseases.
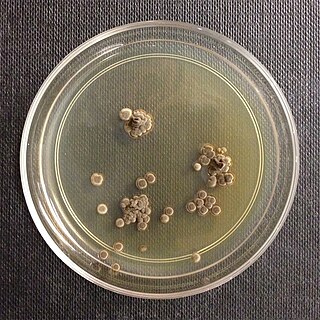
The Wallemiomycetes are a class of fungi in the division Basidiomycota. It consists of the single order Wallemiales, containing the single family Wallemiaceae, which in turn contains the single genus Wallemia. The phylogenetic origin of the lineage was placed to various parts of Basidiomycota, but according to the analysis of a larger dataset it is a sister group of Agaricomycotina. The genus contains species of xerophilic molds that are found worldwide. The seven described species are distinguished by conidial size, xerotolerance, halotolerance, chaotolerance, growth temperature regimes, extracellular enzyme activity profiles, and secondary metabolite patterns. They are typically isolated from low-moisture foods, indoor air dust, salterns and soil. W. sebi is thought to be one of the causes of the hypersensitivity pneumonitis known as the farmer's lung disease, but since the other species were recognised and separated from W. sebi only recently, their role in the disease cannot be excluded.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.

Penicillium rubens is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium and was the first species known to produce the antibiotic penicillin. It was first described by Philibert Melchior Joseph Ehi Biourge in 1923. For the discovery of penicillin from this species Alexander Fleming shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945. The original penicillin-producing type has been variously identified as Penicillium rubrum, P. notatum, and P. chrysogenum among others, but genomic comparison and phylogenetic analysis in 2011 resolved that it is P. rubens. It is the best source of penicillins and produces benzylpenicillin (G), phenoxymethylpenicillin (V) and octanoylpenicillin (K). It also produces other important bioactive compounds such as andrastin, chrysogine, fungisporin, roquefortine, and sorbicillins.
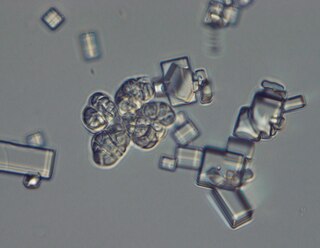
Wallemia ichthyophaga is one of the three species of fungi in the genus Wallemia, which in turn is the only genus of the class Wallemiomycetes. The phylogenetic origin of the lineage was placed to various parts of Basidiomycota, but according to the analysis of larger datasets it is a (495-million-years-old) sister group of Agaricomycotina. Although initially believed to be asexual, population genomics found evidence of recombination between strains and a mating type locus was identified in all sequenced genomes of the species.
Aureobasidium melanogenum, formerly known as Aureobasidium pullulans var. melanogenum is a ubiquitous black, yeast-like fungus that is found mainly in freshwater habitats. The species also includes strains causing human infections, which were previously classified as A. pullulans. It was named due to abundant melanin production and accumulation in the cell walls, which leads to dark green, brown or black appearance of the cells and colonies The species was established when the genomes of the four former varieties of Aureobasidium pullulans were sequenced and the large differences between them were discovered.
Penicillium concentricum is a coprophilic, anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces roquefortine C and patulin.
Penicillium coprobium is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces pyripyropene A, roquefortine C, penicillic acid and patulin.
Penicillium dipodomyicola is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces peniphenone A, peniphenone B, peniphenone C, peniphenone D, cyclopiazonic acid and patulin.

Penicillium glandicola is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which produces penitrem A, patulin, 2,4,6-trichloroanisole and roquefortine C
Penicillium nordicum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces ochratoxin A. Penicillium nordicum contaminates protein rich foods and foods with high NaCl-konzentration. It is mostly found on dry-cured meat products and cheese products
Penicillium osmophilum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from agricultural soil in Wageningen in the Netherlands
Penicillium persicinum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from soil from the Qinghai Province in China. Penicillium persicinum produces griseofulvin, lichexanthone, roquefortine C, roquefortine D, patulin and chrysogine
Penicillium salamii is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which occurs on dry-cured meat products.
Penicillium spathulatum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces asperphenamate.
Rasamsonia is a genus of fungi in the family Trichocomaceae, circumscribed in 2011 by mycologists Jos Houbraken and Jens Frisvad. It is characterized from other genera of the Trichocomaceae by the following combination of features: species are thermotolerant or thermophilic; their conidiophores have distinctly rough-walled stipes; conidia are olive brown; and ascomata, if present, have minimal covering. Rasamsonia phenotypically resembles Paecilomyces, in that both have thermotolerant species, produce olive-brown conidia, and form ascomata with no or scarce ascomatal covering; Rasamsonia, however, differs from Paecilomyces in having more regularly branched conidiophores with distinct rough-walled structures. The type species is Rasamsonia emersonii, a fungus formerly classified in the genus Talaromyces.
Penicillium subrubescens is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces high amounts of inulinase.
Streptomyces gulbargensis is an alkalitolerant and thermotolerant bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Gulbarga in the Karnataka in India.
Streptomyces muensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from a limestone quarry from Tangkhul Hundung in Manipur in India.
Sediminibacillus massiliensis is a Gram-positive, moderately halophilic, aerobic, rod-shaped and motile bacterium from the genus of Sediminibacillus which has been isolated from human feaces from Dielmo in Senegal.





