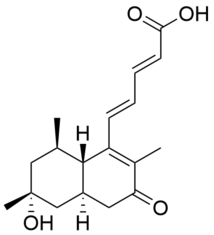
Lovastatin, sold under the brand name Mevacor among others, is a statin medication, to treat high blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its use is recommended together with lifestyle changes. It is taken by mouth.
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or better bioactivity.
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to produce malonyl-CoA through its two catalytic activities, biotin carboxylase (BC) and carboxyltransferase (CT). ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in most prokaryotes and in the chloroplasts of most plants and algae, whereas it is a large, multi-domain enzyme in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotes. The most important function of ACC is to provide the malonyl-CoA substrate for the biosynthesis of fatty acids. The activity of ACC can be controlled at the transcriptional level as well as by small molecule modulators and covalent modification. The human genome contains the genes for two different ACCs—ACACA and ACACB.

Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid.
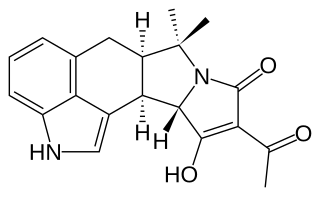
Cyclopiazonic acid (α-CPA), a mycotoxin and a fungal neurotoxin, is made by the molds Aspergillus and Penicillium. It is an indole-tetramic acid that serves as a toxin due to its ability to inhibit calcium-dependent ATPases found in the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. This inhibition disrupts the muscle contraction-relaxation cycle and the calcium gradient that is maintained for proper cellular activity in cells.

Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase is found in bacteria and humans and has important roles in regulating fatty acid metabolism and food intake, and it is an attractive target for drug discovery. It is an enzyme associated with Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency. In humans, it is encoded by the MLYCD gene.
Propionyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of propionic acid. It is composed of a 24 total carbon chain and its production and metabolic fate depend on which organism it is present in. Several different pathways can lead to its production, such as through the catabolism of specific amino acids or the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids. It later can be broken down by propionyl-CoA carboxylase or through the methylcitrate cycle. In different organisms, however, propionyl-CoA can be sequestered into controlled regions, to alleviate its potential toxicity through accumulation. Genetic deficiencies regarding the production and breakdown of propionyl-CoA also have great clinical and human significance.

In molecular biology, Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase EC 2.3.1.41, is an enzyme involved in fatty acid synthesis. It typically uses malonyl-CoA as a carbon source to elongate ACP-bound acyl species, resulting in the formation of ACP-bound β-ketoacyl species such as acetoacetyl-ACP.
In enzymology, a 6-methylsalicylic-acid synthase (EC 2.3.1.165) is a polyketide synthase that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an erythronolide synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Xanthohumol is a natural product found in the female inflorescences of Humulus lupulus, also known as hops. This compound is also found in beer and belongs to a class of compounds that contribute to the bitterness and flavor of hops. Xanthohumol is a prenylated chalconoid, biosynthesized by a type III polyketide synthase (PKS) and subsequent modifying enzymes.

Chrysophanol, also known as chrysophanic acid, is a fungal isolate and a natural anthraquinone. It is a C-3 methyl substituted chrysazin of the trihydroxyanthraquinone family.
Fungal isolates have been researched for decades. Because fungi often exist in thin mycelial monolayers, with no protective shell, immune system, and limited mobility, they have developed the ability to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds for survival. Researchers have discovered fungal isolates with anticancer, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, and other bio-active properties. The first statins, β-Lactam antibiotics, as well as a few important antifungals, were discovered in fungi.

Ketoacyl synthases (KSs) catalyze the condensation reaction of acyl-CoA or acyl-acyl ACP with malonyl-CoA to form 3-ketoacyl-CoA or with malonyl-ACP to form 3-ketoacyl-ACP. This reaction is a key step in the fatty acid synthesis cycle, as the resulting acyl chain is two carbon atoms longer than before. KSs exist as individual enzymes, as they do in type II fatty acid synthesis and type II polyketide synthesis, or as domains in large multidomain enzymes, such as type I fatty acid synthases (FASs) and polyketide synthases (PKSs). KSs are divided into five families: KS1, KS2, KS3, KS4, and KS5.
Penicillium herquei is an anamorph, filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which produces citreorosein, emodin, hualyzin, herquline B, janthinone, citrinin and duclauxin,.
Penicillium paneum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which can spoil cereal grains. Penicillium paneum produces 1-Octen-3-ol and penipanoid A, penipanoid B, penipanoid C, patulin and roquefortine C

Dihydromaltophilin, or heat stable anti-fungal factor (HSAF), is a secondary metabolite of Streptomyces sp. and Lysobacter enzymogenes. HSAF is a polycyclic tetramate lactam containing a single tetramic acid unit and a 5,5,6-tricyclic system. HSAF has been shown to have anti-fungal activity mediated through the disruption of the biosynthesis of Sphingolipid's by targeting a ceramide synthase unique to fungi.
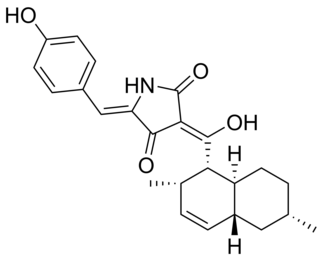
Conipyridoin E is a tetramic acid derivative produced by the fungus Coniochaeta cephalothecoides which was found on a Tibetan Plateau. This natural product has been shown to exhibit antibacterial and antifungal activity against a variety of bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphyloccusaureus, and Enterococcus faecalis with MIC50 values of around 0.97 μM. Isolation of a number of analogs of conipyridoin has been accomplished by Han et al. in order to discover novel antibiotic natural products to combat antibiotic resistance.

Thraustochytrids are single-celled saprotrophic eukaryotes (decomposers) that are widely distributed in marine ecosystems, and which secrete enzymes including, but not limited to amylases, proteases, phosphatases. They are most abundant in regions with high amounts of detritus and decaying plant material. They play an important ecological role in mangroves, where they aid in nutrient cycling by decomposing decaying matter. Additionally, they contribute significantly to the synthesis of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs): docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which are essential fatty acids for the growth and reproduction of crustaceans. Thraustochytrids are members of the class Labyrinthulea, a group of protists that had previously been incorrectly categorized as fungi due to their similar appearance and lifestyle. With the advent of DNA sequencing technology, labyrinthulomycetes were appropriately placed with other stramenopiles and subsequently categorized as a group of Labyrinthulomycetes.