 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
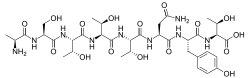
| IUPAC name L-Alanyl-L-seryl-L-threonyl-L-threonyl-L-threonyl-L-asparaginyl-L-tyrosyl-L-threonine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C35H55N9O16 | |
| Molar mass | 857.872 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Peptide T is an HIV entry inhibitor discovered in 1986 by Candace Pert and Michael Ruff, a US neuroscientist and immunologist. [1] Peptide T, and its modified analog Dala1-peptide T-amide (DAPTA), a drug in clinical trials, is a short peptide derived from the HIV envelope protein gp120 which blocks binding [2] and infection [3] of viral strains which use the CCR5 receptor to infect cells. DAPTA was initially administered as a nasal spray, but this formulation was found to be unstable. A more stable oral form, called RAP-103, is a shorter pentapeptide derived from DAPTA. RAP-103 is a CCR2/CCR5 antagonist that protects synapses by blocking the synaptotoxic actions of oligomeric forms of amyloid beta [4] and alpha-synuclein., [5] as well as HIV gp120, via a PrPc dependent pathway. Synapse loss underlies the cognitive losses attributed to these toxic proteins and the ensuing clinical conditions of AD, LBD, and HAND, which these peptide chemokine receptor antagonists may safely treat. In preclinical studies, RAP-103 has also been shown to prevent and reverse neuropathic pain [6] and to reduce opioid addiction liability. [7]
Contents
Peptide T has several positive effects related to HIV disease and Neuro-AIDS. [8] A FDG-PET neuro-imaging study in an individual with AIDS dementia who completed a 12-wk treatment with intranasal DAPTA, showed remission in 34 out of 35 brain regions after treatment. [9] A placebo-controlled, three site, 200+ patient NIH-funded clinical trial, which focused on neurocognitive improvements, was conducted between 1990 and 1995. The results showed that DAPTA was not significantly different from placebo on the study primary end points. However, 2 of 7 domains, abstract thinking and speed of information processing, did show improvement in the DAPTA group (p<0.05). Furthermore, twice as many DAPTA-treated patients improved, whereas twice as many placebo patients deteriorated (P=0.02). A sub-group analysis showed that DAPTA had a treatment effect and improved global cognitive performance (P=0.02) in the patients who had more severe cognitive impairment. [10]
An analysis of antiviral effects from the 1996 NIH study showed peripheral viral load (combined plasma and serum) was significantly reduced in the DAPTA-treated group. [11] An eleven-person study for peptide T effects on cellular viral load showed reductions in the persistently infected monocyte reservoir to undetectable levels in most of the patients. [12] Elimination of viral reservoirs, such as the persistently infected monocytes or brain microglia, is an important treatment goal. [13]
Peptide T clinical development was stopped due to the propensity of the liquid nasal spray to lose potency upon storage and shifted to its shorter oral analog, the pentapeptide CCR2/CCR5 antagonist RAP-103 (Receptor Active Peptide) for neuropathic pain and neurodegeneration. [14] RAP-103 also blocks CCR8, [15] which may be important in neuropathic pain. [16] Inhibitors of CCR5, including DAPTA, [17] [18] prevent and reverse neurodegeneration and are therapeutic targets in stroke/brain injury [19] and dementia, such as in Parkinson's disease. [20]