
Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the generation and propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or other planetary bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic microseism, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions and human activities. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time, created by a seismograph is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist works in basic or applied seismology.
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthquakes are the planet's most powerful, with moment magnitudes (Mw) that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes.

The Okhotsk microplate is a proposed minor tectonic plate covering the Kamchatka Peninsula, Magadan Oblast, and Sakhalin Island of Russia; Hokkaido, Kantō and Tōhoku regions of Japan; the Sea of Okhotsk, as well as the disputed Kuril Islands.
The Farallon Trench was a subduction related tectonic formation located off the coast of the western California continental margin during the late to mid Cenozoic era, around 50 miles southeast of modern-day Monterey Bay. The time duration of subduction began from around 165 Ma when the Farallon Plate replaced the Mezcalera promontory, until the San Andreas Fault straightening around 35 Ma. As data accumulated over time, a common view developed that one large oceanic plate, the Farallon Plate, acted as a conveyor belt, conveying accreted terranes onto the North American west coast. As the continent overran the subducting Farallon Plate, the denser plate became subducted into the mantle below the continent. When the plates converged, the dense oceanic plate sank into the mantle to form a slab below the lighter continent. Rapid subduction under the southwestern North America continent began 40 to 60 million years ago (Ma), during the mid Paleocene to mid Eocene epochs. This convergent subduction margin created a distinctive geomorphologic feature called an oceanic trench, which occurs at a convergent plate boundaries as a heavy metal rich, lithospheric plate moves below a light silica rich continental plate. The trench marks the position at which the flexed subducting slab begins to descend beneath and deform the continental plate margin. By 43 Ma, during the Eocene, worldwide plate motions changed and the Pacific Plate began to move away from North America and subduction of the Farallon Plate slowed dramatically. By around 36 Ma, the easternmost part of the East Pacific Rise, located between the Pioneer and Murray fracture zones at that time, approached the trench and the young, hot, buoyant lithosphere appears to have clogged part of the subduction zone, resulting in widespread dramatic uplift on land. The eventual complete subduction of this plate, consequential contact of the Pacific Plate with the California continental margin, and creation of the Mendocino Triple Junction (MTJ), took place around 30 to 20 Ma. The partial complete subduction and division of the Farallon Plate by the Pacific Plate, created the Juan de Fuca Plate to the north and the Cocos Plate to the south. The final stages of the evolution of California's continental margin was the growth of the San Andreas transform fault system, which formed as the Pacific Plate came into contact with the continental margin and the MTJ was formed. As subduction of the Pacific Plate continued along this margin, and the contact zone grew, the San Andreas proportionally grew as well.
Earthquake forecasting is a branch of the science of seismology concerned with the probabilistic assessment of general earthquake seismic hazard, including the frequency and magnitude of damaging earthquakes in a given area over years or decades. While forecasting is usually considered to be a type of prediction, earthquake forecasting is often differentiated from earthquake prediction, Earthquake forecasting estimates the likelihood of earthquakes in a specific timeframe and region, while earthquake prediction attempts to pinpoint the exact time, location, and magnitude of an impending quake, which is currently not reliably achievable.Wood & Gutenberg (1935). Kagan says: "This definition has several defects which contribute to confusion and difficulty in prediction research." In addition to specification of time, location, and magnitude, Allen suggested three other requirements: 4) indication of the author's confidence in the prediction, 5) the chance of an earthquake occurring anyway as a random event, and 6) publication in a form that gives failures the same visibility as successes. Kagan & Knopoff define prediction "to be a formal rule where by the available space-time-seismic moment manifold of earthquake occurrence is significantly contracted ...."</ref> Both forecasting and prediction of earthquakes are distinguished from earthquake warning systems, which, upon detection of an earthquake, provide a real-time warning to regions that might be affected.
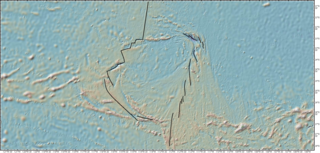
Easter Plate is a tectonic microplate located to the west of Easter Island off the west coast of South America in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, bordering the Nazca Plate to the east and the Pacific Plate to the west. It was discovered from looking at earthquake distributions that were offset from the previously perceived Nazca-Pacific Divergent boundary. This young plate is 5.25 million years old and is considered a microplate because it is small with an area of approximately 160,000 square kilometres (62,000 sq mi). Seafloor spreading along the Easter microplate's borders have some of the highest global rates, ranging from 50 to 140 millimetres /yr.
The Walker Lane is a geologic trough roughly aligned with the California/Nevada border southward to where Death Valley intersects the Garlock Fault, a major left lateral, or sinistral, strike-slip fault. The north-northwest end of the Walker Lane is between Pyramid Lake in Nevada and California's Lassen Peak where the Honey Lake Fault Zone, the Warm Springs Valley Fault, and the Pyramid Lake Fault Zone meet the transverse tectonic zone forming the southern boundary of the Modoc Plateau and Columbia Plateau provinces. The Walker Lane takes up 15 to 25 percent of the boundary motion between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, the other 75 percent being taken up by the San Andreas Fault system to the west. The Walker Lane may represent an incipient major transform fault zone which could replace the San Andreas as the plate boundary in the future.
The historical development of geophysics has been motivated by two factors. One of these is the research curiosity of humankind related to planet Earth and its several components, its events and its problems. The second is economical usage of Earth's resources and Earth-related hazards such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, tides, and floods.

The Aegean Sea Plate is a small tectonic plate located in the eastern Mediterranean Sea under southern Greece and western Turkey. Its southern edge is the Hellenic subduction zone south of Crete, where the African Plate is being swept under the Aegean Sea Plate. Its northern margin is a divergent boundary with the Eurasian Plate.
The Chixoy-Polochic Fault, also known as Cuilco-Chixoy-Polochic Fault, is a major fault zone in Guatemala and southeast Mexico. It runs in a light arc from the east coast of Guatemala to Chiapas, following the deep valleys of the Polochic River, Chixoy River and Cuilco River.

This timeline of volcanism on Earth includes a list of major volcanic eruptions of approximately at least magnitude 6 on the Volcanic explosivity index (VEI) or equivalent sulfur dioxide emission during the Quaternary period. Other volcanic eruptions are also listed.
The Brawley Seismic Zone (BSZ), also known as the Brawley fault zone, is a predominantly extensional tectonic zone that connects the southern terminus of the San Andreas Fault with the Imperial Fault in Southern California. The BSZ is named for the nearby town of Brawley in Imperial County, California, and the seismicity there is characterized by earthquake swarms.

John "Jack" Ertle Oliver was an American scientist. Oliver, who earned his PhD at Columbia University in 1953, studied earthquakes and ultimately provided seismic evidence supporting plate tectonics. In the 1960s, Oliver and his former graduate student, Bryan Isacks, set up seismographic stations in the South Pacific to record earthquake activity, and the data collected led to the insight that part of the ocean floor was being pushed downward.
The 1959 Kamchatka earthquake occurred on May 4 at with a moment magnitude of 8.0–8.3, and a surface wave magnitude of 8.25. The epicenter was near the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russian SFSR, USSR. Building damage was reported in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. The maximum intensity was VIII (Damaging) on the Medvedev–Sponheuer–Karnik scale. The intensity in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky was about VIII MSK.
The 1931 Myitkyina earthquake, or also known as the 1931 Kamaing earthquake, occurred on January 28 at 02:35 local time. It was located in northern Burma, then part of British India. The magnitude of this earthquake was put at 7.6. According to some sources the depth was 35 km, and according to a study of Phyo M. M. the depth was 5 to 30 km.
The 1981 Playa Azul earthquake occurred on October 24, 1981, at 21:22 local time. It was located near Playa Azul, Michoacán, Mexico. The magnitude of the earthquake was 7.2, or 7.3. Three deaths were reported, two from Michoacán and one from Mexico City. Some buildings were damaged in both Michoacán and Mexico City. A small tsunami was registered in Acapulco with a maximum height of 9 cm.
The 1976 Longling earthquake in Yunnan Province, People's Republic of China, was a doublet earthquake, with two main shocks striking just east of Longling at 12:23:20 and 14:00:22 UTC. The magnitudes were estimated at 6.7 and 6.6, respectively, on the (GCMT) scale, and 6.9 and 7.0 on the scale; Chinese sources put these at 7.4 and 7.3 on the scale. The region is noted for the quantity and intensity of its earthquakes, and the complexity of its tectonics, which are closely related to the collision between the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates.

Jeanne L. Hardebeck is an American research geophysicist studying earthquakes and seismology who has worked at the United States Geological Survey (USGS) since 2004. Hardebeck studies the state of stress and the strength of faults.
Suzanne Carbotte is a marine geophysicist known for her research on the formation of new oceanic crust.
Seth Avram Stein is an American geophysicist with an international reputation for his research in plate tectonics, seismology, and space geodesy. He has also done important work in public policy for coping with earthquake hazards.







