
Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a fully synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben, in Germany. Pethidine is the prototype of a large family of analgesics including the pethidine 4-phenylpiperidines, the prodines, bemidones, and others more distant, including diphenoxylate and analogues.
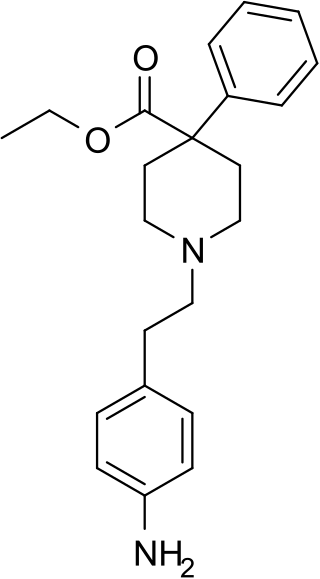
Anileridine is a synthetic analgesic drug and is a member of the piperidine class of analgesic agents developed by Merck & Co. in the 1950s. It differs from pethidine (meperidine) in that the N-methyl group of meperidine is replaced by an N-aminophenethyl group, which increases its analgesic activity.

Phenoperidine, is an opioid analgesic which is structurally related to pethidine and is used clinically as a general anesthetic.

Thebacon, or dihydrocodeinone enol acetate, is a semisynthetic opioid that is similar to hydrocodone and is most commonly synthesised from thebaine. Thebacon was invented in Germany in 1924, four years after the first synthesis of hydrocodone. Thebacon is a derivative of acetyldihydrocodeine, where only the 6–7 double bond is saturated. Thebacon is marketed as its hydrochloride salt under the trade name Acedicon, and as its bitartrate under Diacodin and other trade names. The hydrochloride salt has a free base conversion ratio of 0.846. Other salts used in research and other settings include thebacon's phosphate, hydrobromide, citrate, hydroiodide, and sulfate.

Properidine is an opioid, an analgesic, and the isopropyl analog of pethidine. Properidine is under international control and is listed in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act (1970) as a Schedule I substance. It is a narcotic, with an Administrative Controlled Substances Code Number (ACSCN) of 9644 and a 2 gramme annual aggregate manufacturing quota as of 2014. The salt in use is hydrochloride, with a free base conversion ratio of 0.88.

Benzylmorphine (Peronine) is a semi-synthetic opioid narcotic introduced to the international market in 1896 and that of the United States very shortly thereafter. It is much like codeine, containing a benzyl group attached to the morphine molecule just as the methyl group creates codeine and the ethyl group creates ethylmorphine or dionine. It is about 90% as strong as codeine by weight.

Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the more commonly used pethidine (meperidine). Hydroxypethidine is slightly more potent than meperidine as an analgesic, 1.5x meperidine in potency, and it also has NMDA antagonist properties like its close relative ketobemidone.

Allylprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of prodine. It was discovered by Hoffman-La Roche in 1957 during research into the related drug pethidine. Derivatives were tested to prove the theory that phenolic and non-phenolic opioids bind at different sites of the opiate receptor.

Meprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of pethidine (meperidine). It is closely related to the drug prodine, the only difference being that meprodine has an ethyl group rather than a methyl at the 3-position of the piperidine ring.
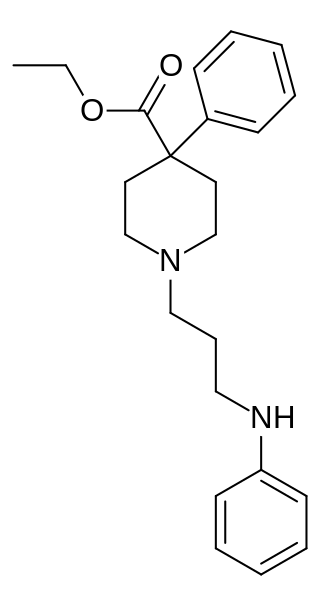
Piminodine (Alvodine) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of pethidine (meperidine). It was used in medicine briefly during the 1960s and 70s, but has largely fallen out of clinical use. It was used particularly for obstetric analgesia and in dental procedures and, like pethidine, could be combined with hydroxyzine to intensify the effects. The duration of action is 2–4 hours; 7.5–10 mg via the subcutaneous route is the most common starting dose, being equal to 80–100 mg of pethidine, 40–60 mg of alphaprodine and 10 mg of morphine. Oral formulations were also available.
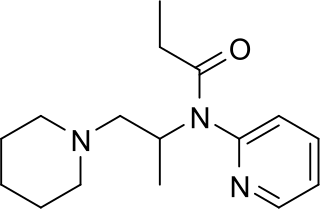
Propiram is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist and weak μ antagonist analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs related to other drugs such as phenampromide and diampromide. It was invented in 1963 in the United Kingdom by Bayer but was not widely marketed, although it saw some limited clinical use, especially in dentistry. Propiram reached Phase III clinical trials in the United States and Canada.

Proheptazine is an opioid analgesic related to pethidine. It was invented in the 1960s.

Norpethidine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is both a precursor to, and the toxic metabolite of, pethidine (meperidine). It is scheduled by UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. It is a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance in the United States and has an ACSCN of 9233. The 2014 annual manufacturing quota was 11 grams (0.39 oz).

Pethidinic acid is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is both a metabolite of and a precursor to pethidine (meperidine). It is scheduled by UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. It is a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance in the United States and has an ACSCN of 9234. The 2014 annual manufacturing quota was 6 grams.

Benzethidine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine.

Etoxeridine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine).
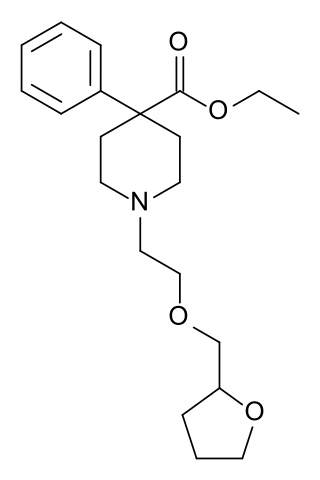
Furethidine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine), but with around 25x higher potency. According to another source, Furethidine is 500/30 = 16.7 x the potency of pethidine.

Morpheridine (Morpholinoethylnorpethidine) is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine). It is a strong analgesic with around 4 times the potency of pethidine, and unlike pethidine, does not cause convulsions, although it produces the standard opioid side effects such as sedation and respiratory depression.

Oxpheneridine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine).

Methadone intermediate is a methadone precursor scheduled by UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. It is a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance in the United States and has an ACSCN of 9254. The 2014 annual manufacturing quota was 32 875 kilos. It is listed as a Schedule I drug in Canada, but is only significant as a precursor for methadone, as it does not have analgesic activity in its own right, though it does show some atropine-like activity.




















