Petroleum engineering is a field of engineering concerned with the activities related to the production of hydrocarbons, which can be either crude oil or natural gas. Exploration and production are deemed to fall within the upstream sector of the oil and gas industry. Exploration, by earth scientists, and petroleum engineering are the oil and gas industry's two main subsurface disciplines, which focus on maximizing economic recovery of hydrocarbons from subsurface reservoirs. Petroleum geology and geophysics focus on provision of a static description of the hydrocarbon reservoir rock, while petroleum engineering focuses on estimation of the recoverable volume of this resource using a detailed understanding of the physical behavior of oil, water and gas within porous rock at very high pressure.

Schlumberger NV, doing business as SLB, also known as Schlumberger Limited, is an American oilfield services company. As of 2022, it is both the world's largest offshore drilling company and the world's largest offshore drilling contractor by revenue.

Hydrocarbon exploration is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology.

Baker Hughes Company is an American energy company based in Houston, Texas. As one of the world's largest oil field services companies, it provides products and services for oil well drilling, formation evaluation, completion, production, reservoir consulting, and tubular running services. It operates in over 120 countries, with research and manufacturing facilities in Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, India, Dubai, Saudi Arabia, Italy, Germany, Norway, Oklahoma, Louisiana and Missouri. From 2017 to 2020, the company was majority owned by General Electric (GE); however, GE no longer owns an economic stake in the company. The company is incorporated in Delaware.

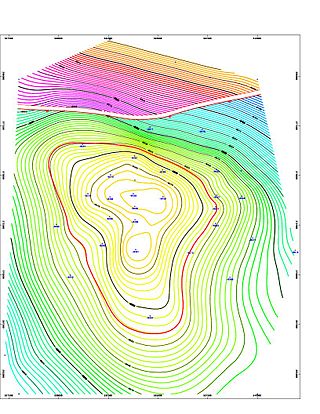
Geologic modelling,geological modelling or geomodelling is the applied science of creating computerized representations of portions of the Earth's crust based on geophysical and geological observations made on and below the Earth surface. A geomodel is the numerical equivalent of a three-dimensional geological map complemented by a description of physical quantities in the domain of interest. Geomodelling is related to the concept of Shared Earth Model; which is a multidisciplinary, interoperable and updatable knowledge base about the subsurface.
Depth conversion is an important step of the seismic reflection method, which converts the acoustic wave travel time to actual depth, based on the acoustic velocity of subsurface medium.
IBM Planning Analytics powered by TM1 is a business performance management software suite designed to implement collaborative planning, budgeting and forecasting solutions, interactive "what-if" analyses, as well as analytical and reporting applications.

A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations. Such reservoirs form when kerogen is created in surrounding rock by the presence of high heat and pressure in the Earth's crust.
Geosteering is the optimal placement of a wellbore based on the results of realtime downhole geological and geophysical logging measurements rather than three-dimensional targets in space. The objective is usually to keep a directional wellbore within a hydrocarbon pay zone defined in terms of its resistivity, density or even biostratigraphy. In mature areas, geosteering may be used to keep a wellbore in a particular reservoir section to minimize gas or water breakthrough and maximize economic production from the well. In the process of drilling a borehole, geosteering is the act of adjusting the borehole position on the fly to reach one or more geological targets. These changes are based on geological information gathered while drilling.
Petrophysics is the study of physical and chemical rock properties and their interactions with fluids.
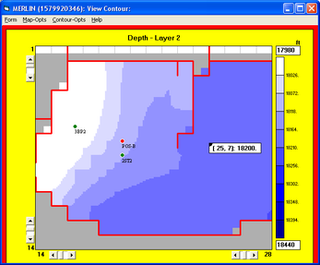
Reservoir simulation is an area of reservoir engineering in which computer models are used to predict the flow of fluids through porous media.

CGG SA (CGG) is a multinational geoscience technology services company that specializes on solving complex natural resource, environmental and infrastructure challenges.

BricsCAD® is a software application for computer-aided design (CAD), developed by Bricsys nv. The company was founded in 2002 by Erik de Keyser, a longtime CAD entrepreneur. In 2011 Bricsys acquired the intellectual property rights from Ledas for constraints-based parametric design tools, permitting the development of applications in the areas of direct modeling and assembly design. Bricsys is headquartered in Ghent, Belgium, and has additional development centers in Nizhny Novgorod and Novosibirsk, Russia; Bucharest, Romania and Singapore. Bricsys is a founding member of the Open Design Alliance, and joined the BuildingSMART International consortium in December 2016.
In geophysics, seismic inversion is the process of transforming seismic reflection data into a quantitative rock-property description of a reservoir. Seismic inversion may be pre- or post-stack, deterministic, random or geostatistical; it typically includes other reservoir measurements such as well logs and cores.

Roxar RMS is a reservoir characterization and modeling software suite. It is primarily designed for use in the oil and gas industry, helping engineers gather data from a wide variety of sources to efficiently build reliable reservoirs.
KNIME, the Konstanz Information Miner, is a free and open-source data analytics, reporting and integration platform. KNIME integrates various components for machine learning and data mining through its modular data pipelining "Building Blocks of Analytics" concept. A graphical user interface and use of JDBC allows assembly of nodes blending different data sources, including preprocessing, for modeling, data analysis and visualization without, or with minimal, programming.

In the oil and gas industry, reservoir modeling involves the construction of a computer model of a petroleum reservoir, for the purposes of improving estimation of reserves and making decisions regarding the development of the field, predicting future production, placing additional wells and evaluating alternative reservoir management scenarios.
In reflection seismology, a seismic attribute is a quantity extracted or derived from seismic data that can be analysed in order to enhance information that might be more subtle in a traditional seismic image, leading to a better geological or geophysical interpretation of the data. Examples of seismic attributes can include measured time, amplitude, frequency and attenuation, in addition to combinations of these. Most seismic attributes are post-stack, but those that use CMP gathers, such as amplitude versus offset (AVO), must be analysed pre-stack. They can be measured along a single seismic trace or across multiple traces within a defined window.

Techlog is a Schlumberger owned Windows based software platform intended to aggregate all the wellbore information. It allows the user to interpret any log and core data. It addresses the need for a single platform able to support all the wellbore data and interpretation integration workflows, reducing the need for a multitude of highly specialized tools. By bringing the whole workflow into a single platform risk and uncertainty can be assessed throughout the life of the wellbore.








