
Abolboda is a genus of flowering plants, traditionally and nowadays assigned to family Xyridaceae. It is native to South America and to the island of Trinidad, generally on marshy savanna.
- Abolboda abbreviataMalme - Pará in Brazil
- Abolboda acaulisMaguire - Venezuela, Guyana
- Abolboda acicularisIdrobo & L.B.Sm. - Venezuela, Colombia
- Abolboda americana(Aubl.) Lanj. - Trinidad & Tobago, Colombia, Venezuela, the Guianas, northern Brazil
- Abolboda bellaMaguire - Cerro Yapacana in Venezuela
- Abolboda ciliataMaguire & Wurdack - Sierra de la Neblina in Venezuela
- Abolboda dunstervilleiMaguire ex Kral - Cerro Avispa in Venezuela
- Abolboda ebracteataMaguire & Wurdack - Venezuela, Colombia
- Abolboda egleriL.B.Sm. & Downs - Venezuela, Colombia, Pará
- Abolboda × glomerataMaguire - Venezuela (A. linearifolia × A. macrostachya)
- Abolboda grandisGriseb. - Venezuela, Colombia, Guyana, Suriname, northwestern Brazil
- Abolboda granularis(Maguire) L.M.Campb. & Kral - Venezuela, Colombia
- Abolboda killipiiLasser - Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, northwestern Brazil
- Abolboda linearifoliaMaguire - State of Amazonas in southern Venezuela
- Abolboda macrostachyaSpruce ex Malme - Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, Brazil
- Abolboda neblinaeMaguire - Sierra de la Neblina in Venezuela, northwestern Brazil
- Abolboda paniculataMaguire - Venezuela, northwestern Brazil
- Abolboda poarchonSeub. - Brazil, Paraguay
- Abolboda pulchellaHumb. & Bonpl. - Venezuela, Colombia, the Guianas, Brazil
- Abolboda scabridaKral - Cerro Aracamuni in Venezuela
- Abolboda spruceiMalme - Colombia, State of Amazonas in southern Venezuela
- Abolboda unifloraMaguire - Cerro Duida in Venezuela

Heliamphora heterodoxa is a species of marsh pitcher plant native to Gran Sabana and the plateau of Ptari Tepui in Venezuela. It was first discovered in 1951 upon Ptari Tepui. This Heliamphora is closely related to H. glabra and the latter was for a long time considered a form of H. heterodoxa. It is one of four Heliamphora taxa formally described by Julian A. Steyermark.

Bonnetia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bonnetiaceae. Most of the roughly 30 species are shrubs. The remaining species, all trees, are among the dominant species in the forest vegetation on the tepui plateaus of northern South America, such as B. roraimae on the summit of Mount Roraima.
Imeria is a genus of South American flowering plants in the sunflower family.
- Imeria memorabilis(Maguire & Wurdack) R.M.King & H.Rob. - Amazonas State in Venezuela, Amazonas State in Brazil
- Imeria serratifoliaV.M.Badillo - Amazonas State in Venezuela
Achnopogon is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, Asteraceae described as a genus in 1957.
Eurydochus is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, Asteraceae.
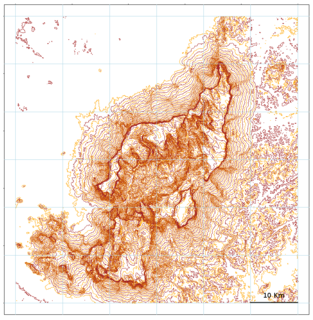
Cerro de la Neblina, also known as Serra da Neblina in Brazil and Sierra de la Neblina in Venezuela, is a sandstone massif located in the northern Amazon Basin. It is a tilted, heavily eroded plateau, with a deep canyon in its central portion, drained by the Baria River.
Achlyphila is a genus of plants in the Xyridaceae, first described as a genus in 1960. It contains only one known species, Achlyphila disticha, endemic to the Serranía de la Neblina National Park in the State of Amazonas in southern Venezuela, very close to the border with Brazil.

Orectanthe is a genus of flowering plants, in the family Xyridaceae, first described as a genus in 1958. It is native to the tepui of northern South America. It is closely related to Abolboda, and both known species were originally classified as members of Abolboda before being transferred to Orectanthe.
- Orectanthe ptaritepuiana (Steyerm.) Maguire - Venezuela, Guyana, northwestern Brazil
- Orectanthe sceptrum (Oliv.) Maguire - Venezuela, Guyana, northwestern Brazil
Pyrrorhiza is a genus of herbs in the family Haemodoraceae, first described as a genus in 1957. It contains only one known species, Pyrrorhiza neblinae, endemic to the Sierra de la Neblina in Amazonas State, Venezuela.
Duckea is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1958.
Guacamaya is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1931.
Schoenocephalium is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1845.
Spathanthus is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1828.
Kunhardtia is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1958.
Marahuacaea is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1984.
Monotrema is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1872.
Potarophytum is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1939.

Stegolepis is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1872.
Bassett Maguire was an American botanist, head curator of the New York Botanical Garden, and a leader of scientific expeditions to the Guyana Highlands in Brazil and Venezuela.






