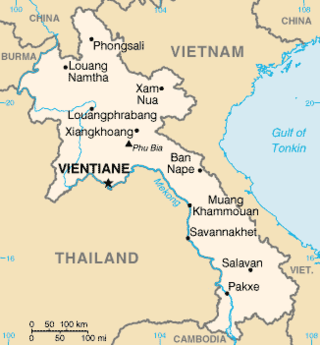
Laos is a country in and the only landlocked nation in mainland Southeast Asia, northeast of Thailand and west of Vietnam. It covers approximately 236,800 square kilometers in the center of the Southeast Asian peninsula and it is surrounded by Myanmar (Burma), Cambodia, the People's Republic of China, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Hin Namno National Park is in Boualapha District, Khammouane Province, Laos. The park borders Phong Nha-Kẻ Bàng National Park of Vietnam to the east and Nakai-Nam Theun National Park of Laos to the north. Hin Namno National Park was created by prime ministerial decree in January 2020. It is managed by the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (MAF).
Nakai-Nam Theun National Park in Nakai District, Khammouane Province, Laos, is one of the last remaining wildernesses in Southeast Asia. Nakai-Nam Theun covers approximately 4,270 km2 of the Annamite Range and the adjacent Nakai Plateau in Khammouane and Bolikhamsai Provinces. It was designated a national park on 15 February 2019 by Prime Ministerial Decree No. 36, 15 February 2019. It is managed by the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (MAF). It is adjacent to the Vu Quang National Park of Vietnam.

The Khao Kho National park is located in Lom Kao, Lom Sak, Khao Kho and Mueang Phetchabun districts in Thailand's Phetchabun province. The national park covers an area of 483 square kilometres (186 sq mi) and was established in 2012.
Nam Et-Phou Louey National Park is a protected area in northern Laos, covering 4,107.1 km2 (1,585.8 sq mi) in three provinces: Houaphan, Luang Prabang, and Xieng Khouang. It was designated a national park in 2019, and was previously designated a national protected area. The protected area included a 3,000 km2 (1,200 sq mi) core area where human access and wildlife harvest is prohibited and a 2,950 km2 buffer area where pre-existing villages are allocated land for subsistence living.
Dong Ampham National Biodiversity Conservation Area is an extensive protected area which covers a significant part of Attapeu Province and Sekong Province in the southeast corner of Laos on the border with Vietnam. It covers the northeastern part of Attapeu Province and southeastern part of Sekong Province.

Bolikhamsai is a province of Laos. Pakxan, Thaphabat, Pakkading, Borikhane, Viengthong, and Khamkeut are its districts and Pakxan is its capital city. The province is the site of the Nam Theun 2 Dam, the country's largest hydroelectric project.

Vientiane province is a province of Laos in the country's northwest. As of 2015 the province had a population of 419,090. Vientiane province covers an area of 15,610 square kilometres (6,030 sq mi) composed of 11 districts. The principal towns are Vang Vieng and Muang Phôn-Hông.

Salavan is a province of Laos, located in the south of the country. Its earlier name was Saravan which was changed by Thai to Salavan in 1828. It was part of the Champasak Kingdom in an area known as Muang Mang inhabited by minorities of Mon-Khmer groups.
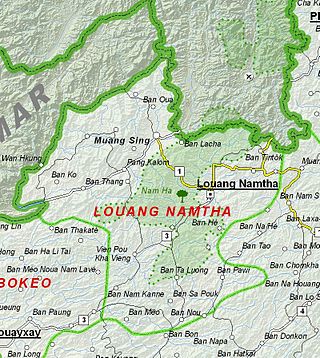
Luang Namtha is a province of Laos in the country's north. From 1966 to 1976 it formed, together with Bokeo, the province of Houakhong. Luang Namtha province covers an area of 9,325 square kilometres (3,600 sq mi). Its provincial capital is Luang Namtha. The province borders Yunnan, China to the north, Oudomxai province to the east and southeast, Bokeo province to the southwest, and Shan State, Myanmar to the northwest.

Vientiane is a prefecture of Laos, in the northwest Laos. The national capital, Vientiane, is in the prefecture. The prefecture was created in 1989, when it was split off from Vientiane province.

Champasak is a province in southwestern Laos, near the borders with Thailand and Cambodia. It is one of the three principalities that succeeded the Lao kingdom of Lan Xang. As of the 2015 census, it had a population of 694,023. The capital is Pakse, but the province takes its name from Champasak, the former capital of the Kingdom of Champasak.

Xaisomboun is a mountainous province in central Laos, between Vientiane province and Xiangkhouang province. The province covers an area of 8,300 square kilometres (3,200 sq mi) and had a population of 85,168 in 2015. Xaisomboun town in Anouvong District is the economic centre. There are extensive copper and gold mining operations nearby at Sana Somboun.

Protected areas in Laos include:

The Phou Khao Khouay leaf-nosed bat is a species of bat found in Laos and Vietnam. It was described as a new species in 2006. It is considered vulnerable to extinction by the IUCN.

The Luang Prabang montane rain forests ecoregion covers elevations over 800 meters in the Luang Prabang mountains that straddle the border between northern Thailand and north-central Laos, and the highlands that stretch eastward across north-central Laos. While much of the forest cover has been degraded, there are still large areas of relatively untouched forest.

The Northern Khorat Plateau moist deciduous forests ecoregion covers a small area on the border between northeastern Thailand and Laos, in the transition zone between the drier Khorat Plateau to the south and the wetter Annamite Range and Luang Prabang Range mountains to the north. Much of the ecoregion has been converted to agriculture along the floodplain of the middle course of the Mekong River.

Ton Sak Yai National Park is a national park in Nam Pat, Tha Pla, Thong Saen Khan and Mueang Uttaradit districts in Uttaradit Province, Thailand, it was formerly known as Khlong Tron National Park.
Phu Pha Daeng Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary in Lom Sak District of Thailand's Phetchabun Province. The sanctuary covers an area of 235 square kilometres (91 sq mi) and was established in 1999.
Phu Khat Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary in Nakhon Thai District of Thailand's Phitsanulok Province. The sanctuary covers an area of 241 square kilometres (93 sq mi) and was established in 2017.

















