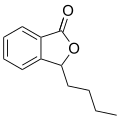
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Benzofuran-1(3H)-one | |
| Other names Phthalolactone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.586 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 134.134 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 75 to 77 °C (167 to 171 °F; 348 to 350 K) [1] |
| Boiling point | 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K) [2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Phthalide is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C8H6O2. It is a white solid and the simplest benzo lactone. It is prepared from hydroxymethylbenzoic acid. [3]