
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships, gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons.

A blimp, or non-rigid airship, is an airship (dirigible) without an internal structural framework or a keel. Unlike semi-rigid and rigid airships, blimps rely on the pressure of the lifting gas inside the envelope and the strength of the envelope itself to maintain their shape.

An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.

Thrust vectoring, also known as thrust vector control (TVC), is the ability of an aircraft, rocket, or other vehicle to manipulate the direction of the thrust from its engine(s) or motor(s) to control the attitude or angular velocity of the vehicle.

An aerostat is a lighter-than-air aircraft that gains its lift through the use of a buoyant gas. Aerostats include unpowered balloons and powered airships. A balloon may be free-flying or tethered. The average density of the craft is lower than the density of atmospheric air, because its main component is one or more gasbags, a lightweight skin containing a lifting gas to provide buoyancy, to which other components such as a gondola containing equipment or people are attached. Especially with airships, the gasbags are often protected by an outer envelope.
The AEREON III was an experimental hybrid airship of rigid construction built by the AEREON Corporation in the early 1960s. Of unconventional design, the airship featured three gas envelopes attached side-by-side, with the connecting structures shaped as airfoils to create extra lift as the craft moved forward. Intended as a small prototype craft that would precede the development of much larger hybrid airships, the AEREON III was constructed between 1959 and 1965 but was destroyed during taxiing tests in 1966 and scrapped without having flown. It was "the first rigid airship to be built since Graf Zeppelin II".

The Piasecki X-49 "SpeedHawk" is an American four-bladed, twin-engined experimental high-speed compound helicopter developed by Piasecki Aircraft. The X-49A is based on the airframe of a Sikorsky YSH-60F Seahawk, but utilizes Piasecki's proprietary vectored thrust ducted propeller (VTDP) design and includes the addition of lifting wings. The concept of the experimental program was to apply the VTDP technology to a production military helicopter to determine any benefit gained through increases in performance or useful load.

A hybrid airship or plimp is a powered aircraft that obtains some of its lift as a lighter-than-air (LTA) airship and some from aerodynamic lift as a heavier-than-air aerodyne.
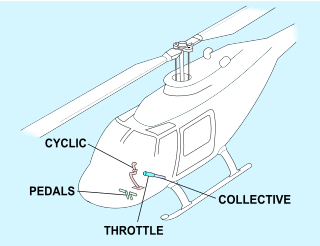
A helicopter pilot manipulates the helicopter flight controls to achieve and maintain controlled aerodynamic flight. Changes to the aircraft flight control system transmit mechanically to the rotor, producing aerodynamic effects on the rotor blades that make the helicopter move in a deliberate way. To tilt forward and back (pitch) or sideways (roll) requires that the controls alter the angle of attack of the main rotor blades cyclically during rotation, creating differing amounts of lift (force) at different points in the cycle. To increase or decrease overall lift requires that the controls alter the angle of attack for all blades collectively by equal amounts at the same time, resulting in ascent, descent, acceleration and deceleration.

The N-Class, or as popularly known, the "Nan ship", was a line of non-rigid airships built by the Goodyear Aircraft Company of Akron, Ohio for the US Navy. This line of airships was developed through many versions and assigned various designators as the airship designation system changed in the post World War II era. These versions included airships configured for both anti-submarine warfare and airborne early warning (AEW) missions.

A thermal airship is an airship that generates buoyancy by heating air in a large chamber or envelope. The lower density of interior hot air compared to cool ambient air causes an upward force on the envelope. This is very similar to a hot air balloon, with the notable exception that an airship has a powered means of propulsion, whilst a hot air balloon relies on winds for navigation. An airship that uses steam would also qualify as a thermal airship.

A quadcopter or quadrotor is a type of helicopter with four rotors.
Worldwide Aeros Corp is an American manufacturer of airships based in Montebello, California. It was founded in 1993 by the current CEO and Chief Engineer, Igor Pasternak, who was born in Soviet Kazakhstan, raised in Soviet Ukraine, and moved to the U.S. after the Soviet collapse to build airships there. It currently employs more than 100 workers.

The SkyHook JHL-40 was a proposed hybrid airship/helicopter. On July 9, 2008, Boeing announced that it had teamed up with SkyHook International, a Canadian company, to develop this aircraft. No further press releases appear after 2009 and Skyhook International has abandoned its domain name registration since 2010 as shown by the Internet Archive.
The static buoyancy of airships in flight is not constant. It is therefore necessary to control the altitude of an airship by controlling its buoyancy: buoyancy compensation.

The Hybrid Air Vehicles Airlander 10, originally developed as the HAV 304, is a hybrid airship designed and built by British manufacturer Hybrid Air Vehicles (HAV). Comprising a helium airship with auxiliary wing and tail surfaces, it flies using both aerostatic and aerodynamic lift and is powered by four diesel engine-driven ducted propellers.

The AeroLift CycloCrane was a unique US hybrid airship which adopted helicopter derived airfoil control for low speed flight manoeuvring by spinning on its axis. It was intended to be a heavy load lifter, initially aimed at the Canadian logging industry. A proof of concept vehicle flew at times during the 1980s, but no large production aircraft were built.

The Sikorsky S-97 Raider is a high-speed scout and attack compound helicopter based on the Advancing Blade Concept (ABC) with a coaxial rotor system under development by Sikorsky Aircraft. Sikorsky planned to offer it for the United States Army's Armed Aerial Scout program, along with other possible uses. The S-97 made its maiden flight on 22 May 2015.

The 2016 Bell 525 Relentless prototype crash occurred during a test flight on July 6, 2016 near Italy, Texas, destroying the prototype Bell 525 Relentless helicopter and killing the two occupants. The helicopter broke up in flight while traveling about 229 mph (199 kn) at an altitude of about 2,000 feet (610 m); the main rotor contacted and severed the tail boom due to severe vertical oscillations. The crew were performing one engine inoperative (OEI) recovery testing; the test induced a scissors-mode vibration in the main rotor, which resulted in involuntary collective control input. The unintended biomechanical feedback loop exacerbated the vibration, until the rotor contacted the tail-boom.

















