
The Pyrenees is a range of mountains in southwest Europe that forms a natural border between Spain and France. Reaching a height of 3,404 metres (11,168 ft) altitude at the peak of Aneto, the range separates the Iberian Peninsula from the rest of continental Europe, and extends for about 491 km (305 mi) from the Bay of Biscay to the Mediterranean Sea.

Mont Blanc, meaning "White Mountain", is the highest mountain in the Alps and the highest in Europe west of Russia's Caucasus peaks. It rises 4,808.7 m (15,777 ft) above sea level and is ranked 11th in the world in topographic prominence. The mountain stands in a range called the Graian Alps, between the regions of Aosta Valley, Italy, and Savoie and Haute-Savoie, France. The location of the summit is on the watershed line between the valleys of Ferret and Veny in Italy and the valleys of Montjoie, and Arve in France, in the middle of what is generally considered to be the border between the two countries.

Col du Tourmalet is the highest paved mountain pass in the French Pyrenees, located in the department of Hautes-Pyrénées. Sainte-Marie-de-Campan is at the foot on the eastern side and the ski station La Mongie two-thirds of the way up. The village of Barèges lies on the western side, above the town of Luz-Saint-Sauveur.

The Piton des Neiges is a massive 3,069 m (10,069 ft) shield volcano on Réunion, one of the French volcanic islands in the Mascarene Archipelago in the southwestern Indian Ocean. It is located about 800 kilometres (500 mi) east of Madagascar. Piton des Neiges is the highest point on Réunion and is considered to be the highest point in the Indian Ocean. The volcano was formed by the Réunion hotspot and emerged from the sea about two million years ago. Now deeply eroded, the volcano has been inactive for 20,000 years and is surrounded by three massive crater valleys, the Cirques. Piton des Neiges forms the northwestern two thirds of Réunion, with the very active Piton de la Fournaise comprising the rest. As it name suggests, snow is occasionally seen on its summit in winter.

The Pic du Midi d'Ossau is a mountain rising above the Ossau Valley in the French Pyrenees. Despite possessing neither a glacier nor, in the context of the range, a particularly high summit, its distinctive shape makes it a symbol of the French side of the Pyrenees. This familiar shape also makes it easily recognisable from afar, and it is particularly distinctive from the Boulevard des Pyrénées in Pau, some 55 km to the north.

The Col d'Aubisque is a mountain pass in the Pyrenees 30 km (19 mi) south of Tarbes and Pau in the department of the Pyrénées-Atlantiques, in the Aquitaine region of France.
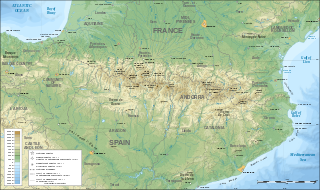
The Balaitús (Spanish) or Pic du Balaïtous (French) is a granitic massif of the Pyrenees, located right on the border between Spain and France.

The Dent de Crolles is a karstic mountain of the Chartreuse Mountains range, 17 kilometres north east of Grenoble, Isère, France. It has a characteristic "tooth-like" profile and is easily recognizable in the Isère Valley (Grésivaudan) in the Grenoble area. Its name is derived from the town of Crolles, located next to the mountain.

The Kröndlhorn is a 2,444 m above sea level (AA) high mountain in the Kitzbühel Alps in Austria. It is one of the highest mountains on the main crest of the Kitzbühel Alps. The state border between Tyrol and Salzburger Land runs over its summit.

Mont Valier is a mountain of the Pyrenees in Ariège, France.

The Grande Tête de l'Obiou is a mountain in the French Prealps belonging to the French department of Isère. It is the highest peak of the Dévoluy Mountains and of the Dauphiné Prealps and the seventh most prominent summit of metropolitan France.

The Hohneck is, at 1,363 m (4,472 ft) the third highest summit of the Vosges Mountains and the highest point of Lorraine. On its summit stands a mountain hut, clearly visible in the distance. Nearby the mountain's top is located the ski resort of La Bresse Hohneck.

The Serre Mourene is a pyrenean summit, located on the Franco-Spanish border between the cirques of Troumouse and Barrosa, culminating at 3,090 m (10,140 ft); it is the second highest summit of the massif de la Munia after the pic de la Munia.

The Casque du Marboré, or Casque de Gavarnie or simply le Casque, is a pyrenean summit, culminating at 3,006 m (9,862 ft), located on the crest of three-thousanders in the Monte Perdido Range above Cirque de Gavarnie on the Franco-Spanish border.

La Pointe Chausenque, culminating at 3,204 m is a summit in the Massif du Vignemale in the French Pyrenees.

Pic du Taillon or Pico Taillón is a summit in the Pyrenees, culminating at 3,144 m (10,315 ft) on the Franco-Spanish border in the Monte Perdido Range.

The Cascade Peaks are three summits in the Monte Perdido Range of the Pyrenees, culminating at 3,161 m (10,371 ft) on the eastern peak. The central peak, known as Brulle, and the western peak are 3,106 m (10,190 ft) and 3,095 m (10,154 ft) high, respectively. The peaks are located on the 3,000 m French-Spanish borderline crest.

Pic de Montcalm is a French pyrenean summit, culminating at 3,077 m (10,095 ft), located in the Ariège department, Midi-Pyrénées region of France.

Le refuge des Sarradets, or refuge de la Brèche de Roland is a mountain refuge in the Pyrenees. It is located in Gavarnie, near la brèche de Roland, in the Pyrenees National Park, at 2,587 m (8,488 ft) high.

The Grande Aiguille Rousse is a mountain peak of the Graian Alps in Savoie, France, situated between the Maurienne and Tarentaise valleys near the Italian border. Reaching an altitude of 3,482 meters, it exceeds its junior to the west, the Petite Aiguille Rousse, by just 50 m (160 ft). Not far from Levanna, the Grande Aiguille Rousse overlooks Serrù Lake and the Gran Paradiso National Park in Italy.


























