
The Piccadilly line is a deep level London Underground line running from the north to the west of London. It has two branches, which split at Acton Town, and serves 53 stations. The line is known for serving Heathrow Airport, and is near popular attractions such as Buckingham Palace. The District and Metropolitan lines share some sections of tracks with the Piccadilly line. Coloured dark blue on the Tube map, it is the fourth-busiest line on the Underground network with over 210 million passenger journeys in 2011/12.

Charing Cross is a London Underground station at Charing Cross in the City of Westminster. The station is served by the Bakerloo and Northern lines and provides an interchange with Charing Cross mainline station. On the Bakerloo line it is between Embankment and Piccadilly Circus stations and on the Northern line it is between Embankment and Leicester Square stations. The station is in fare zone 1.

Aldwych is a closed station on the London Underground, located in the City of Westminster in Central London. It was opened in 1907 with the name Strand, after the street on which it is located, and was the terminus of the short Piccadilly line branch from Holborn that was a relic of the merger of two railway schemes. The station building is close to the Strand's junction with Surrey Street, near Aldwych. During its lifetime, the branch was the subject of a number of unrealised extension proposals that would have seen the tunnels through the station extended southwards, usually to Waterloo.

Holborn is a London Underground station in Holborn, Central London, located at the junction of High Holborn and Kingsway. It is served by the Central and Piccadilly lines. On the Central line the station is between Tottenham Court Road and Chancery Lane stations; on the Piccadilly line it is between Covent Garden and Russell Square and is in Travelcard Zone 1. Close by are the British Museum, Lincoln's Inn Fields, Red Lion Square, Bloomsbury Square, London School of Economics and Sir John Soane's Museum.

Green Park is a London Underground station located on the edge of Green Park, with entrances on both sides of Piccadilly. It is served by the Jubilee, Piccadilly and Victoria lines. On the Jubilee line it is between Bond Street and Westminster; on the Piccadilly line it is between Piccadilly Circus and Hyde Park Corner and on the Victoria line it is between Victoria and Oxford Circus. It is in fare zone 1.

South Kensington is a London Underground station in the district of South Kensington, south west London. It is served by the District, Circle and Piccadilly lines. On the District and Circle lines, the station is between Gloucester Road and Sloane Square, and on the Piccadilly line, it is between Gloucester Road and Knightsbridge. It is in Travelcard Zone 1. The main station entrance is located at the junction of Old Brompton Road (A3218), Thurloe Place, Harrington Road, Onslow Place and Pelham Street. Subsidiary entrances are located in Exhibition Road giving access by pedestrian tunnel to the Natural History, Science and Victoria and Albert Museums. Also close by are the Royal Albert Hall, Imperial College London, the Royal College of Music, the London branch of the Goethe-Institut and the Ismaili Centre.

Covent Garden is a London Underground station serving Covent Garden and the surrounding area in the West End of London. It is on the Piccadilly line between Leicester Square and Holborn stations and is in Travelcard Zone 1. The station is at the corner of Long Acre and James Street and the street-level concourse is a Grade II listed building.

Gloucester Road is a London Underground station in Kensington, west London. The station entrance is located close to the junction of Gloucester Road and Cromwell Road. Close by are the Cromwell Hospital and Baden-Powell House.

The City and South London Railway (C&SLR) was the first deep-level underground "tube" railway in the world, and the first major railway to use electric traction. The railway was originally intended for cable-hauled trains, but owing to the bankruptcy of the cable contractor during construction, a system of electric traction using electric locomotives—an experimental technology at the time—was chosen instead.

The Metropolitan District Railway was a passenger railway that served London from 1868 to 1933. Established in 1864 to complete the inner circle, an underground railway in London, the first part of the line opened using gas-lit wooden carriages hauled by steam locomotives. The Metropolitan Railway operated all services until the District introduced its own trains in 1871. The railway was soon extended westwards through Earl's Court to Fulham, Richmond, Ealing and Hounslow. After completing the inner circle and reaching Whitechapel in 1884, it was extended to Upminster in Essex in 1902.
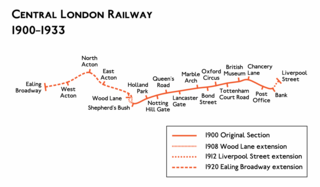
The Central London Railway (CLR), also known as the Twopenny Tube, was a deep-level, underground "tube" railway that opened in London in 1900. The CLR's tunnels and stations form the central section of the London Underground's Central line.

The history of the London Underground began in the 19th century with the construction of the Metropolitan Railway, the world's first underground railway. The Metropolitan Railway, which opened in 1863 using gas-lit wooden carriages hauled by steam locomotives, worked with the District Railway to complete London's Circle line in 1884. Both railways expanded, the Metropolitan eventually extending as far as Verney Junction in Buckinghamshire, more than 50 miles (80 km) from Baker Street and the centre of London. The first deep-level tube line, the City and South London Railway, opened in 1890 with electric trains. This was followed by the Waterloo & City Railway in 1898, the Central London Railway in 1900, and the Great Northern and City Railway in 1904. The Underground Electric Railways Company of London (UERL) was established in 1902 to fund the electrification of the District Railway and to complete and operate three tube lines, the Baker Street and Waterloo Railway, the Charing Cross, Euston and Hampstead Railway and the Great Northern, Piccadilly and Brompton Railway, which opened in 1906–07. By 1907 the District and Metropolitan Railways had electrified the underground sections of their lines.

Hornsey railway station is in Hornsey in the London Borough of Haringey, north London. It is on the Great Northern Route that forms part of the East Coast Main Line, 4 miles 4 chains (6.5 km) down the line from London King's Cross, and is situated between Harringay to the south and Alexandra Palace to the north.

The Charing Cross, Euston and Hampstead Railway (CCE&HR), also known as the Hampstead Tube, was a railway company established in 1891 that constructed a deep-level underground "tube" railway in London. Construction of the CCE&HR was delayed for more than a decade while funding was sought. In 1900 it became a subsidiary of the Underground Electric Railways Company of London (UERL), controlled by American financier Charles Yerkes. The UERL quickly raised the funds, mainly from foreign investors. Various routes were planned, but a number of these were rejected by Parliament. Plans for tunnels under Hampstead Heath were authorised, despite opposition by many local residents who believed they would damage the ecology of the Heath.

The Great Northern, Piccadilly and Brompton Railway (GNP&BR), also known as the Piccadilly tube, was a railway company established in 1902 that constructed a deep-level underground "tube" railway in London. The GNP&BR was formed through a merger of two older companies, the Brompton and Piccadilly Circus Railway (B&PCR) and the Great Northern and Strand Railway (GN&SR). It also incorporated part of a tube route planned by a third company, the District Railway (DR). The combined company was a subsidiary of the Underground Electric Railways Company of London (UERL).

The Baker Street and Waterloo Railway (BS&WR), also known as the Bakerloo tube, was a railway company established in 1893 that built a deep-level underground "tube" railway in London. The company struggled to fund the work, and construction did not begin until 1898. In 1900, work was hit by the financial collapse of its parent company, the London & Globe Finance Corporation, through the fraud of Whitaker Wright, its main shareholder. In 1902, the BS&WR became a subsidiary of the Underground Electric Railways Company of London (UERL) controlled by American financier Charles Yerkes. The UERL quickly raised the funds, mainly from foreign investors.

Sir Edgar Speyer, 1st Baronet was an American-born financier and philanthropist. He became a British subject in 1892 and was chairman of Speyer Brothers, the British branch of the Speyer family's international finance house, and a partner in the German and American branches. He was chairman of the Underground Electric Railways Company of London from 1906 to 1915, a period during which the company opened three underground railway lines, electrified a fourth and took over two more.
The transport system now known as the London Underground began in 1863 with the Metropolitan Railway, the world's first underground railway. Over the next forty years, the early sub-surface lines reached out from the urban centre of the capital into the surrounding rural margins, leading to the development of new commuter suburbs. At the turn of the nineteenth century, new technology—including electric locomotives and improvements to the tunnelling shield—enabled new companies to construct a series of "tube" lines deeper underground. Initially rivals, the tube railway companies began to co-operate in advertising and through shared branding, eventually consolidating under the single ownership of the Underground Electric Railways Company of London (UERL), with lines stretching across London.
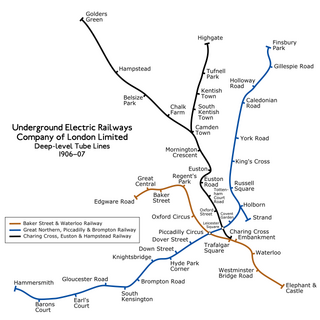
The Underground Electric Railways Company of London Limited (UERL), known operationally as the Underground for much of its existence, was established in 1902. It was the holding company for the three deep-level "tube" underground railway lines opened in London during 1906 and 1907: the Baker Street and Waterloo Railway, the Charing Cross, Euston and Hampstead Railway and the Great Northern, Piccadilly and Brompton Railway. It was also the parent company from 1902 of the District Railway, which it electrified between 1903 and 1905. The UERL is a precursor of today's London Underground; its three tube lines form the central sections of today's Bakerloo, Northern and Piccadilly lines.

The Royal Commission on London Traffic was a Royal commission established in 1903 with a remit to review and report on how transport systems should be developed for London and the surrounding area. It produced a report in eight volumes published in 1905 and made recommendations on the character, administration and routing of traffic in London.


















