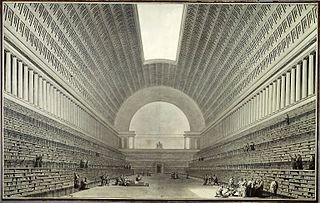
Étienne-Louis Boullée was a visionary French neoclassical architect whose work greatly influenced contemporary architects.

Jacques-François Blondel was an 18th-century French architect and teacher. After running his own highly successful school of architecture for many years, he was appointed Professor of Architecture at the Académie Royale d'Architecture in 1762, and his Cours d'architecture largely superseded a similarly titled book published in 1675 by his famous namesake, François Blondel, who had occupied the same post in the late 17th century.

(Pierre Louis) Philippe de La Guêpière was an 18th-century French architect whose main commissions were from Karl Eugen, Duke of Württemberg.

Pierre Contant d'Ivry, was a French architect and designer working in a chaste and sober Rococo style and in the goût grec phase of early Neoclassicism.

François Blondel was a soldier, engineer of fortifications, mathematician, diplomat, military and civil engineer and architect, called "the Great Blondel", to distinguish him in a dynasty of French architects. He is remembered for his Cours d'architecture which remained a central text for over a century. His precepts placed him in opposition with Claude Perrault in the larger culture war known under the heading Querelle des anciens et des modernes. If François Blondel was not the most highly reputed among the académiciens of his day, his were the writings that most generally circulated among the general public, the Cours de Mathématiques, the Art de jetter les Bombes, the Nouvelle manière de fortifier les places and, above all his Cours d'Architecture.

The Académie Royale d'Architecture was a French learned society founded in 1671. It had a leading role in influencing architectural theory and education, not only in France, but throughout Europe and the Americas from the late 17th century to the mid-20th.

Germain Boffrand was a French architect. A pupil of Jules Hardouin-Mansart, Germain Boffrand was one of the main creators of the precursor to Rococo called the style Régence, and in his interiors, of the Rococo itself. In his exteriors he held to a monumental Late Baroque classicism with some innovations in spatial planning that were exceptional in France. His major commissions, culminating in his interiors at the Hôtel de Soubise, were memorialised in his treatise Livre d'architecture, published in 1745, which served to disseminate the French Louis XV style throughout Europe.

Paul Sédille was a French architect and theorist; and designed the 1880 reconstruction of the iconic Magasins du Printemps department store in Paris.

The Salon d'Hercule is on the first floor of the Château de Versailles and connects the Royal Chapel in the North Wing of the château with the grand appartement du roi.

Marie-Joseph Peyre was a French architect who designed in the Neoclassical style.

The Cité de l'architecture et du patrimoine is a museum of architecture and monumental sculpture located in the Palais de Chaillot (Trocadéro), in Paris, France. Its permanent collection is also known as Musée national des monuments français. It was established in 1879 by Eugène Viollet-le-Duc. The museum was renovated in 2007 and covers 9,000 square meters of gallery space. As a whole, the Cité de l'architecture et du patrimoine spreads across 22,000 square meters, which makes it the largest museum devoted to architecture in the world, even surpassing the Design Museum of London.

Architecture terrible was an architectural style advocated by French architect Jacques-François Blondel in his nine-volume treatise Cours d'architecture (1771–77). Blondel promoted the style for the exterior design of prisons: the form of the building itself would proclaim its function and serve as a deterrent, and so achieve a "repulsive style" of heaviness that would "declare to the spectators outside the confused lives of those detained inside, along with the force required for those in charge to hold them confined". Blondel further described it as "...a style where the principles of art seem to be crushed under the weight of the Artist's ignorance".

Jean-François de Neufforge was an architect and engraver, known for his Recueil elementaire d'architecture, a book of architectural engravings. He was born in the Holy Roman Empire.
Charles Hubert Rohault de Fleury was a French architect who was responsible for many public buildings in Paris in the first half of the 19th century.

The French Château de Chaumont-la-Guiche [or -Laguiche], located in Saint-Bonnet-de-Joux (Saône-et-Loire), in a region formerly known as Charolais in southern Burgundy, was constructed beginning in 1500 for the La Guiche family. The most famous feature of the château is the monumental 17th-century stable block, designed by the noted French architect, François Blondel.
Jacques-Guillaume Legrand was a French architect and critic.

Neoclassicism is a movement in architecture, design and the arts which emerged in France in the 1740s and became dominant in France between about 1760 to 1830. It emerged as a reaction to the frivolity and excessive ornament of the baroque and rococo styles. In architecture it featured sobriety, straight lines, and forms, such as the pediment and colonnade, based on Ancient Greek and Roman models. In painting it featured heroism and sacrifice in the time of the ancient Romans and Greeks. It began late in the reign of Louis XV, became dominant under Louis XVI, and continued through the French Revolution, the French Directory, and the reign of Napoleon Bonaparte, and the Bourbon Restoration until 1830, when it was gradually replaced as the dominant style by romanticism and eclecticism.

Augustin-Charles d'Aviler was a 17th-century French architect. He was one of the main promoters of the vignolesc canon, but far from simply publishing it, he developed it by proposing variations of motifs to give more flexibility and expressiveness to the rigid system of the five orders.

The Château de Chanteloup was an imposing 18th-century French château with elaborate gardens, compared by some contemporaries to Versailles. It was located in the Loire Valley on the south bank of the river Loire, downstream from the town of Amboise and about 2.3 kilometres (1.4 mi) southwest of the royal Château d'Amboise. From 1761 to 1785 Chanteloup belonged to King Louis XV's prime minister, the Duke of Choiseul. The château was mostly demolished in 1823, but some features of the park remain, notably the Pagoda of Chanteloup, a significant tourist attraction.

César Denis Daly was a French architect, publisher, and writer. He was one of the most important figures in the architectural press in nineteenth-century France, whose role as owner and editor of the famed periodical the Revue générale de l'architecture et des travaux publics shaped several generations of architects in France and beyond.


















