
Pima County is a county in the south central region of the U.S. state of Arizona. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,043,433, making it Arizona's second-most populous county. The county seat is Tucson, where most of the population is centered. The county is named after the Pima Native Americans who are indigenous to this area.

The following is a list of public holidays in Romania. According to Romanian law, Romania had 51 public holidays as of 2011, which cover 14% of the days of the year in the country.
Oʼodham or Papago-Pima is a Uto-Aztecan language of southern Arizona and northern Sonora, Mexico, where the Tohono Oʼodham and Akimel Oʼodham reside. In 2000 there were estimated to be approximately 9,750 speakers in the United States and Mexico combined, although there may be more due to underreporting.

The Pima are a group of Native Americans living in an area consisting of what is now central and southern Arizona, as well as northwestern Mexico in the states of Sonora and Chihuahua. The majority population of the two current bands of the Akimel O'odham in the United States are based in two reservations: the Keli Akimel Oʼodham on the Gila River Indian Community (GRIC) and the On'k Akimel O'odham on the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community (SRPMIC).

The Maricopa or Piipaash are a Native American tribe, who live in the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community and Gila River Indian Community along with the Pima, a tribe with whom the Maricopa have long held a positive relationship. The Maricopa at the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community consist mostly of Xalychidom Piipaash members and are concentrated in Lehi. The Maricopa at the Gila River Indian Community are concentrated in Maricopa Colony. The Maricopa are a River Yuman group, formerly living along the banks of the Colorado River.

The Pima Air & Space Museum, located in Tucson, Arizona, is one of the world's largest non-government funded aerospace museums. The museum features a display of nearly 300 aircraft spread out over 80 acres (320,000 m²) on a campus occupying 127 acres (513,000 m²). It has also been the home to the Arizona Aviation Hall of Fame since 1991.

Grêmio Esportivo Novorizontino, usually known simply as Novorizontino was a Brazilian football club from Novo Horizonte, São Paulo state.

The Salt River Pima–Maricopa Indian Community comprises two distinct Native American tribes—the Pima and the Maricopa —many of whom were originally of the Halchidhoma (Xalchidom) tribe. The community was officially created by an Executive Order of US President Rutherford B. Hayes on June 14, 1879. The community area includes 53,600 acres (217 km2), of which 19,000 remain a natural preserve. As of 2022, the total population is 7,386. The community is a federally recognized tribe located in Arizona.
Pima Bajo is a Mexican indigenous language of the Piman branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family, spoken by around 1,000 speakers in northern Mexico. The language is called O'ob No'ok by its speakers. The closest related languages are O'odham and the O'othams.

The Zacatecan deer mouse or southern rock mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found only in Mexico, and is not considered endangered.
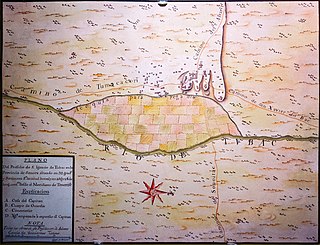
The Pima Revolt, also known as the O'odham Uprising or the Pima Outbreak, was a revolt of Pima native Americans in 1751 against colonial forces in Spanish Arizona and one of the major northern frontier conflicts in early New Spain.

Technomyrmex albipes, commonly known as the white-footed ant, is a species of ant first described in 1861 from Sulawesi, Indonesia by the British entomologist Frederick Smith. Invasive pest ants in Florida, previously identified as T. albipes, have now been separated as Technomyrmex difficilis, both forming part of a species complex with a worldwide distribution.
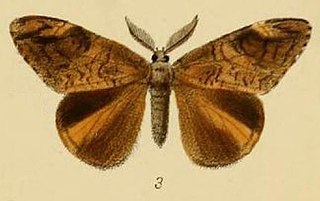
Aroa is a genus of moths in the subfamily Lymantriinae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. Species are distributed in South Africa, China, throughout India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and Java.

The Pima Bajo people are indigenous people of Mexico who reside in a mountainous region along the line between the states of Chihuahua and Sonora in northern Mexico. They are related to the Pima and Tohono O’odham of Arizona and northern Sonora, speaking a similar but distinct language.

Pima is a genus of snout moths described by George Duryea Hulst in 1888.
Pima flavidorsella is a species of snout moth. It lives in Mozambique.
Epicampoptera is a genus of moths in the family Drepanidae. The genus was first described by Felix Bryk in 1913.
Stomopteryx difficilis is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It was described by Anthonie Johannes Theodorus Janse in 1951. It is found in South Africa.
Pan Tak is a populated place situated in Pima County, Arizona, United States. Throughout its existence, it has been known by a number of names, including Cajote Spring, Coyote, Coyote Indian Village, Coyote Spring, Coyote Village, Coyotes Spring, Ojo de los Coyotes, and Pantak. Pan Tak become the official name as a result of a Board on Geographic Names decision in 1941. The name comes from the O'odham, meaning "coyote sits". It has an estimated elevation of 3,412 feet (1,040 m) above sea level.
San Luis is a populated place situated in Pima County, Arizona, United States. It is one of two locations in Pima County with this name. It has an estimated elevation of 1,795 feet (547 m) above sea level.












