
Benzoic acid is a white solid organic compound with the formula C6H5COOH, whose structure consists of a benzene ring with a carboxyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only source.

Piper, the pepper plants or pepper vines, is an economically and ecologically important genus in the family Piperaceae.

Humulus, hop, is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The hop is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Hops are the female flowers of the hop species H. lupulus; as a main flavor and aroma ingredient in many beer styles, H. lupulus is widely cultivated for use by the brewing industry.

Black pepper is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, known as a peppercorn, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about 5 mm (0.20 in) in diameter, dark red, and contains a stone which encloses a single pepper seed. Peppercorns and the ground pepper derived from them may be described simply as pepper, or more precisely as black pepper, green pepper, or white pepper.

The Piperaceae, also known as the pepper family, are a large family of flowering plants. The group contains roughly 3,600 currently accepted species in 5 genera. The vast majority of species can be found within the two main genera: Piper and Peperomia.

Sodium benzoate is the sodium salt of benzoic acid, widely used as a food preservative (with an E number of E211) and a pickling agent. It appears as a white crystalline chemical with the formula C6H5COONa.

Capsicum pubescens is a plant of the genus Capsicum (pepper). The species name, pubescens, refers to the hairy leaves of this pepper. The hairiness of the leaves, along with the black seeds, make Capsicum pubescens distinguishable from other Capsicum species. Capsicum pubescens has pungent yellow, orange, red, green or brown fruits.
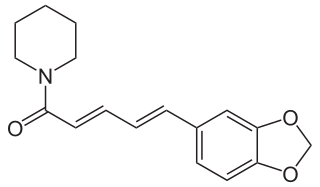
Piperine, along with its isomer chavicine, is the alkaloid responsible for the pungency of black pepper and long pepper. It has been used in some forms of traditional medicine.

Styrax is a genus of about 130 species of large shrubs or small trees in the family Styracaceae, mostly native to warm temperate to tropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere, with the majority in eastern and southeastern Asia, but also crossing the equator in South America. The resin obtained from the tree is called benzoin or storax.

Ilex guayusa is a species of tree of the holly genus, native to the Amazon Rainforest. One of four known caffeinated holly trees, the leaves of the guayusa tree are harvested fresh and brewed like a tea for their stimulative effects.

Desmoncus is a genus of mostly climbing, spiny palms native to the Neotropics. The genus extends from Mexico in the north to Brazil and Bolivia in the south, with two species present in the southeastern Caribbean.

Trichoderma is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae that is present in all soils, where they are the most prevalent culturable fungi. Many species in this genus can be characterized as opportunistic avirulent plant symbionts. This refers to the ability of several Trichoderma species to form mutualistic endophytic relationships with several plant species. The genomes of several Trichoderma specieshave been sequenced and are publicly available from the JGI.

Roupala is a Neotropical genus of woody shrubs and trees in the plant family Proteaceae. Its 34 species are generally found in forests from sea level to 4000 m altitude from Mexico to Argentina.

Naupactus is a genus of beetles in the weevil family Curculionidae, the true weevils. They are known commonly as whitefringed beetles. Many species of the genus are considered pests, both as larvae and as adults. The genus is native to the Americas, where it is distributed from Mexico to Argentina; the highest species diversity is in Brazil. Several species have been introduced to the United States and New Zealand.

Prenylated flavonoids or prenylflavonoids are a sub-class of flavonoids. They are widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom. Some are known to have phytoestrogenic or antioxidant properties. They are given in the list of adaptogens in herbalism. Chemically they have a prenyl group attached to their flavonoid backbone. It is usually assumed that the addition of hydrophobic prenyl groups facilitate attachment to cell membranes. Prenylation may increase the potential activity of its original flavonoid.

Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function. Two important naturally occurring types of phenolic acids are hydroxybenzoic acids and hydroxycinnamic acids, which are derived from non-phenolic molecules of benzoic and cinnamic acid, respectively.
PhytoKeys is a peer-reviewed, open-access online and print botanical journal. Its stated goal is "to support free exchange of ideas and information in systematic botany".
Short chain ω-phenylalkanoic acids have long been known to occur in natural products. Phenylacetic, 3-phenylpropanoic and 3-phenylpropenoic (cinnamic) acids are found in propolis, mammalian exocrine secretions or plant fragrances. During a systematic study of the lipids from seeds of the plant Araceae, the presence of 13-phenyltridecanoic acid as a major component was discovered. Other similar compounds but with 11 and 15 carbon chain lengths and saturated or unsaturated were shown to be also present but in lower amounts. At the same time, the even carbon chain ω-phenylalkanoic acids of C10 up to C16 were discovered in halophilic bacteria.

Capsicum rhomboideum is a perennial member of the genus Capsicum with 2n=2x=26, and is considered a distant wild relative of the chili pepper. Its fruit do not have any pungency, and are a 0 on the Scoville Heat Unit scale. It gets its name from the rhomboidal to elliptical shape of its leaves. It is native to Mexico, Central America, and Andean region of South America.

Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is a cannabinoid found in cannabis plants. It is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers or more accurately infructescence often colloquially referred to as buds. CBDA is the chemical precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). Through the process of decarboxylation cannabidol is derived via a loss of a carbon and two oxygen atoms from the 1 position of the benzoic acid ring. Cannabinoids are a class of compounds that are essentially unique to the cannabis genus. Both marijuana and hemp belong to this genus.

















