Related Research Articles

Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.

Geckos are small lizards belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, found in warm climates throughout the world. They range from 1.6 to 60 cm.

Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are a component of blood whose function is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm that are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow, which then enter the circulation. Circulating unactivated platelets are biconvex discoid (lens-shaped) structures, 2–3 µm in greatest diameter. Activated platelets have cell membrane projections covering their surface. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates, thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells.

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another.

A label is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling.

Synthetic setae emulate the setae found on the toes of a gecko and scientific research in this area is driven towards the development of dry adhesives. Geckos have no difficulty mastering vertical walls and are apparently capable of adhering themselves to just about any surface. The five-toed feet of a gecko are covered with elastic hairs called setae and the ends of these hairs are split into nanoscale structures called spatulae. The sheer abundance and proximity to the surface of these spatulae make it sufficient for van der Waals forces alone to provide the required adhesive strength. Following the discovery of the gecko's adhesion mechanism in 2002, which is based on van der Waals forces, biomimetic adhesives have become the topic of a major research effort. These developments are poised to yield families of novel adhesive materials with superior properties which are likely to find uses in industries ranging from defense and nanotechnology to healthcare and sport.

Hot melt adhesive (HMA), also known as hot glue, is a form of thermoplastic adhesive that is commonly sold as solid cylindrical sticks of various diameters designed to be applied using a hot glue gun. The gun uses a continuous-duty heating element to melt the plastic glue, which the user pushes through the gun either with a mechanical trigger mechanism on the gun, or with direct finger pressure. The glue squeezed out of the heated nozzle is initially hot enough to burn and even blister skin. The glue is sticky when hot, and solidifies in a few seconds to one minute. Hot melt adhesives can also be applied by dipping or spraying, and are popular with hobbyists and crafters both for affixing and as an inexpensive alternative to resin casting.

Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1) also known as cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PECAM1 gene found on chromosome17q23.3. PECAM-1 plays a key role in removing aged neutrophils from the body.

P-selectin is a type-1 transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the SELP gene.

Pressure-sensitive adhesive is a type of non reactive adhesive which forms a bond when pressure is applied to bond the adhesive with a surface. No solvent, water, or heat is needed to activate the adhesive. It is used in pressure-sensitive tapes, labels, glue dots, note pads, automobile trim, and a wide variety of other products.

Adhesions are fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery. They may be thought of as internal scar tissue that connects tissues not normally connected.

Leukocyte extravasation is the movement of leukocytes out of the circulatory system and towards the site of tissue damage or infection. This process forms part of the innate immune response, involving the recruitment of non-specific leukocytes. Monocytes also use this process in the absence of infection or tissue damage during their development into macrophages.
Platelet membrane glycoproteins are surface glycoproteins found on platelets (thrombocytes) which play a key role in hemostasis. When the blood vessel wall is damaged, platelet membrane glycoproteins interact with the extracellular matrix.
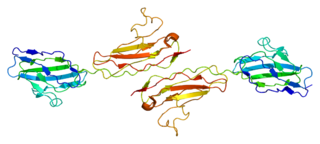
Junctional adhesion molecule A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the F11R gene. It has also been designated as CD321.

Glycoprotein Ib (platelet), beta polypeptide (GP1BB) also known as CD42c, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP1BB gene.

Glycoprotein V (platelet) (GP5) also known as CD42d, is a human gene.

Dispersive adhesion, also called adsorptive adhesion, is a mechanism for adhesion which attributes attractive forces between two materials to intermolecular interactions between molecules of each material. This mechanism is widely viewed as the most important of the five mechanisms of adhesion due to its presence in every type of adhesive system and its relative strength.

Pressure-sensitive tape, known also in various countries as PSA tape, adhesive tape, self-stick tape, sticky tape, Sellotape, or just tape, is an adhesive tape that will stick with application of pressure, without the need for a solvent or heat for activation. It can be used in the home, office, industry, and institutions for a wide variety of purposes.
The platelet plug, also known as the hemostatic plug or platelet thrombus, is an aggregation of platelets formed during the earlier stage of hemostasis in response to blood vessel wall injury. After platelets are recruited and begin to accumulate around the breakage, their “sticky” nature allows them to adhere to each other. This forms a platelet plug, which prevents more blood from leaving the body as well as any outside contaminants from getting in. The plug provides a temporary blockage of the break in the vasculature. As such, platelet plug formation occurs after vasoconstriction of the blood vessels but before the creation of the fibrin mesh clot, which is the more permanent solution to the injury. The result of the platelet plug formation is the coagulation of blood. It can also be referred to as primary hemostasis.
Adhesive bonding is a joining technique used in the manufacture and repair of a wide range of products. Along with welding and soldering, adhesive bonding is one of the basic joining processes. In this technique, components are bonded together using adhesives. The broad range of types of adhesives available allows numerous materials to be bonded together in products as diverse as vehicles, mobile phones, personal care products, buildings, computers and medical devices.
References
- ↑ Platelet+adhesiveness at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)