
The Bahamas, known officially as the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is a country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 700 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and Hispaniola Island, northwest of the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the US state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically it has sometimes been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase it comes from the old meaning of "wealth", which is "well-being", and is itself a loose translation of the Latin res publica (republic). The term literally meant "common well-being". In the 17th century, the definition of "commonwealth" expanded from its original sense of "public welfare" or "commonweal" to mean "a state in which the supreme power is vested in the people; a republic or democratic state".
The Pledge of Allegiance of the United States is an expression of allegiance to the flag of the United States and the republic of the United States of America. Such a pledge was first composed, with a text different from the one used at present, by Captain George Thatcher Balch, a Union Army Officer during the Civil War and later a teacher of patriotism in New York City schools. The form of the pledge used today was largely devised by Francis Bellamy in 1892, and formally adopted by Congress as the pledge in 1942. The official name of The Pledge of Allegiance was adopted in 1945. The most recent alteration of its wording came on Flag Day in 1954, when the words "under God" were added.

Francis Julius Bellamy (1855–1931) was an American Christian socialist minister and author, best known for writing the original version of the US Pledge of Allegiance in 1892.
The Irish Oath of Allegiance was a controversial provision in the Anglo-Irish Treaty of 1921, which Irish TDs and Senators were required to swear before taking their seats in Dáil Éireann and Seanad Éireann before the 'Constitution Act 1933' was passed on 3 May 1933. The controversy surrounding the Oath was one of the principal issues that led to the Irish Civil War of 1922–23 between supporters and opponents of the Treaty.

"March On, Bahamaland" is the national anthem of The Bahamas. Timothy Gibson composed the music and authored the lyrics. This was adopted as the national anthem in 1973, when the country gained independence from the United Kingdom. The previous anthem, "God Save the Queen", has been retained as the royal anthem.

An oath of allegiance is an oath whereby a subject or citizen acknowledges a duty of allegiance and swears loyalty to monarch or country. In republics, modern oaths are sworn to the country in general, or to the country's constitution. For example, officials in the United States, a republic, take an oath of office that includes swearing allegiance to the United States Constitution. However, typically in a constitutional monarchy, such as in the United Kingdom, Australia and other Commonwealth realms, oaths are sworn to the monarch. Armed forces typically require a military oath.

The Bellamy salute is a palm-out salute described by Francis Bellamy, the author of the American Pledge of Allegiance, as the gesture which was to accompany the pledge. During the period when it was used with the Pledge of Allegiance, it was sometimes known as the "flag salute". Both the Pledge and its salute originated in 1892. Later, during the 1920s and 1930s, Italian fascists and Nazi Germans adopted a salute which was very similar, and which was derived from the Roman salute, a gesture that was popularly believed to have been used in ancient Rome. This resulted in controversy over the use of the Bellamy salute in the United States. It was officially replaced by the hand-over-heart salute when Congress amended the Flag Code on December 22, 1942.

The flag of the Commonwealth of Kentucky, United States, was adopted on March 26, 1918.

Local government in the Bahamas exists in two forms, namely second-schedule and third-schedule district councils. There are a total of 32 local government districts: 13 second-schedule districts, which are further sub-divided into town areas, and 19 third-schedule districts, which are all unitary authorities. The second and third schedules together make up the first schedule. Local government policy is formulated and administered by the Department of Lands and Local Government through the Office of the Prime Minister. The day-to-day policy handling of the portfolio falls to the Minister of Local Government who also is empowered to create new local government areas from time to time based on demographics. The administrative and financial management is overseen by the ministry’s permanent secretary.
The Government of New South Wales, known most often as the NSW Government, is the Australian state democratic administrative authority of New South Wales. It is currently held by a coalition of the Liberal Party and the National Party. The Government of New South Wales, a parliamentary constitutional monarchy, was formed in 1856 as prescribed in its Constitution, as amended from time to time. Since the Federation of Australia in 1901, New South Wales has been a state of the Commonwealth of Australia, and the Constitution of Australia regulates its relationship with the Commonwealth. Under the Australian Constitution, New South Wales, as with all states, ceded legislative and judicial supremacy to the Commonwealth, but retained powers in all matters not in conflict with the Commonwealth.

The Parliament of The Bahamas is the bicameral national parliament of Commonwealth of The Bahamas. The parliament is formally made up of the Queen, an appointed Senate, and an elected House of Assembly. It currently sits at Nassau, the national capital.

Bayʿah, in Islamic terminology, is an oath of allegiance to a leader. It is known to have been practiced by the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Bayʿah is sometimes taken under a written pact given on behalf of the subjects by leading members of the tribe with the understanding that as long as the leader abides by certain requirements towards his people, they are to maintain their allegiance to him. Bayʿah is still practiced in countries such as Saudi Arabia and Sudan. In Morocco, bayʿah is one of the foundations of the monarchy.
In Australia, an Oath of Allegiance or an Affirmation of Allegiance are oaths of allegiance required to be made to the monarch of Australia in some situations. Oaths of Allegiance are usually made on a Bible, or some other book holy to the person, such as a Koran; but the person may opt to make an affirmation in lieu of an oath. Note that this oath is not the same as the Australian Citizenship Pledge which is required to be made when being naturalized as an Australian citizen.

The monarchy of the Bahamas is a system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign of the Commonwealth of The Bahamas. The current monarch and head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who has reigned since the country became independent on 10 July 1973. The Bahamas share the Sovereign with the other Commonwealth realms. The Queen does not personally reside in the islands, and most of her constitutional roles are therefore delegated to her representative in the country, the Governor-General of the Bahamas. Royal succession is governed by the English Act of Settlement of 1701, as amended by the Succession to the Crown Act 2013 of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, with the latter statute reflecting the Perth Agreement, to which the Bahamas government acceded. The two acts are part of constitutional law.

The 2017 Commonwealth Youth Games was the sixth edition of the Commonwealth Youth Games which started in 2000. The games were held from 19 to 23 July 2017 64 nations participated at the games. The Bahamas 2017 was the largest international sporting event ever to be hosted in The Bahamas, and the largest-ever edition of the Youth Games, with up to 1300 athletes. During the opening ceremony the Prime Minister of the Bahamas Hubert Minnis declared the games officially open.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Commonwealth of the Bahamas.
The Pledge of Allegiance of the United States is an expression of allegiance to the flag of the United States and the republic of the United States of America.
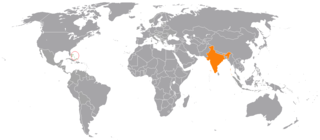
The Bahamas–India relations refers to the international relations that exist between The Bahamas and India. The Bahamas maintains an Honorary Consulate in New Delhi. The High Commission of India in Kingston, Jamaica concurrently accredited to The Bahamas. India does not have a resident diplomatic mission in The Bahamas.
"God Bless our Sunny Clime" is the national song of The Commonwealth of the Bahamas. Its music was composed by Timothy Gibson and E. Clement Bethel. The lyrics were written by the Rev. Philip Rahming, a Baptist minister and lecturer at the College of the Bahamas.









