Transport in Poland involves air, water, road and rail transportation. The country has a large network of municipal public transport, such as buses, trams and the metro. As a country located at the 'cross-roads' of Europe, Poland is a nation with a large and increasingly modern network of transport infrastructure.

Rzeszów is the largest city in southeastern Poland. It is located on both sides of the Wisłok River in the heartland of the Sandomierz Basin. Rzeszów is the capital of the Subcarpathian Voivodeship and the seat of Rzeszów County.

Subcarpathian Voivodeship is a voivodeship, or province, in the southeastern corner of Poland. Its administrative capital and largest city is Rzeszów. Along with the Marshal, it is governed by the Subcarpathian Regional Assembly.
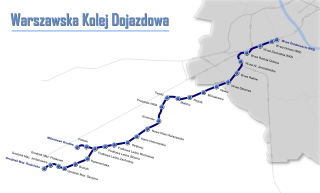
Warsaw Commuter Railway is a light rail commuter line in Poland's capital city of Warsaw. The line, together with its two branches, links Warsaw with the municipalities of Michałowice, Pruszków, Brwinów, Podkowa Leśna, Milanówek and Grodzisk Mazowiecki to the south-west of Warsaw.

Rzeszów Ulma Airport is an international airport located in southeastern Poland, in Jasionka, a village ten kilometres (6.2 mi) from the center of the city of Rzeszów. Not to be confused with the much smaller Rzeszów (EPRJ) airport used by Rzeszów University of Technology and Rzeszów Aeroclub, it is the eighth-busiest airport in Poland.

Szybka Kolej Miejska is a mixed rapid transit and commuter rail system in the Warsaw metropolitan area, operated by the city owned company Szybka Kolej Miejska Sp. z o.o. under the management of Public Transport Authority in Warsaw on shared, general railway lines managed by the PKP Polskie Linie Kolejowe.

The Polish railways network consists of around 18,510 kilometres (11,500 mi) of track as of 2019, of which 11,998 km (7,455 mi) is electrified. The national electrification system runs at 3 kV DC.

Boguchwała is a town in Rzeszów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. It is the seat of the administrative district of Gmina Boguchwała. It was officially granted town status on 1 January 2008. The name of the town means "praise to God".
Zdziary is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Jarocin, within Nisko County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. It lies approximately 5 kilometres (3 mi) west of Jarocin, 10 km (6 mi) north-east of Nisko, and 63 km (39 mi) north of the regional capital Rzeszów.

LKS Igloopol Dębica is a Polish sports club from Dębica, Subcarpathian Voivodeship. Their football team currently competes in the IV liga Subcarpathia, the fifth level of the national football league system.

Kutno railway station is a railway station in Kutno, in the Łódź Voivodeship, Poland. The station opened in 1861 and is located on the Warsaw–Kunowice railway, Łódź–Kutno railway, Kutno–Piła railway and Kutno–Brodnica railway. The train services are operated by PKP, Koleje Mazowieckie, Koleje Wielkopolskie, Łódzka Kolej Aglomeracyjna and Polregio.

Warszawa Zachodnia station, in English Warsaw West, is a railway and long-distance bus station in Warsaw, Poland on the border of Ochota and Wola districts. The railway station is the westernmost terminus of the Warsaw Cross-City Line. It serves trains from PKP Intercity, Polregio, Koleje Mazowieckie, Szybka Kolej Miejska and Warszawska Kolej Dojazdowa as well as international trains passing through Warsaw. It is one of the busiest railway stations in Poland, with over 800 daily trains.

Łowicz Główny is a railway station serving the town of Łowicz, in the Łódź Voivodeship, Poland. The station opened in 1861 and is located on the Warsaw–Kunowice railway, Skierniewice–Łowicz railway and Łowicz–Łódź railway. The train services are operated by PKP, Koleje Mazowieckie, Łódzka Kolej Aglomeracyjna and Przewozy Regionalne.

Łódzka Kolej Aglomeracyjna is a commuter and regional rail service operating between the Polish city of Łódź and surrounding towns in the Łódź Voivodeship (province).
IV liga Subcarpathia group is one of the groups of IV liga, the 5th level of Polish football league system. The league was created in season 2000/2001 after introducing new administrative division of Poland. Until the end of the 2007/08 season IV liga laid at 4th tier of league system but this was changed with the formation of the Ekstraklasa as the top-level league in Poland. The clubs from Subcarpathian Voivodeship compete in this group. The winner of the league is promoted to III liga, group IV. The bottom teams are relegated to the groups of the regional league from Subcarpathian Voivodeship. These groups are Dębica, Jarosław, Krosno, Rzeszów and Stalowa Wola.

Resovia Rzeszów, formally known as Apklan Resovia Rzeszów for sponsorship reasons, and commonly referred to as Resovia; is a professional Polish association football club from Rzeszów, Subcarpathian Voivodeship. It is part of the multi-sports club CWKS Resovia and is one of the oldest football clubs in Poland. As of the 2024–25 season, they compete in the II liga, following relegation from the second division.
Dobroń is a commuter station and a block post located in the village of Dobroń, in Pabianice County, Łódź Voivodeship, Poland, serving a section of Łódź-Tuplice railway between Pabianice and Łask stations.

Ewa Maria Leniart is a Polish politician. She was elected to the Sejm representing the constituency of Rzeszów.

The Pesa 214M is a family of standard-gauge diesel railcars produced by Pesa Bydgoszcz between 2001 and 2016, intended for regional transport on non-electrified lines. The family includes: 214M (SA106), 214Ma (SA103), and 214Mb (SA135). A total of 56 units were produced, which are operated by Arriva, Koleje Dolnośląskie, Masovian Railways, and Polregio.

Pesa 218M is a family of two-car standard-gauge diesel multiple units (DMUs) produced by Pesa between 2005 and 2015. Only one single-engine unit of the original 218M model was built, while the remaining dual-engine units were designated as subtypes 218Ma-218Md. A total of 76 units were produced, which are operated by Arriva, Koleje Dolnośląskie, Koleje Wielkopolskie, Polregio, and Szybka Kolej Miejska in Tricity.
















