Petroleum geology is the study of origin, occurrence, movement, accumulation, and exploration of hydrocarbon fuels. It refers to the specific set of geological disciplines that are applied to the search for hydrocarbons.

Chevron Corporation is an American multinational energy corporation. One of the successor companies of Standard Oil, it is headquartered in San Ramon, California, and active in more than 180 countries. Chevron is engaged in every aspect of the oil, natural gas, and geothermal energy industries, including hydrocarbon exploration and production; refining, marketing and transport; chemicals manufacturing and sales; and power generation. Chevron is one of the world's largest oil companies; as of 2017, it ranked nineteenth in the Fortune 500 list of the top US closely held and public corporations and sixteenth on the Fortune Global 500 list of the top 500 corporations worldwide. It was also one of the Seven Sisters that dominated the global petroleum industry from the mid-1940s to the 1970s.

Channel Islands National Park is an American national park that consists of five of the eight Channel Islands off the coast of the U.S. state of California, in the Pacific Ocean. Although the islands are close to the shore of densely populated Southern California, their isolation has left them relatively undeveloped. The park covers 249,561 acres (100,994 ha) of which 79,019 acres (31,978 ha) are owned by the federal government. The Nature Conservancy owns and manages 76% of Santa Cruz Island, the largest island in the park.
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. Though geographically part of the South American continent, from a socio-economic standpoint it is often referred to as the southernmost island in the Caribbean. With an area of 4,768 km2 (1,841 sq mi), it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies.

The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, San Bernardino and Riverside counties. The Peninsular Ranges lie to the south. The name Transverse Ranges is due to their east–west orientation, making them transverse to the general northwest–southeast orientation of most of California's coastal mountains.

The Los Angeles Basin is a sedimentary basin located in southern California, in a region known as the Peninsular Ranges. The basin is also connected to an anomalous group of east-west trending chains of mountains collectively known as the California Transverse Ranges. The present basin is a coastal lowland area, whose floor is marked by elongate low ridges and groups of hills that is located on the edge of the Pacific plate. The Los Angeles Basin, along with the Santa Barbara Channel, the Ventura Basin, the San Fernando Valley, and the San Gabriel Basin, lies within the greater southern California region. On the north, northeast, and east, the lowland basin is bound by the Santa Monica Mountains and Puente, Elysian, Repetto hills. To the southeast, the basin is bordered by the Santa Ana mountains and the San Joaquin Hills. The western boundary of the basin is marked by the Continental Borderland and is part of the onshore portion. The California borderland is characterized by north-west trending offshore ridges and basins. The Los Angeles Basin is notable for its great structural relief and complexity in relation to its geologic youth and small size for its prolific oil production. Yerkes et al. identify 5 major stages of the basin's evolution that begins in the Upper Cretaceous and ends in the Pleistocene. This basin can be classified as an irregular pull-apart basin accompanied by rotational tectonics during the post-early Miocene.

The Santa Barbara Channel is a portion of the Pacific Ocean which separates the mainland of California from the northern Channel Islands. It is generally south of the city of Santa Barbara, and west of the city of Ventura.

The Sierra Madre Mountains are a mountain range primarily in northern Santa Barbara County and extending into northwestern Ventura County in Southern California, western United States. It is a range of the Inner South Coast Ranges group, and is the southernmost reach of the California Coast Ranges, which are themselves part of the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America.
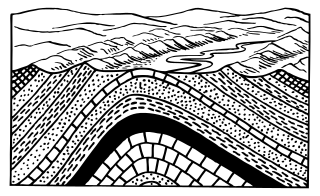
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used.

Doheny State Beach is a protected beach in the state park system of California, USA, located on the Pacific Ocean in the city of Dana Point. The beach is a popular surf spot located at the mouth of San Juan Creek, which flows from the Santa Ana Mountains southwest to the beach, where it forms a fresh-water lagoon. It is also one of the most polluted beaches in Southern California.

A petroleum seep is a place where natural liquid or gaseous hydrocarbons escape to the earth's atmosphere and surface, normally under low pressure or flow. Seeps generally occur above either terrestrial or offshore petroleum accumulation structures. The hydrocarbons may escape along geological layers, or across them through fractures and fissures in the rock, or directly from an outcrop of oil-bearing rock.

Neft Daşları is an industrial settlement in Baku, Azerbaijan. The settlement forms part of the municipality of Çilov-Neft Daşları in the Khazar raion. It lies 100 km (62 mi) away from the Azerbaijani capital Baku, and 55 km (34 mi) from the nearest shore in the Caspian Sea. A full town on the sea, it was the first oil platform in Azerbaijan, and the first operating offshore oil platform in the world, incorporating numerous drilling platforms. It is featured in Guinness World Records as the world's first offshore oil platform.

Salt Point State Park is a state park in Sonoma County, California, United States. The park covers 6,000 acres (2,400 ha) on the coast of Northern California, with 20 miles (32 km) of hiking trails and over 6 miles (9.7 km) of a rough rocky coast line including Salt Point which protrudes into the Pacific Ocean. The park also features the first underwater preserves in California. The constant impact of the waves forms the rocks into many different shapes. These rocks continue underwater providing a wide variety of habitats for marine organisms. The activities at Salt Point include hiking, camping, fishing, scuba diving and many others. The weather is cool with fog and cold winds even during the summer.
In petroleum geology, source rock refers to rocks from which hydrocarbons have been generated or are capable of being generated. They form one of the necessary elements of a working petroleum system. They are organic-rich sediments that may have been deposited in a variety of environments including deep water marine, lacustrine and deltaic. Oil shale can be regarded as an organic-rich but immature source rock from which little or no oil has been generated and expelled. Subsurface source rock mapping methodologies make it possible to identify likely zones of petroleum occurrence in sedimentary basins as well as shale gas plays.

The Monterey Formation is an extensive Miocene oil-rich geological sedimentary formation in California, with outcrops of the formation in parts of the California Coast Ranges, Peninsular Ranges, and on some of California's off-shore islands. The type locality is near the city of Monterey, California. The Monterey Formation is the major source-rock for 37 to 38 billion barrels of oil in conventional traps such as sandstones. This is most of California's known oil resources. The Monterey has been extensively investigated and mapped for petroleum potential, and is of major importance for understanding the complex geological history of California. Its rocks are mostly highly siliceous strata that vary greatly in composition, stratigraphy, and tectono-stratigraphic history.

The Riverside Mountains are a mountain range in Riverside County, California. The town of Vidal, California is located in the West Riverside Mountains.

Point Sal State Beach is a beach on the Pacific coast of California, located near the city of Guadalupe, in the northwestern part of Santa Barbara County. There are approximately 80 acres (320,000 m2) of property with 1.5 miles (2.4 km) of ocean frontage. The rocks around the headland constitute part of the Coast Range Ophiolite, one of the largest ophiolite terranes in the world. This beach is at risk of landslides as there are rocky shorelines and extremely steep slopes.

The Orcutt Oil Field is a large oil field in the Solomon Hills south of Orcutt, in Santa Barbara County, California. Discovered in 1901 by William Warren Orcutt, it was the first giant field to be found in Santa Barbara County, and its development led to the boom town of Orcutt, now the major unincorporated southern suburb of Santa Maria. With a cumulative production in 2008 of 870,000 barrels (138,000 m3) of oil, it is the largest onshore producing field in Santa Barbara County.

Pigeon Point Light Station or Pigeon Point Lighthouse is a lighthouse built in 1871 to guide ships on the Pacific coast of California. It is the tallest lighthouse on the West Coast of the United States. It is still an active Coast Guard aid to navigation. Pigeon Point Light Station is located on the coastal highway, 5 miles (8 km) south of Pescadero, California, between Santa Cruz and San Francisco. The 115-foot (35 m), white masonry tower, resembles the typical New England structure. Because of its location and ready access from the main highway, Pigeon Point entertains a large number of public visitors.
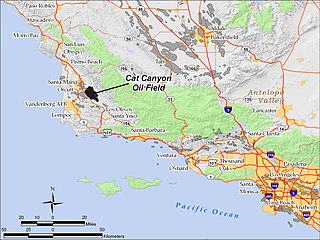
The Cat Canyon Oil Field is a large oil field in the Solomon Hills of central Santa Barbara County, California, about 10 miles southeast of Santa Maria. It is the largest oil field in Santa Barbara County, and as of 2010 is the 20th-largest in California by cumulative production.























