
The Comoros archipelago consists of four main islands aligned along a northwest–southeast axis at the north end of the Mozambique Channel, between Mozambique and the island of Madagascar. Still widely known by their French names, the islands officially have been called by their Swahili names by the Comorian government. They are Grande Comore (Njazidja), Mohéli (Mwali), Anjouan (Nzwani), and Mayotte (Mahoré). The islands' distance from each other—Grande Comore is some 200 kilometers from Mayotte, forty kilometers from Mohéli, and eighty kilometers from Anjouan—along with a lack of good harbor facilities, make transportation and communication difficult. Comoros are sunny islands.

Mayotte, officially the Department of Mayotte, is an overseas department and region and single territorial collectivity of France. It is located in the northern part of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean off the coast of Southeastern Africa, between Northwestern Madagascar and Northeastern Mozambique. Mayotte consists of a main island, Grande-Terre, a smaller island, Petite-Terre, as well as several islets around these two. Mayotte is the most prosperous territory in the Mozambique Channel, making it a major destination for immigration.

Anjouan is an autonomous volcanic island in the Comoro Islands in the southwestern Indian Ocean, part of the Union of the Comoros. It is known in Shikomori as Ndzuani, Ndzuwani or Nzwani, and, until the early twentieth century when the name fell out of general use, in English as Johanna. Historically it was also called Hinzuan or Hanzoan.

Phelsuma is a large genus of geckos in the family Gekkonidae. Species in the genus Phelsuma are commonly referred to as day geckos.

Robert Mertens's day gecko is diurnal species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to the Comoros.

The Mascarene Islands or Mascarenes or Mascarenhas Archipelago is a group of islands in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar consisting of islands belonging to the Republic of Mauritius as well as the French department of La Réunion. Their name derives from the Portuguese navigator Pedro Mascarenhas, who first visited them in April 1512. The islands share a common geological origin beneath the Mascarene Plateau known as the Mauritia microcontinent which was a Precambrian microcontinent situated between India and Madagascar until their separation about 70 million years ago. They form a distinct ecoregion with unique biodiversity and endemism of flora and fauna.

The Comoro Islands or the Comoros are an archipelago of volcanic islands situated off the southeastern coast of Africa, to the east of Mozambique and northwest of Madagascar. The islands are politically divided between the Union of the Comoros, a sovereign country, and Mayotte, an Overseas Department of France.
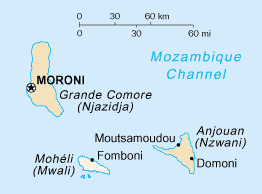
Mohéli, also known as Mwali, is an autonomously-governed island that forms part of the Union of the Comoros. It is the smallest of the three major islands in the country. It is located in the Indian Ocean off the coast of Africa and it is the smallest of the four major Comoro Islands. Its capital and largest city is Fomboni.

Mount Karthala or Karthola is an active volcano and the highest point of the Comoros at 2,361 m (7,746 ft) above sea level. It is the southernmost and larger of the two shield volcanoes forming Grande Comore island, the largest island in the nation of Comoros. The Karthala volcano is very active, having erupted more than 20 times since the 19th century. Frequent eruptions have shaped the volcano's 3 km by 4 km summit caldera, but the island has largely escaped broad destruction. Eruptions on April 17, 2005 and May 29, 2006 ended a period of quiet.
Cousin Island is a small granitic island of the Seychelles, lying 2 km (1.2 mi) west of Praslin. It is a nature reserve protected under Seychelles law as a Special Reserve. It is managed by Nature Seychelles, a national nonprofit organization and Partner of BirdLife International, by which it has been identified as an Important Bird Area.
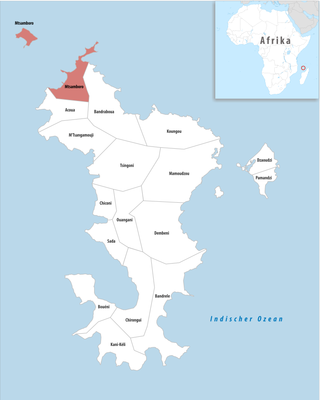
Mtsamboro is a small fishing town and commune in northwest Mayotte, a French overseas department in the Indian Ocean. Its population according to the 2017 census is 7,705. Included in the commune are the Choazil Islands and Chissioua Mtsamboro. The main economic activity is fishing and orange production.

Dapani is a village in the commune of Bandrele on Mayotte. It is located near the Pointes et plages de Saziley et Charifou protected area on the south-east of Mayotte. The protected area includes Dapani Beach and mangroves, and is a notable bird habitat known for its "botanical trail" through the mangroves.
Benara, or Mlima Bénara, is the highest peak of Grande-Terre, Mayotte, an overseas collectivity of France in the western Indian Ocean, with a height of 660 m (2,165 ft).

The Comoros forests is a terrestrial ecoregion which covers the Comoro Islands, which lie in the Mozambique Channel between Madagascar and East Africa. These include four main islands: Grande Comore, Anjouan and Mohéli, of the Union of the Comoros, and Mayotte, a department and region of France.

Mont Choungui is a distinctively conical volcanic mountain in the southern part of the French island of Mayotte, in the Comoro archipelago of the western Indian Ocean. It is the second highest point of the island at 593 m (1,946 ft), the highest being Mont Bénara, and is visible from far out at sea.

The Baie de Bouéni is a large bay in the south-west of the French island territory of Mayotte, in the Comoro Islands lying at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel between the East African country of Mozambique and Madagascar. It is about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) wide at its mouth, and 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) in length. It was made a protected area in 2007.

The Hachiroungou Important Bird Area lies in the north-west of the French island territory of Mayotte in the Comoro Islands, lying at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel between the East African country of Mozambique and Madagascar. The nearest towns are Dzoumonyé to the east, and Mtsamboro and Acoua to the west.

The Mlima Combani and Mlima Mtsapéré Important Bird Area lies in the north-central part of the French island territory of Mayotte in the Comoro Islands, lying at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel between the East African country of Mozambique and Madagascar.

The Mayotte Marine Natural Park is a marine park surrounding Mayotte, a French overseas region. Mayotte is part of the Comoro Islands archipelago, which lies within the Mozambique Channel in the western Indian Ocean. Established in 2010, the park covers the entirety of Mayotte's territorial waters and exclusive economic zone. It is contiguous with the Glorioso Islands Marine Natural Park, which was established two years later.

The Forests of Mayotte National Nature Reserve is a protected area on Mayotte, an island overseas department of France in the Indian Ocean.




















