Related Research Articles

The Afroasiatic languages, also known as Hamito-Semitic or Semito-Hamitic, are a language family of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara and Sahel. Over 500 million people are native speakers of an Afroasiatic language, constituting the fourth-largest language family after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo. Most linguists divide the family into six branches: Berber, Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Semitic, and Omotic. The vast majority of Afroasiatic languages are considered indigenous to the African continent, including all those not belonging to the Semitic branch.

The Chadic languages form a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken in parts of the Sahel. They include 150 languages spoken across northern Nigeria, southern Niger, southern Chad, the Central African Republic, and northern Cameroon. By far the most widely spoken Chadic language is Hausa, a lingua franca of much of inland Eastern West Africa, particularly Niger and the northern half of Nigeria.
The Kujargé language is spoken in seven villages in eastern Chad near Jebel Mirra, and in villages scattered along the lower Wadi Salih and Wadi Azum in Darfur, Sudan. It is estimated to have about 1000 speakers.

The Biu–Mandara or Central Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken in Nigeria, Chad and Cameroon.
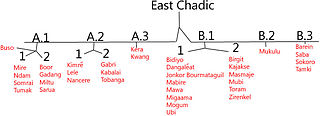
The three dozen East Chadic languages of the Chadic family are spoken in Chad and Cameroon.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language and most widely spoken lingua franca is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. Nigerian Pidgin – an English-based creole – is spoken by 30 million people in Nigeria.

The West Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken principally in Niger and Nigeria. They include Hausa, the most populous Chadic language and a major language of West Africa.
Chakato is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was identified by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in one village, Dokan Tofa, which is located on the Jos-Shendam road in Plateau State. Blench (2017) suggests that Chakato may be related to spurious records of the Jorto language. Chakato speakers claim that their language is closely related to Goemai.

The Angas, Angas–Sura, or Central West Chadic languages are a branch of West Chadic languages spoken in Plateau State, north-central Nigeria.
Baldemu, or Mbazlam, is a nearly extinct Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon. Baldamu is spoken in Bogo commune, Diamaré department, Far North Region by only 5 speakers as of 2012. Speakers have been shifting to Fulfulde.

The Bole–Tangale languages are a branch of West Chadic languages that are spoken in various states of northeastern Nigeria.
Bure, also known as Bubbure, is an Afro-Asiatic language belonging to the Bole-Tangale group of the West branch of the Chadic family. It is spoken in northern Nigeria in the village of Bure and in some small settlements nearby. The language is used mostly by a very few speakers, of great-grandparental generation. Except for Hausa, which is lingua franca in the area, Bure is surrounded by other Chadic languages such as Gera, Giiwo and Deno.

The South Bauchi languages are a branch of West Chadic languages that are spoken in Bauchi State and Plateau State, Nigeria.
Mantsi is an endangered Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Mangas town in Bauchi State, Nigeria. Blench (2020) reports that it is also called Mantsi. According to Blench, the structure of Mantsi differs significantly from the other South Bauchi languages.
Sha is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Plateau State and Kaduna State, Nigeria. As of 2018, the language is used for face-to-face communication and lacks a standardized written form. It is spoken by approximately 1000 people and is considered sustainable.
Tarok is a regionally important Plateau language in the Langtang area of southeast Plateau State, Nigeria, where it serves as a local lingua franca. Blench (2004) estimates around 150,000 speakers.
Polci is an Afro-Asiatic language of Bauchi State, Nigeria. It is part of the Barawa cluster, which is in turn part of the West Chadic language family.
Pero, also known as Filiya, is a West Chadic language of Nigeria.

The Hausa–Gwandara languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken principally in Niger and Nigeria. They include Gwandara and Hausa, the most populous Chadic language and a major language of West Africa.
Kulung (Wurkum) is a minor West Chadic language of Karim Lamido LGA, Taraba State, Nigeria that was recently discovered by Roger Blench. The language is not reported in Ethnologue or Glottolog. Blench (2019) gives a rough estimate of about 2,000 speakers.
References
- ↑ Blench, 2006. The Afro-Asiatic Languages: Classification and Reference List (ms)