Related Research Articles
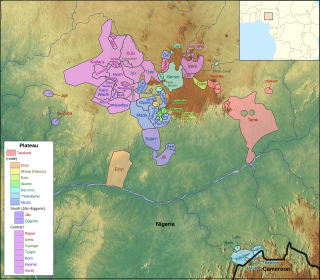
The forty or so Plateau languages are a tentative group of Benue–Congo languages spoken by 15 million people on the Jos Plateau, Southern Kaduna, Nasarawa State and in adjacent areas in central Nigeria.

The West Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken principally in Niger and Nigeria. They include Hausa, the most populous Chadic language and a major language of West Africa.
Cakfem-Mushere is an Afro-Asiatic language cluster spoken in Bokkos LGA, Plateau State, Nigeria. Dialects are Kadim-Kaban and Jajura. Mutual intelligibility with Mwaghavul is high.
Chakato is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was identified by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in one village, Dokan Tofa, which is located on the Jos-Shendam road in Plateau State. Blench (2017) suggests that Chakato may be related to spurious records of the Jorto language. Chakato speakers claim that their language is closely related to Goemai.
Pan is an Afro-Asiatic dialect cluster spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria.
Tal is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. Tal is spoken in a cluster of 53 villages located east of the Panyam-Shendam road. There are 6 dialects of Tal, namely Bongmuut, Buzuk, Nbaal, Muɗak, Muɗong, and Takong.

The Angas, Angas–Sura, or Central West Chadic languages are a branch of West Chadic languages spoken in Plateau State, north-central Nigeria.
Mundat is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria in Mundat village of Bokkos LGA.

Ron is an Afro-Asiatic language cluster spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. Dialects include Bokkos, Daffo-Mbar-Butura, Monguna. Blench (2006) considers these to be separate languages.
Sha is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Plateau State and Kaduna State, Nigeria. As of 2018, the language is in use for face-to-face communication and has no standardized written form. The language is spoken by roughly 1000 people and is sustainable.
The five Tarokoid languages are a branch of the Plateau family spoken in central Nigeria, just north of the middle reaches of the Benue River. Tarok itself has 300,000 speakers, with Pe and Sur about 5,000 each. Yangkam is severely endangered, being spoken by around fifty elderly men.
Ahwai, also called the Ndunic languages, is a Plateau language cluster spoken to the southwest of Fadan Karshi in Sanga LGA, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Most villages are located at the foot of the Ahwai Mountains in Kaduna State.
Hasha, also known as Yashi, is a Plateau language of Nasarawa State Nigeria. It has an idiosyncratic system of reduplicating the first syllable of noun stems, apparently under the influence of the Chadic language Sha.
The Rigwe language, Nkarigwe, is a Plateau language of Nigeria spoken by the Irigwe people mainly found in Bassa Local Government Area of Plateau State.
Geji (Gezawa) is a minor Chadic dialect cluster of Bauchi State, Nigeria. The three varieties are Buu, Gyaazi and Mәgang. The latter two are quite close.

The Ron, Ronic or Ron–Fyer languages, group A.4 of the West Chadic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family, are spoken in Plateau State, north-central Nigeria.
Jibyal is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was discovered by Roger Blench in 2017.
Nteng is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. Nteng is spoken in the villages of Nteng, Geer, Ɗok, Kelaghal, Lool, Kwaki, Jekmorop, and Gorom, with Gorom being a primarily Bwal-speaking village. Roger Blench (2017) estimates that there are 2,000 speakers as of 2017.
Belnəng is a West Chadic language of Shendam LGA, Plateau State, Nigeria closely related to Angas. It is spoken by about 500 people in the single village of Langung, which is surrounded by Tal villages in the east and Miship villages in the west. It is documented in Blench & Bulkaam (2019).
Nigbo is an extinct Plateau language of Nigeria. It was spoken near Agameti on the Fadan Karshi-Wamba road near Sanga LGA, Kaduna State. The language, listed in Blench (2012) and (2019), is not reported in Ethnologue or Glottolog. It is presumably an Alumic language based on its proximity to Akpondu, a language closely related to Alumu and Tesu.
References
- 1 2 Blench, Roger (2022). Contact between West Chadic and Plateau languages: new evidence languages: new evidence . 11-12 November 2022, presentation given at Universität Wien.
- ↑ Blench, Roger. 2022. "Miler, an undocumented Chadic language of Central Nigeria." Manuscript. Jos, Nigeria.
- ↑ Blench, Roger & Michael Bulkaam. 2019. "Belnəng, an undocumented Chadic language of Central Nigeria." Manuscript. Jos, Nigeria.