Related Research Articles

Hausa ; Ajami: هَرْشٜن هَوْسَ) is a Chadic language that is spoken by the Hausa people in the northern parts of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern parts of Niger, Chad and Sudan, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast.

Niger–Congo is a hypothetical language family spoken over the majority of sub-Saharan Africa. It unites the Mande languages, the Atlantic-Congo languages, and possibly several smaller groups of languages that are difficult to classify. If valid, Niger-Congo would be the world's largest in terms of member languages, the third-largest in terms of speakers, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area. It is generally considered to be the world's largest language family in terms of the number of distinct languages, just ahead of Austronesian, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.
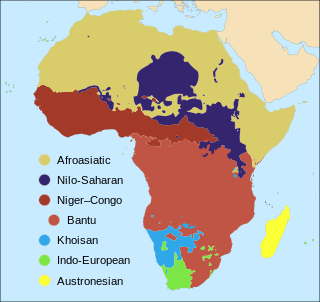
The number of languages natively spoken in Africa is variously estimated at between 1,250 and 2,100, and by some counts at over 3,000. Nigeria alone has over 500 languages, one of the greatest concentrations of linguistic diversity in the world. The languages of Africa belong to many distinct language families, among which the largest are:

Yoruba is a language spoken in West Africa, primarily in Southwestern and Central Nigeria. It is spoken by the ethnic Yoruba people. The number of Yoruba speakers is roughly 44 million, plus about 2 million second-language speakers. As a pluricentric language, it is primarily spoken in a dialectal area spanning Nigeria, Benin, and Togo with smaller migrated communities in Côte d'Ivoire, Sierra Leone and The Gambia.
The Eleme people are one of the various groups of indigenous peoples that inhabit the Niger Delta region of South-South Nigeria.
Kay Williamson, born Ruth Margaret Williamson, was a linguist who specialised in the study of African languages, particularly those of the Niger Delta in Nigeria, where she lived for nearly fifty years. She has been called "The Mother of Nigerian Linguistics" and is also notable for proposing the Pan-Nigerian alphabet.
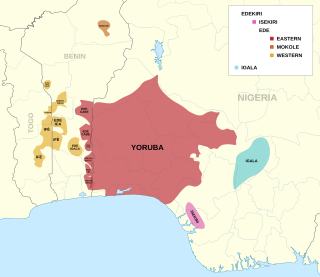
Yoruboid is a language family composed of the Igala group of dialects spoken in south central Nigeria, and the Edekiri group spoken in a band across Togo, Ghana, Benin and southern Nigeria, including the Itsekiri of Warri Kingdom.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language and most widely spoken lingua franca is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. Nigerian Pidgin – an English-based creole – is spoken by 30 million people in Nigeria.
The Izonlanguages, otherwise known as the Ịjọ languages, are the languages spoken by the Izon people in southern Nigeria.
Orring (Korring) is an Upper Cross River language spoken by the Orring people of Nigeria. Korring language is spoken by the Orring people who are found in Benue, Cross River and Ebonyi states of Nigeria.
Nupe is a Volta–Niger language of the Nupoid branch primarily spoken by the Nupe people of the North Central region of Nigeria. Its geographical distribution stretches and maintains pre-eminence in Niger State as well as Kwara, Kogi, Nasarawa and the Federal Capital Territory.
Eleme is a local government area in Rivers State, Nigeria. It is part of the Port Harcourt metropolitan city.
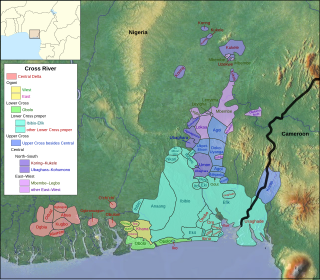
The Cross River or Delta–Cross languages are a branch of the Benue–Congo language family spoken in south-easternmost Nigeria, with some speakers in south-westernmost Cameroon. The branch was first formulated by Joseph Greenberg; it is one of the few of his branches of Niger–Congo that has withstood the test of time.
Cipu (Cicipu), or Western Acipa, is a Kainji language spoken by about 20,000 people in northwest Nigeria. The people call themselves Acipu, and are called Acipawa in Hausa.
Akpes (Àbèsàbèsì) is an endangered language of Nigeria. It is spoken by approximately 7,000 speakers in the North of Ondo State. The language is surrounded by several other languages of the Akoko area, where Yoruba is the lingua franca. Yoruba replaces Akpes in more and more informal domains and thus forwards a gradual shift from Akpes towards Yoruba. Akpes is generally attributed to the Volta-Congo Branch of the Niger-Congo phylum.
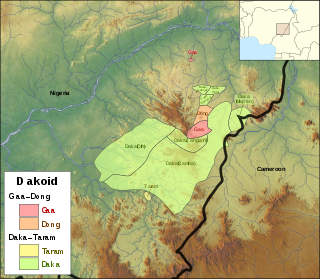
The Dakoid languages are a branch of the Northern Bantoid languages spoken in Taraba and Adamawa states of eastern Nigeria.
Odual is a poorly studied Central Delta language spoken by the Odual community in the Abua–Odual Local Government Area of Rivers State and Ogbia LGA of Bayelsa State, Nigeria.
The Itsekiri language is a major branch of the Yoruboid group of languages, which as a group, is a key member of the Volta–Niger sub-family of the Niger–Congo family of African languages. Itsekiri is spoken by nearly 900,000 people in Nigeria as a first language and by many others as an additional language notably in the Niger Delta and in parts of Edo and Ondo states of Nigeria. The other key members of the Yoruboid group are Yoruba and Igala along with the various Yoruba dialects spoken in Benin and Togo.
Kalabari is an Ijo language of Nigeria spoken in Rivers State and Bayelsa State by the Awome people. Its three dialects are mutually intelligible. The Kalabari dialect is one of the best-documented varieties of Ijo, and as such is frequently used as the prime example of Ijo in linguistic literature.
Ekpeye is one of many languages spoken in Rivers State, Nigeria. According to Roger Blench, Ekpeye is classified as an Igboid language. Although an Igboid language, Ekpeye has evolved to a very distinct Igboid language that is phonologically different from other Igboid languages. The Engenni, Ogba and Ikwerre languages are closely related to Ekpeye. Ekpeye has many mutually intelligible dialects.
References
- ↑ Eleme at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ "Eleme - Surrey Morphology Group". www.smg.surrey.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-05-01.
- ↑ Harrison, K. David. (2007). When languages die : the extinction of the world's languages and the erosion of human knowledge. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 216. ISBN 978-0-19-518192-0. OCLC 65425996.
- ↑ Eyi Ngulube 2011.
Works cited
- Eyi Ngulube, Isaac (2011). "The Eleme orthography". In Ozo-mekuri Ndimele; Tony Enyia (eds.). Orthographies of Nigerian languages: manual X. Nigeria Educational Research & Development Council. pp. 36–59.