Related Research Articles

Haiku is a type of short form poetry originally from Japan. Traditional Japanese haiku consist of three phrases that contain a kireji, or "cutting word", 17 on in a 5, 7, 5 pattern, and a kigo, or seasonal reference. Similar poems that do not adhere to these rules are generally classified as senryū.

Hepburn romanization is the most widely used system of romanization for the Japanese language. Originally published in 1867 by American missionary James Curtis Hepburn as the standard in the first edition of his Japanese–English dictionary, the system is distinct from other romanization methods in its use of English orthography to phonetically transcribe sounds: for example, the syllable [ɕi] is written as shi and [tɕa] is written as cha, reflecting their spellings in English.
Kunrei-shiki romanization is the Cabinet-ordered romanization system for transcribing the Japanese language into the Latin alphabet. Its name is rendered Kunreisiki rômazi in the system itself. Kunrei-shiki is sometimes known as the Monbushō system in English because it is taught in the Monbushō-approved elementary school curriculum. The ISO has standardized Kunrei-shiki, under ISO 3602.

Shiki is a city located in Saitama Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 January 2021, the city had an estimated population of 76,445 in 35,407 households and a population density of 8400 persons per km². The total area of the city is 9.05 square kilometres (3.49 sq mi).
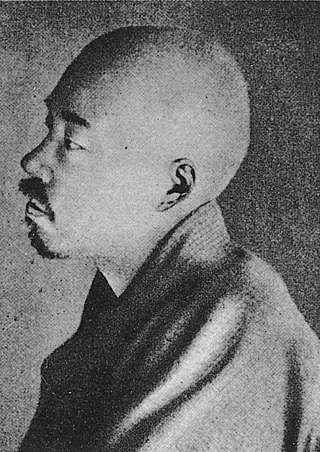
Masaoka Shiki, pen-name of Masaoka Noboru, was a Japanese poet, author, and literary critic in Meiji period Japan. Shiki is regarded as a major figure in the development of modern haiku poetry, credited with writing nearly 20,000 stanzas during his short life. He also wrote on reform of tanka poetry.
Nihon-shiki, is a romanization system for transliterating the Japanese language into the Latin alphabet. Among the major romanization systems for Japanese, it is the most regular one and has an almost one-to-one relation to the kana writing system.

Tsukihime is a Japanese adult visual novel created by the dōjin circle Type-Moon, who first released it at the Winter Comiket in December 2000. In 2003, it was adapted into both an anime television series, Lunar Legend Tsukihime, animated by J.C.Staff, and a manga series, which was serialized between 2003 and 2010 in MediaWorks shōnen magazine Dengeki Daioh, with 10 volumes released.

Shiki-Jitsu is a 2000 art film written and directed by Hideaki Anno. The film is Anno's second live-action feature. The screenplay is an adaption of Ayako Fujitani's novella Tōhimu, which was inspired by an emotionally difficult time in Los Angeles working on her father Steven Seagal's 1998 film The Patriot.
Daume Co.,Ltd. is a Japanese animation studio that was founded in 1986.

One Piece Film: Strong World is a 2009 Japanese anime action adventure film directed by Munehisa Sakai. It is the tenth feature film based on the shōnen manga series One Piece by Eiichiro Oda.
The romanization of Japanese is the use of Latin script to write the Japanese language. This method of writing is sometimes referred to in Japanese as rōmaji.

Shiki is a Japanese horror novel written by Fuyumi Ono. It was originally published in two parts by Shinchosha in 1998, it was then reprinted into five parts in 2002. A manga series adapting the story, drawn by Ryu Fujisaki was serialized in the Japanese monthly magazine Jump SQ. from December 2007 to June 2011. An anime adaptation of the manga by Daume aired on Fuji TV from July to December 2010. North American anime distributor Funimation simulcasted the series on their online video portal and released the series on DVD and Blu-ray in May 2012.

The Garden of Sinners: Overlooking View is a 2007 Japanese animated film produced by ufotable based on The Garden of Sinners novels by Kinoko Nasu. It is the first installment in the series, followed by A Study in Murder – Part 1 (2007). Chronologically, the events that occur in The Garden of Sinners: Overlooking View are the fifth in the timeline of the series.

The Garden of Sinners: A Study in Murder – Part 1 is a 2007 Japanese animated film produced by ufotable based on The Garden of Sinners novels by Kinoko Nasu. It is the second installment in the series, preceded by Overlooking View (2007) and followed by Remaining Sense of Pain (2008). Chronologically, the events that occur in The Garden of Sinners: A Study in Murder – Part 1 are the first in the timeline of the series.
The Garden of Sinners: Remaining Sense of Pain is a 2008 Japanese animated film produced by ufotable based on The Garden of Sinners novels by Kinoko Nasu. It is the third installment in the series, preceded by A Study in Murder – Part 1 (2007) and followed by The Hollow Shrine (2008). Chronologically, the events that occur in The Garden of Sinners: Remaining Sense of Pain are the third in the timeline of the series.
The Garden of Sinners: Paradox Spiral is a 2008 Japanese animated film produced by ufotable based on The Garden of Sinners novels by Kinoko Nasu. It is the fifth installment in the series, preceded by The Hollow Shrine (2008) and followed by Oblivion Recording (2008). Chronologically, the events that occur in The Garden of Sinners: Paradox Spiral are the sixth in the timeline of the series.
The Garden of Sinners: Oblivion Recording is a 2008 Japanese animated film produced by ufotable based on The Garden of Sinners novels by Kinoko Nasu. It is the sixth installment in the series, preceded by Paradox Spiral (2008) and followed by A Study in Murder – Part 2 (2009). Chronologically, the events that occur in The Garden of Sinners: Oblivion Recording are the seventh in the timeline of the series.
The Garden of Sinners: A Study in Murder – Part 2 is a 2009 Japanese animated film produced by ufotable based on The Garden of Sinners novels by Kinoko Nasu. It is the seventh installment in the series, preceded by Oblivion Recording (2008) and followed by a sequel Future Gospel (2013). Chronologically, the events that occur in The Garden of Sinners: A Study in Murder – Part 2 are the eighth in the timeline of the series.
Abū Ṭāher ibn Miṣbāḥ al-Ḥaqq al-Kumillāʾī, commonly known as Abu Taher Misbah Bengali: আবু তাহের মিসবাহ) or Adib Huzur, is a Bangladeshi Deobandi Islamic scholar, academic and author. He is the founder of Madani Nesab, and the first textbook that he wrote for it, Eso Arabi Sikhi, is read as the primary textbook of Arabic learning in Bangladesh..
References
- ↑ Shiki at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)