Related Research Articles
The Edoid languages are a few dozen languages spoken in Southern Nigeria, predominantly in the former Bendel State. The name Edoid derives from its most widely spoken member, Edo, the language of Benin City, which has 30 million native and secondary speakers.
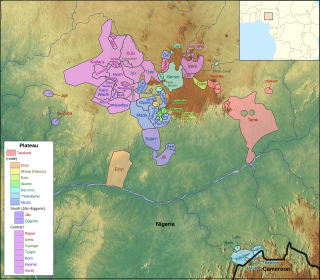
The forty or so Plateau languages are a tentative group of Benue–Congo languages spoken by 15 million people on the Jos Plateau, Southern Kaduna, Nasarawa State and in adjacent areas in central Nigeria.

There are over 520 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. The English-based creole Nigerian Pidgin – first used by the British and African slavers to facilitate the Atlantic slave trade in the late 17th century – is the most widely spoken lingua franca and spoken by over 60 million people.
The Ijaw languages, also spelled Ịjọ, are the languages spoken by the Ijaw people in southern Nigeria.
Chakato is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was identified by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in one village, Dokan Tofa, which is located on the Jos-Shendam road in Plateau State. Blench (2017) suggests that Chakato may be related to spurious records of the Jorto language. Chakato speakers claim that their language is closely related to Goemai.

The Angas, Angas–Sura, or Central West Chadic languages are a branch of West Chadic languages spoken in Plateau State, north-central Nigeria.
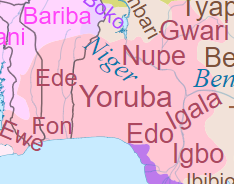
The Volta–Niger family of languages, also known as West Benue–Congo or East Kwa, is one of the branches of the Niger–Congo language family, with perhaps 70 million speakers. Among these are the most important languages of southern Nigeria, Benin, Togo, and southeast Ghana: Yoruba, Igbo, Bini, and Gbe.
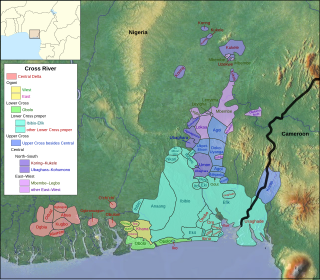
The Cross River or Delta–Cross languages are a branch of the Benue–Congo language family spoken in south-easternmost Nigeria, with some speakers in south-westernmost Cameroon. The branch was first formulated by Joseph Greenberg; it is one of the few of his branches of Niger–Congo that has withstood the test of time.
The Nupoid languages are a branch of Volta–Niger spoken in west-central Nigeria, particularly in southeastern Niger State and northern Kogi State. They include the Nupe, and Ebira languages, each with about 4 million speakers. Most Nupoid languages have 3 level tones.
The Idomoid languages are spoken primarily in Benue State of east-central Nigeria and surrounding regions. Idoma itself is an official language spoken by nearly four million people including the subgroups of Igede, Uffia, Otukpo, and Orokam.
The four scattered and poorly attested Alumic languages form a branch of the Plateau languages of central Nigeria.
The Ayere–Ahan languages are a pair of languages of southwestern Nigeria, Ayere and Àhàn, that form an independent branch of the Volta–Niger languages. These languages are spoken in the border region of Kogi State and Ondo State, Nigeria.
Odual is a poorly studied Central Delta language spoken by the Odual community in the Abua–Odual Local Government Area of Rivers State and Ogbia LGA of Bayelsa State, Nigeria.
Zeem, or Chaari, is an endangered Chadic dialect cluster of Nigeria, whose speakers are shifting to Hausa. Dyarim is closely related.
Alumu is a Plateau language spoken by approximately 7,000 people in Nassarawa State, Nigeria. It has lost the nominal affix system characteristic of the Niger–Congo family.
Ahwai, also called the Ndunic languages, is a Plateau language cluster spoken to the southwest of Fadan Karshi in Sanga LGA, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Most villages are located at the foot of the Ahwai Mountains in Kaduna State.
Ogbia is the most spoken Central Delta language of Nigeria. It is spoken by over 200,000 people.
Pe, also spelled Pai or Pye, is a minor Plateau language of southeastern Plateau State, Nigeria. It is classified as a Tarokoid language by Roger Blench (2023).

The Ron, Ronic or Ron–Fyer languages, group A.4 of the West Chadic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family, are spoken in Plateau State, north-central Nigeria.
Nteng is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. Nteng is spoken in the villages of Nteng, Geer, Ɗok, Kelaghal, Lool, Kwaki, Jekmorop, and Gorom, with Gorom being a primarily Bwal-speaking village. Roger Blench (2017) estimates that there are 2,000 speakers as of 2017.
References
- ↑ Blench, Roger (2019). An Atlas of Nigerian Languages (4th ed.). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.
- Blench, Roger. 2008. The Central Delta languages: comparative word list and historical reconstructions.
![]() This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 3.0 license.
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 3.0 license.