Related Research Articles

Hausa is a Chadic language spoken by the Hausa people in the northern half of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern half of Niger, Chad and Sudan, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast.
The Mandé peoples are ethnic groups who are speakers of Mande languages. Various Mandé speaking ethnic groups are found particularly toward the west of West Africa. The Mandé Speaking languages are divided into two primary groups: East Mandé and West Mandé.

The culture of Nigeria is shaped by Nigeria's multiple ethnic groups. The country has 527 languages, seven of which are extinct. Nigeria also has over 1150 dialects and ethnic groups. The three largest ethnic groups are the Hausas that are predominantly in the north, the Yorubas who predominate in the southwest, and the Igbos in the southeast. There are many other ethnic groups with sizeable populations across the different parts of the country. The Kanuri people are located in the northeast part of Nigeria, the Tiv people of north central and the Efik-Ibibio are in the south south. The Bini people are most frequent in the region between Yorubaland and Igboland.

Kebbi state is a state in the northwestern Nigeria, Kebbi state is bordered east and north of Sokoto and Zamfara states, and to the south by Niger state while its western border forms part of the national borders with Benin Republic and Niger. Named for the city of Birnin Kebbi—the state's capital and largest city, Kebbi state was formed from Sokoto state on 27 August 1991. Of the 36 states of Nigeria, Kebbi is the tenth largest in area and 22nd most populous, with an estimated population of about 4.4 million as of 2016. The state is known as land of equity.

The talking drum is an hourglass-shaped drum from West Africa, whose pitch can be regulated to mimic the tone and prosody of human speech. It has two drumheads connected by leather tension cords, which allow the player to change the pitch of the drum by scraping the cords between their arm and body.

In many parts of sub-Saharan Africa, the use of music is not limited to entertainment: it serves a purpose to the local community and helps in the conduct of daily routines. Traditional African music supplies appropriate music and dance for work and for religious ceremonies of birth, naming, rites of passage, marriage and funerals. The beats and sounds of the drum are used in communication as well as in cultural expression.

Gbagyi or Gbari is the name and the language of Gbagyi/Gbari ethnic group who are predominantly found in Central Nigeria, with a population of about 1 million people. Members of the ethnic group speak two dialects. While speakers of the dialects were loosely called Gwari by both the Hausa Fulani and Europeans during pre-colonial Nigeria they prefer to be known as Gbagyi/Gbari. They live in the Niger, the Federal Capital Territory - Abuja, and Kaduna State. They are also found in Nasarawa central Nigeria Area. Gbagyi/Gbari is one of the most populated ethnic and indigenous group in the middle belt and Federal Capital Territory of Nigeria and their major occupation is farming. Pottery is also an occupation practiced by the women.

There are over 256 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language and most widely spoken lingua franca is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. Nigerian Pidgin – an English-based creole – is spoken as a second language by over a 100 million people in Nigeria.
Bissa, is a Mande ethnic group of south-central Burkina Faso, northeastern Ghana and the northernmost tip of Togo. Their language, Bissa, is a Mande language that is related to, but not the same as, a cluster of languages in the old Borgu Kingdom area of Northeast Benin and Northwest Nigeria, including Busa, Boko, and Kyenga. An alternate name for the Bissa is Busansi or Busanga which is used by the Mossi people.

The Hausa are a native ethnic group in West and Central Africa. They speak the Hausa language, which is the second most spoken language after Arabic in the Afro-Asiatic language family. The Hausa are a diverse but culturally homogeneous people based primarily in the Sahelian and the sparse savanna areas of southern Niger and northern Nigeria respectively, numbering around 75 million people with significant indigenized populations in Benin, Cameroon, Ivory Coast, Chad, Sudan, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Togo, Ghana, Eritrea, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Senegal and the Gambia.
Lau (Law) is a Jukunoid language of Lau LGA, Taraba State, Nigeria. Lau speakers claim that their language is mutually intelligible with the Jukunoid language varieties spoken in Kunini, Bandawa, and Jeshi. They also live alongside the Central Sudanic-speaking Laka, who live in Laka ward of Lau LGA.
Busa, or Bisã, is the Mande language of the former Borgu Emirate in northwestern Nigeria and northern Benin. It is called Busanci in Hausa, and has also been called Zugweya.
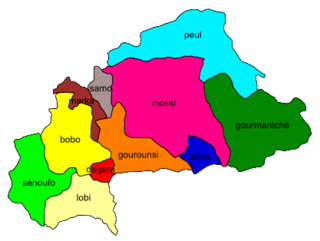
Bissa, is a Mande ethnic group of south-central Burkina Faso, northeastern Ghana and the northernmost tip of Togo. Their language, Bissa, is a Mande language that is related to, but not the same as, a cluster of languages in the old Borgu Kingdom area of Northeast Benin and Northwest Nigeria, including Busa, Boko, and Kyenga. An alternate name for the Bissa is Busansi which is used by the Mossi people or Busanga.
Bariba, also known as Baatonum, is the language of the Bariba people of Benin and Nigeria and was the language of the state of Borgu.
Boko, or Boo, is a Mande language of Benin and Nigeria.
Kyenga, is a Mande language of Nigeria and Benin. Usage is declining, and the Kyenga are shifting to Hausa in Nigeria and Dendi in Benin.
Pero, also known as Filiya,is a West Chadic language of Nigeria.
Tunzu (Tunzuii), or Itunzu, also known as Duguza (Dugusa) in Hausa, is a Kainji language of Nigeria.

BBC Hausa is the Hausa language service of BBC World Service meant primarily for the Hausa-speaking world in Nigeria, Ghana, Niger and the rest of Hausa speakers in West Africa. It is part of BBC foreign language output of 33 languages, of which five are African languages. The language service include radio station, Abuja bureau office and daily updated website which serves as a news portal and provides information as well as analyses in text, audio and video and provides online access to radio broadcasts. The radio service is broadcast from Broadcasting House in London and preliminary editing done at BBC bureau office in Abuja.
The Eastern Mande languages are a branch of the Mande languages spoken in seven areas: northwest Burkina Faso, the border region of northern Benin and Nigeria, and one language, Bissa, also spoken in Ghana, Togo, and Ivory Coast and the Samo languages also spoken in Mali.
References
- 1 2 Shanga at Ethnologue (26th ed., 2023)
