Related Research Articles

Ga is a Kwa language spoken in Ghana, in and around the capital Accra, by the Ga people. There are also some speakers in Togo, Benin and Western Nigeria. It has a phonemic distinction between three vowel lengths.
ǂʼAmkoeAM-koy, formerly called by the dialectal name ǂHoan, is a severely endangered Kxʼa language of Botswana. West ǂʼAmkoe dialect, along with Taa and Gǀui, form the core of the Kalahari Basin sprachbund, and share a number of characteristic features, including the largest consonant inventories in the world. ǂʼAmkoe was shown to be related to the Juu languages by Honken and Heine (2010), and these have since been classified together in the Kxʼa language family.
Gǀui or Gǀwi is a Khoe dialect of Botswana with 2,500 speakers. It is part of the Gǁana dialect cluster, and is closely related to Naro. It has a number of loan words from ǂʼAmkoe. Gǀui, ǂʼAmkoe, and Taa form the core of the Kalahari Basin sprachbund, and share a number of characteristic features, including extremely large consonant inventories.
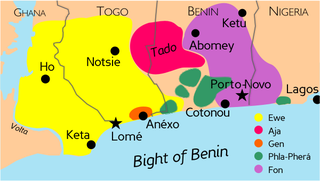
The Gbe languages form a cluster of about twenty related languages stretching across the area between eastern Ghana and western Nigeria. The total number of speakers of Gbe languages is between four and eight million. The most widely spoken Gbe language is Ewe, followed by Fon. The Gbe languages were traditionally placed in the Kwa branch of the Niger–Congo languages, but more recently have been classified as Volta–Niger languages. They include five major dialect clusters: Ewe, Fon, Aja, Gen (Mina), and Phla–Pherá.

The Mandinka language, or Mandingo, is a Mande language spoken by the Mandinka people of Guinea, northern Guinea-Bissau, the Casamance region of Senegal, and in The Gambia where it is one of the principal languages.
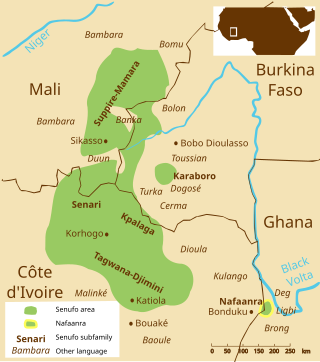
Nafaanra, also known as Nafanan or Nafana, is a Senufo language spoken in northwest Ghana, along the border with Ivory Coast, east of Bondoukou. It is spoken by approximately 90,000 people. Its speakers call themselves Nafana, but others call them Banda or Mfantera. Like other Senufo languages, Nafaanra is a tonal language. It is somewhat of an outlier in the Senufo language group, with the geographically-closest relatives, the Southern Senufo Tagwana–Djimini languages, approximately 200 kilometres (120 mi) to the west, on the other side of Comoé National Park.
The phonology of Vietnamese features 19 consonant phonemes, with 5 additional consonant phonemes used in Vietnamese's Southern dialect, and 4 exclusive to the Northern dialect. Vietnamese also has 14 vowel nuclei, and 6 tones that are integral to the interpretation of the language. Older interpretations of Vietnamese tones differentiated between "sharp" and "heavy" entering and departing tones. This article is a technical description of the sound system of the Vietnamese language, including phonetics and phonology. Two main varieties of Vietnamese, Hanoi and Saigon, which are slightly different to each other, are described below.
Logba is a Kwa language spoken in the south-eastern Ghana by approximately 7,500 people. The Logba people call themselves and their language Ikpana, which means ‘defenders of truth’. Logba is different from Lukpa of Togo and Benin, which is also sometimes referred to as Logba.
Defaka is an endangered and divergent Nigerian language of uncertain classification. It is spoken in the Opobo–Nkoro LGA of Rivers State, in the Defaka or Afakani ward of Nkọrọ town and Ịwọma Nkọrọ. The low number of Defaka speakers, coupled with the fact that other languages dominate the region where Defaka is spoken, edges the language near extinction on a year-to-year basis. It is generally classified in an Ijoid branch of the Niger–Congo family. However, the Ijoid proposal is problematic. Blench (2012) notes that "Defaka has numerous external cognates and might be an isolate or independent branch of Niger–Congo which has come under Ịjọ influence."
Kusaal is a Gur language spoken primarily in northern eastern Ghana, and Burkina Faso. It is spoken by about 121,000 people and takes its name from the Kusaal people, or Kusasi. There is a distinctive dialect division between Agole, to the East of the Volta River, and Toende, to the West. Agole has more speakers. The 6-district capital; Bawku West with Zebilla as capital and the rest; Binduri, Bawku, Tempane, Garu and Pusiga districts mostly Agole dialect speakers. The complete Bible translation is in the Agole dialect.

Mongsen Ao is a member of the Ao languages, a branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages, predominantly spoken in central Mokokchung district of Nagaland, northeast India. Its speakers see the language as one of two varieties of a greater "Ao language," along with the prestige variety Chungli Ao.
Taos is a Tanoan language spoken by several hundred people in New Mexico, in the United States. The main description of its phonology was contributed by George L. Trager in a (pre-generative) structuralist framework. Earlier considerations of the phonetics-phonology were by John P. Harrington and Jaime de Angulo. Trager's first account was in Trager (1946) based on fieldwork 1935-1937, which was then substantially revised in Trager (1948). The description below takes Trager (1946) as the main point of departure and notes where this differs from the analysis of Trager (1948). Harrington's description is more similar to Trager (1946). Certain comments from a generative perspective are noted in a comparative work Hale (1967).
Izi is an Igboid language spoken in Ebonyi state in Nigeria. It forms a dialect cluster with the closely related languages Ikwo, Ezza, and Mgbo.
Mbre or Pere, known as Pεrε among themselves and as Bεrε by the locally dominant Koro, also spelled Pre and Bre, is a moribund language of the Ivory Coast.
Kensiu (Kensiw) is an Austroasiatic language of the Jahaic subbranch. It is spoken by a small community of 300 people in Yala Province in southern Thailand and also reportedly by a community of approximately 300 speakers in Western Malaysia in Perak and Kedah states. Speakers of this language are Negritos who are known as the Mani people or Maniq of Thailand.
The Brokpa language (Brokpa: Brokpakæ; Dzongkha: དྲོག་པ་ཁ།, དྲོགཔ་ཁ།) is a Tibetic language spoken by around 5,000 people. It is spoken by descendants of pastoral yakherd communities.
Foodo is a Guang language spoken in and around the town of Sèmèrè in the north of Benin. There are approximately 37,000 speakers. A large proportion of the population live beyond the homeland in other parts of Benin, as well as in neighboring Togo, Nigeria, and Ghana. There may be as many as 1,000 living in Ghana.
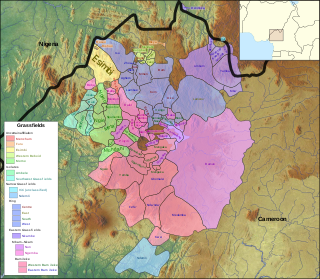
Babanki, or Kejom, is a Bantoid language that is spoken by the Babanki people of the Western Highlands of Cameroon.
Chakali (tʃàkálɪ́ɪ́) is a Gur language of Ghana, spoken by almost 3,500 individuals in several villages in the Wa East District of the Upper West Region. More specifically, Chakali is spoken by inhabitants of the Tiisa, Sogla, Tousa, Motigu, Ducie, Katua and Gurumbele villages. The majority of Chakali speakers also speak Wali or Bulengi. Some believe that the language of Chakali is soon to be extinct, with Wali and Bulengi becoming the only languages that will be spoken in those villages.
Medumba phonology is the way in which the Medumba language is pronounced. Medumba is a Bamileke language of Cameroon; the people who speak it originate from the Nde division of the West Region of the country. It deals with phonetics, phonotactics and their variation across different dialects of Medumba.
References
- Persson, Andrew; Persson, Janet (1980). "Ligbi". In Kropp Dakubu, Mary Esther (ed.). West African Language Data Sheets. Vol. 2. West African Linguistic Society. pp. LIG 1-LIG 6. OCLC 9403639.