Related Research Articles
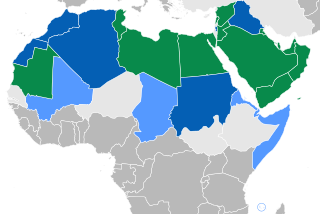
Arabic is a Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The ISO assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ).
C is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code, device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems.

French is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to the French colonial empire, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.

Persian, also known by its endonym Farsi, is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian, Dari Persian, and Tajiki Persian. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivative of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a derivative of the Cyrillic script.

Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.

Modern Standard Hindi, commonly referred to as Hindi, is an Indo-Aryan language written in Devanagari script. It is the official language of India alongside English and the lingua franca of North India. Hindi is considered a Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.

The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family—English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish—have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; another nine subdivisions are now extinct.

Japanese is the principal language of the Japonic language family spoken by the Japanese people. It has around 120 million speakers, primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language, and within the Japanese diaspora worldwide.

Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let programmers write once, run anywhere (WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages.

Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of productivity and displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning.

Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation.

Russian is an East Slavic language, spoken primarily in Russia. It is the native language of the Russians and belongs to the Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. It was the de facto and de jure official language of the former Soviet Union. Russian has remained an official language in independent Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Israel.

Spanish or Castilian (castellano) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a global language with about 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 600 million when including second language speakers. Spanish is the official language of 20 countries, as well as one of the six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's fourth-most spoken language overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language. The country with the largest population of native speakers is Mexico.

Tamil is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. It is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India, along with Sanskrit, attested since c. 300 BCE.

Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan, where it is also an official language alongside English. In India, Urdu is an Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India; and it also has an official status in several Indian states. In Nepal, Urdu is a registered regional dialect and in South Africa it is a protected language in the constitution. It is also spoken as a minority language in Afghanistan and Bangladesh, with no official status.
Assimilation is a sound change in which some phonemes change to become more similar to other nearby sounds. A common type of phonological process across languages, assimilation can occur either within a word or between words.
Tori may refer to:

English is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, whose speakers, called Anglophones, originated in early medieval England on the island of Great Britain. The namesake of the language is the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to Britain.
The Guan languages are languages of the Kwa language family spoken by the Guan people in Ghana and Togo:
Kplang is a Guang language of Ghana. It is partially intelligible with Chumburung, especially with the neighboring dialect.
References
- ↑ Chumburung at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)